Ch7 Competition¶
7.1 The Competitive Firm¶
marginal revenue = price a firm's output: where price = MC (marginal cost)
U-shaped MC curve¶
 if lost in [0,Q1] < profit in [Q1,Q2] → produce Q2
if lost in [0,Q1] < profit in [Q1,Q2] → produce Q2
else → shut down
short run: can shutdown
long run: can exit
shut down or not ?¶
operate profit: TR(total revenue) - TC(total cost)
shut down profit: -FC (fixed cost)
TC = FC + VC (variable cost)
operate if operate profit > shut down profit i.e. TR > VC
(bc fixed cost is there whether shut down or not, so only variable cost matters)
TR = P×Q > VC
→ ==P > AVC== i.e. price > average variable cost then a firm operate
bold part = supply curve
(only produce when P=MC>AVC)
 produce nothing at price < P0
produce nothing at price < P0
MC intersect AVC & AC at min point
原因:marginal < average 時,會讓 average 減少;> average 時,會讓 average 增加,又 fixed cost 不變
elasticity of supply¶
elasticity = \(\(\frac{△Q/Q}{△P/P}\)\) (the flatter the higher)
7.2 The Competitive Industry in the Short Run¶
industry supply curve

changes in variable costs¶

a firm:
- marginal cost rises → supply curve shifts upward/leftward
- in industry, price = P0 → P2, so d→d' in a firm, q2 not necessarily < q0
an industry:
- the sum of firms' supply curves → shifts upward/leftward
- Q2 < Q0
a change in demand¶


changes in variable costs¶

a firm:
- marginal cost rises → supply curve shifts upward/leftward
- in industry, price = P0 → P2, so d→d' in a firm, q2 not necessarily < q0
an industry:
- the sum of firms' supply curves → shifts upward/leftward
- Q2 < Q0
a change in demand¶

7.3 The Competitive Firm in the Long Run¶
min AC point = equilibrium quantity q&p (horizontal demand i.e. price is the tangent of min AC)
- if p > AC, the firm is earning positive economic profits, so more firms will come in, making p decreases
- if p < AC, the firm is earning negative economic profits, so it will quit
i.e. in long run, price = min AC
P0→P1
short run: S
long run: LRS, S'
 p.183
p.183
7.4 The Competitive Industry in the Long Run¶
change in demand¶
constant-cost¶
long run: price don't change

short run: price goes up

change in cost¶
constant-cost¶
changes in variable cost

如果每單位 output 上升相同的 marginal cost,AC 就會垂直上升,讓均衡 output 不變
但若是 variable cost 按比例上升,output 愈大 marginal cost 上升愈多
suppose a lecense fee is charged


短期才會有好處 長期而言都是 0 profit
increasing-cost¶
same as constant-cost except the shape of LRS


applications¶
- apartment rent for $400
- new law: $200 max
- change to $20p
- remove law
- change to $500
- change back to $400 ultimately

7.5 XXXX-Cost Industries¶
Constant-Cost Industries¶
break-even price (price that makes you profit = 0 ) is constant as q ↑
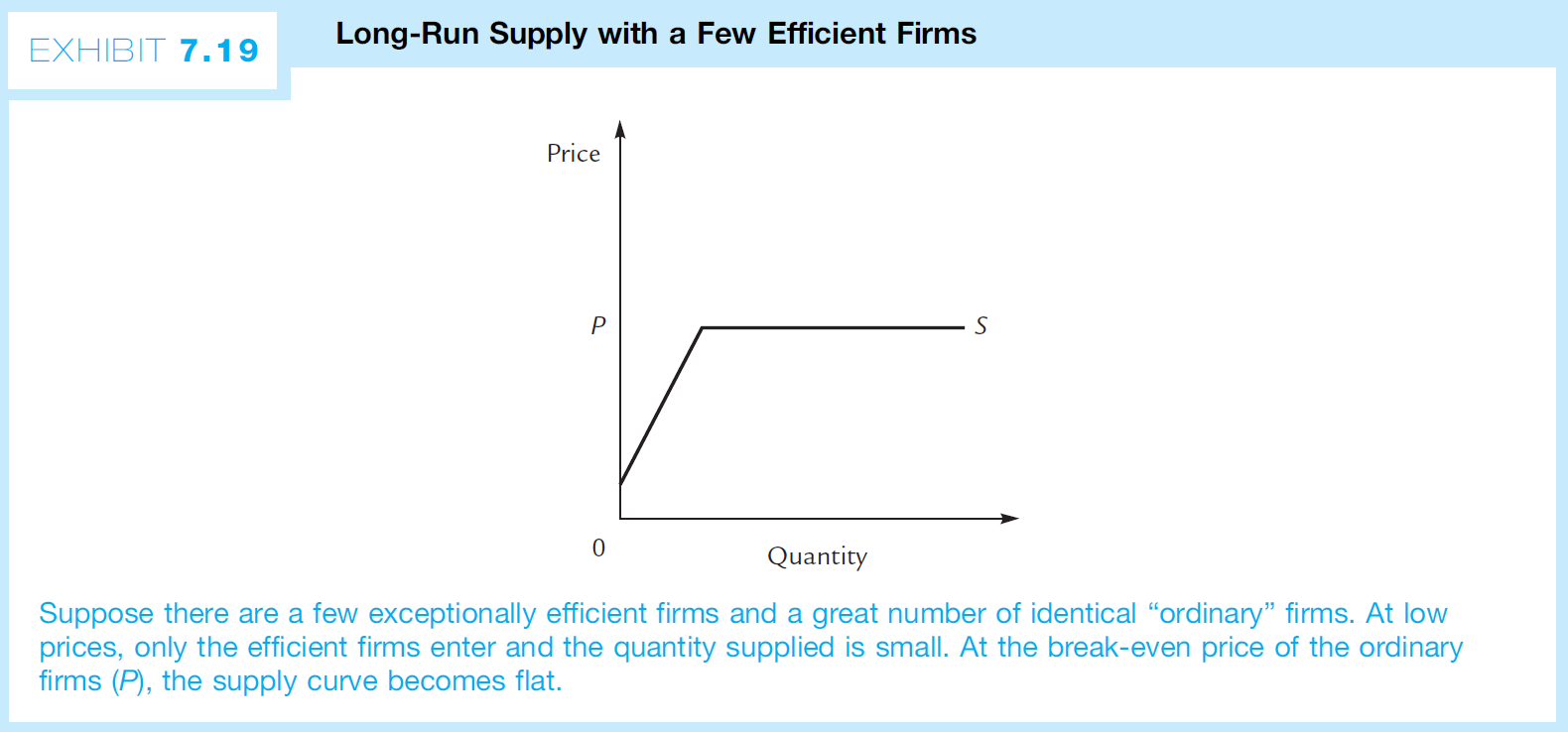
Increasing-Cost Industries¶
break-even price ↑ as q ↑
可能原因
- break-even price 較低者較早進入市場,較高者較晚進入
- factor price ↑ as q ↑ e.g. lands
Decreasing-Cost industries¶
costs ↓ as q ↑ → break-even price ↓ as q ↑ e.g. 3C industry
Homework¶










- a. short(no change in long)
- b. long
- c. short
- d. short