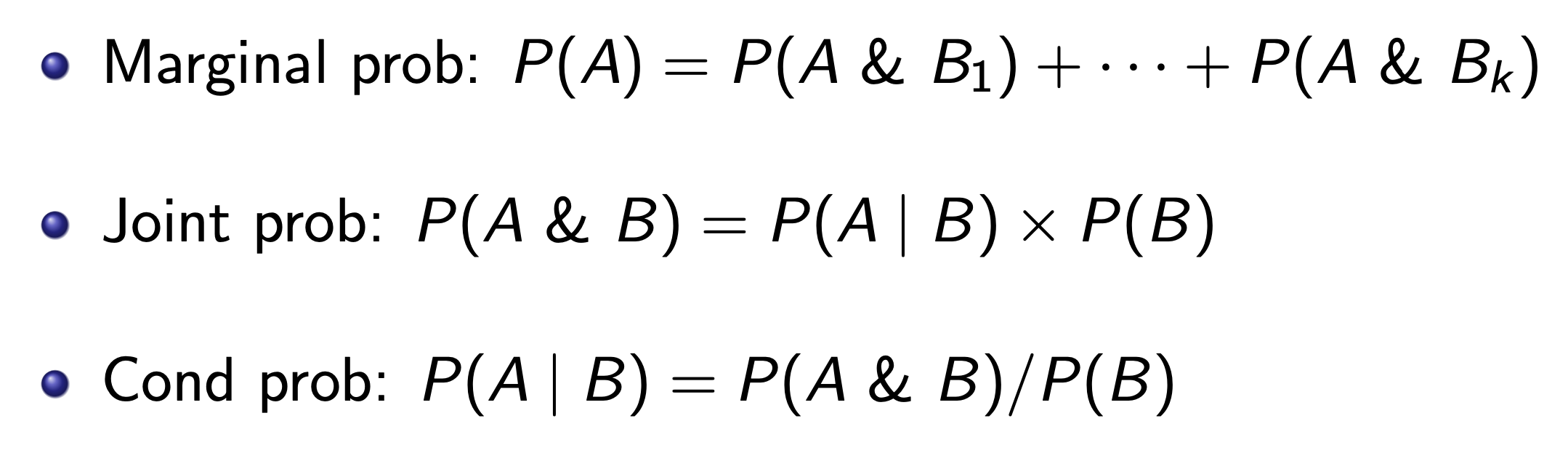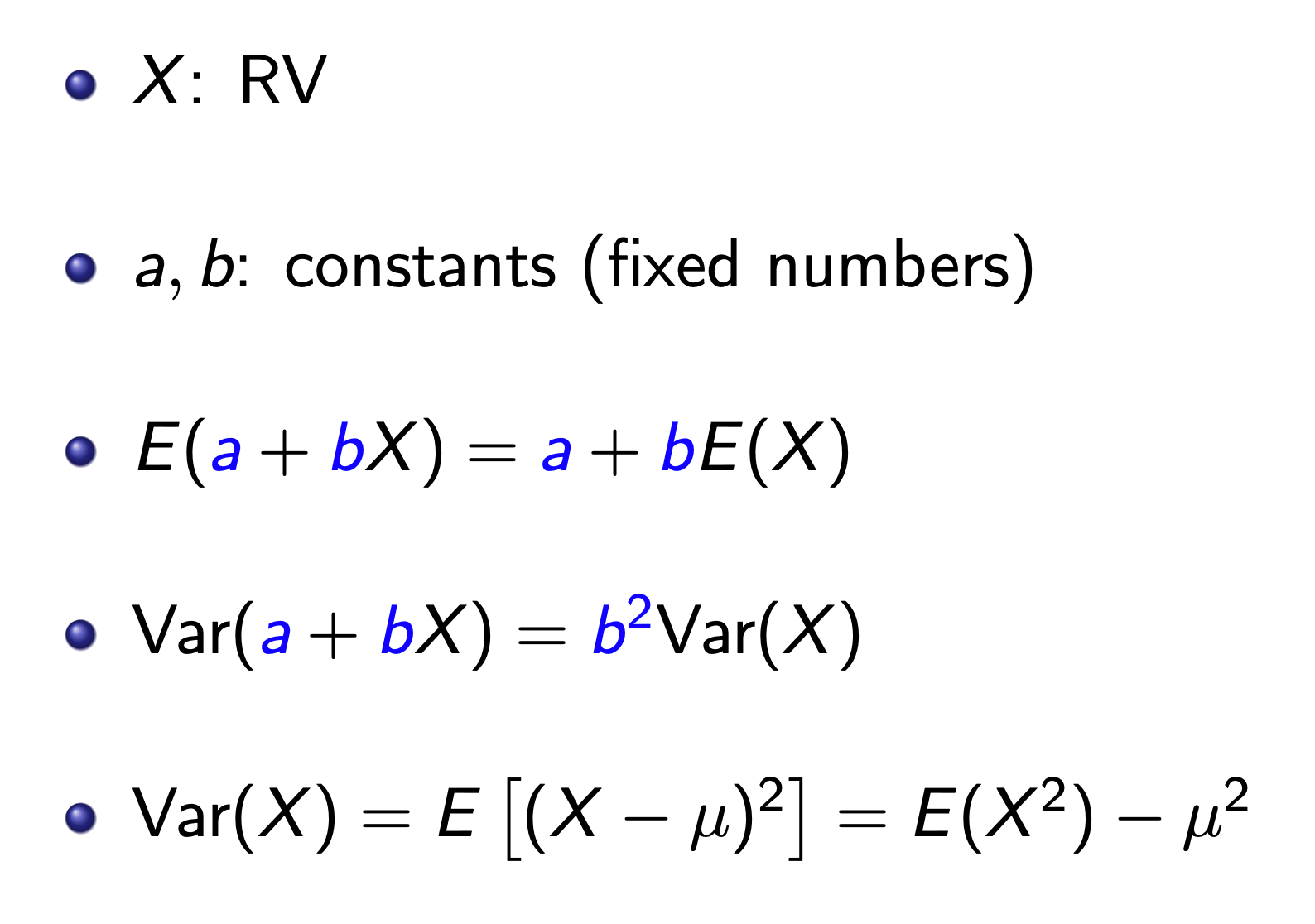