Chap 4 Consumers in Marketplace¶
from https://www.notion.so/Chap-4-Consumers-in-Marketplace-17ac94e393db45709d26c55bedebeb1b
Marginal Willingness to Pay¶
x = 商品數量 ; y = 其他 ; I = 所得
Px x + y = I
Marginal Willingness to Pay
MRS = |dx/dy| = Px/1
4.1 Changes in Income¶
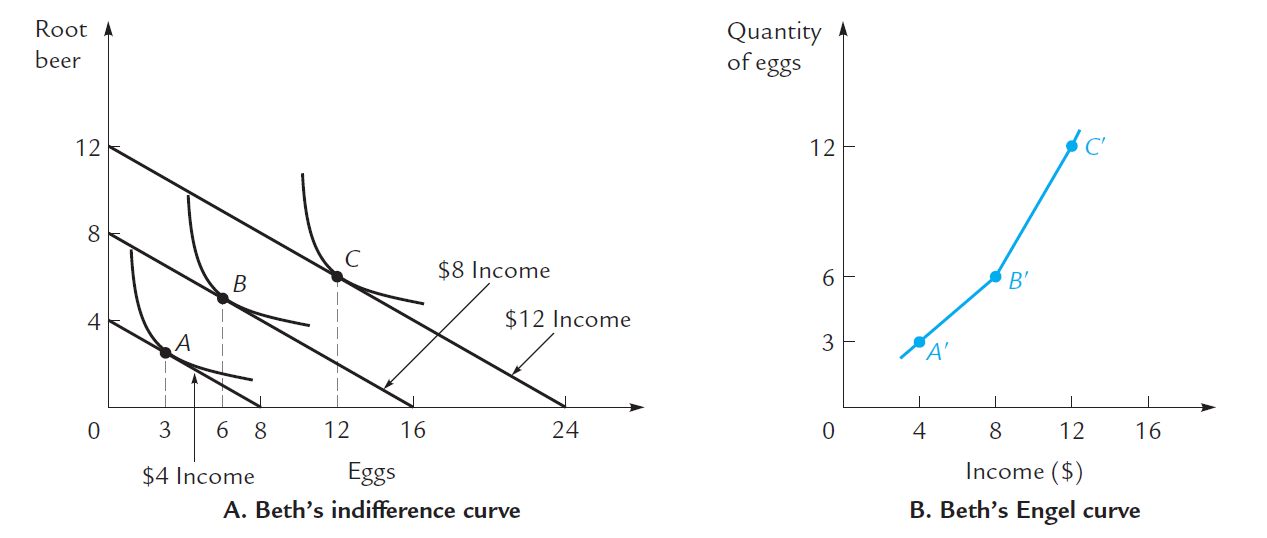
Engel Curve¶
graph of quantity to income for a good (consists of tangent points at each income) 注意 x 軸是 P,y 軸是 Q 函數形式: Q(I) e.g. Qx = I/3 (103上期中 2.)
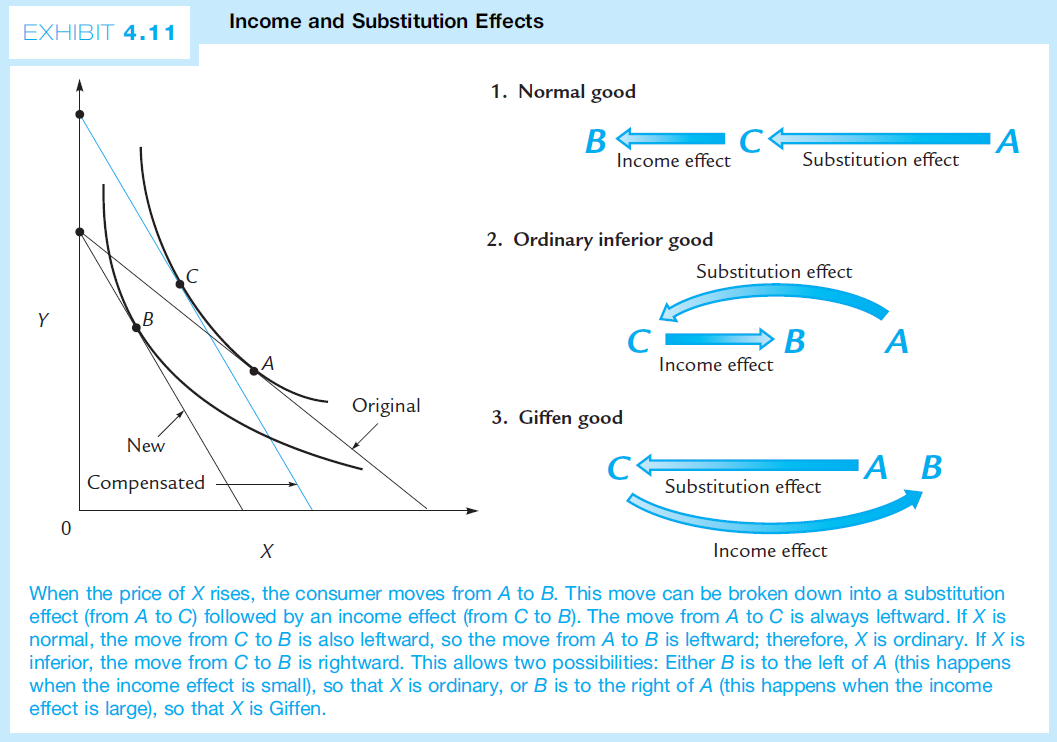
4.3 Income and Substitutions Effects¶

4.4 Elasticities¶
微分!!!
若函數是過原點直線, elasticity 一定為 1 (因為按比例)
Income elasticity¶

I 對 Q 微分
price elasticity¶

P 對 Q 微分
Cross Elasticity¶
the cross elasticity of demand for X with respect to Y = the percent change in consumption of X divided by the percent change in the price of Y
if positive → X & Y are substitutes if negative → X & Y are complements
Constant elasticity demand¶

Problems & Homeworks¶
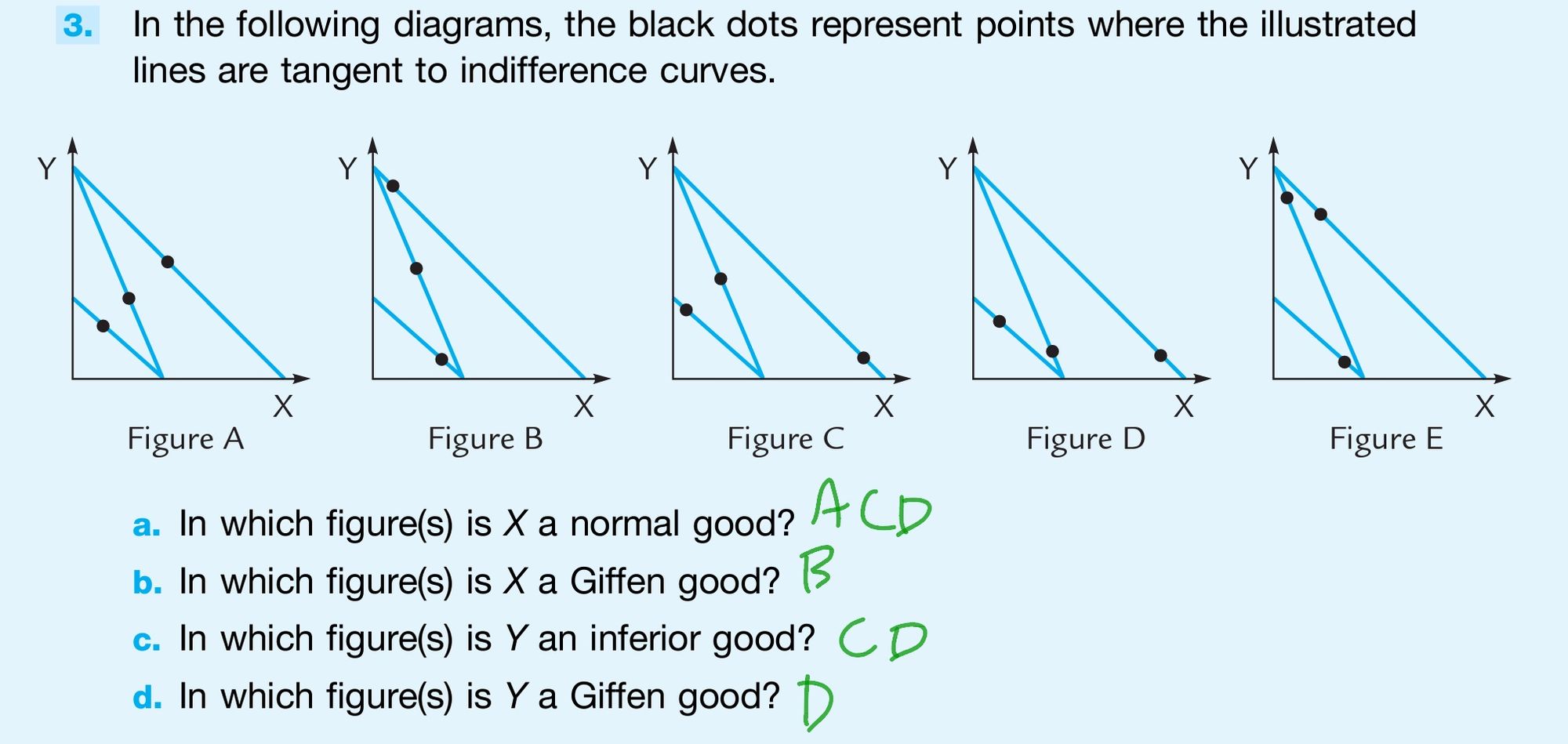
判斷 normal, inferior, Giffen goods



wage 上升時,前者 income 上升較多,對 leisure hours 需求上升較多,working hours 淨上升量因此較少 supply curve 畫起來較陡


凹向下的 indifference curve 的 compensated demand curve (如果凹向下的 indifference curve 的 ordinary demand curve 是凹向下的話)
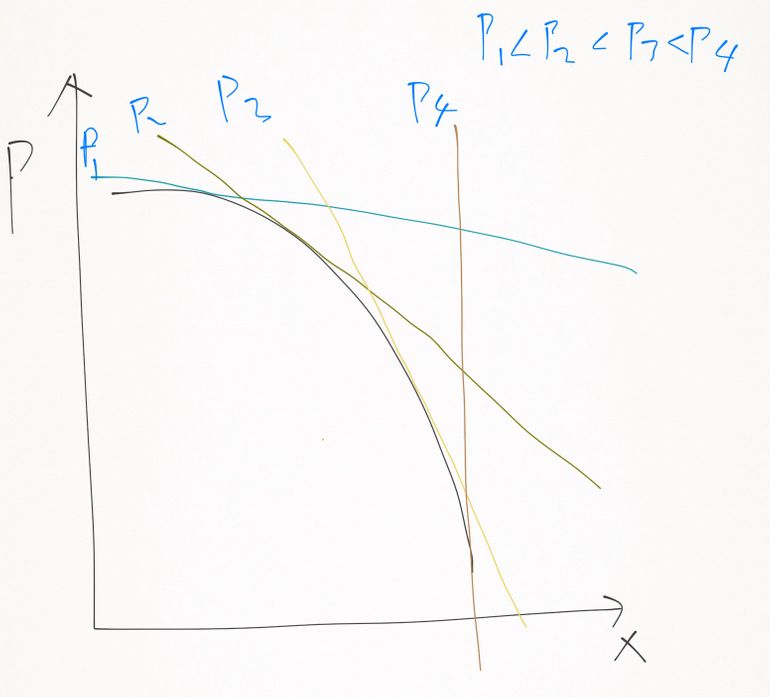
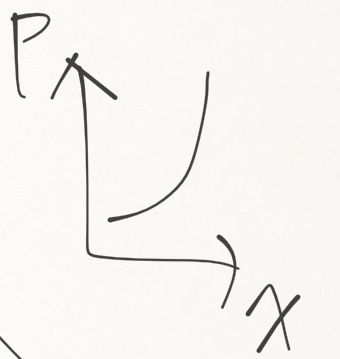
固定一點 P1 畫出其他價格用 sub effect 會切到的點 發現 價格很小時,P 上升一點,X 就上升很多 價格愈來愈高時,與 P1 的 X 的差值的上升幅度就愈來愈小 簡而言之 設 P1 ~ P4 是等加數列 X4 - X1 < 3(X2 - X1) 畫出來就變右圖
Homework¶
很多錯 看上面題目就好
-
作業題目
個經作業, Ch.4 1. Landsburg, Ch.4, numerical exercises, #N1. 2. Landsburg, Ch.4, problem set, #23. 3. Landsburg, Ch.4, problem set, #24. 4. In 2003, tolls were raised on seven bridges across the Delaware River, connecting Pennsylvania to New Jersey. In the first two months of the year, bridge traffic fell by 17%, but revenue increased by 123% because of the higher tolls. What is the price elasticity of demand for using these bridges to cross the Delaware River? (A problem from the previous edition.)

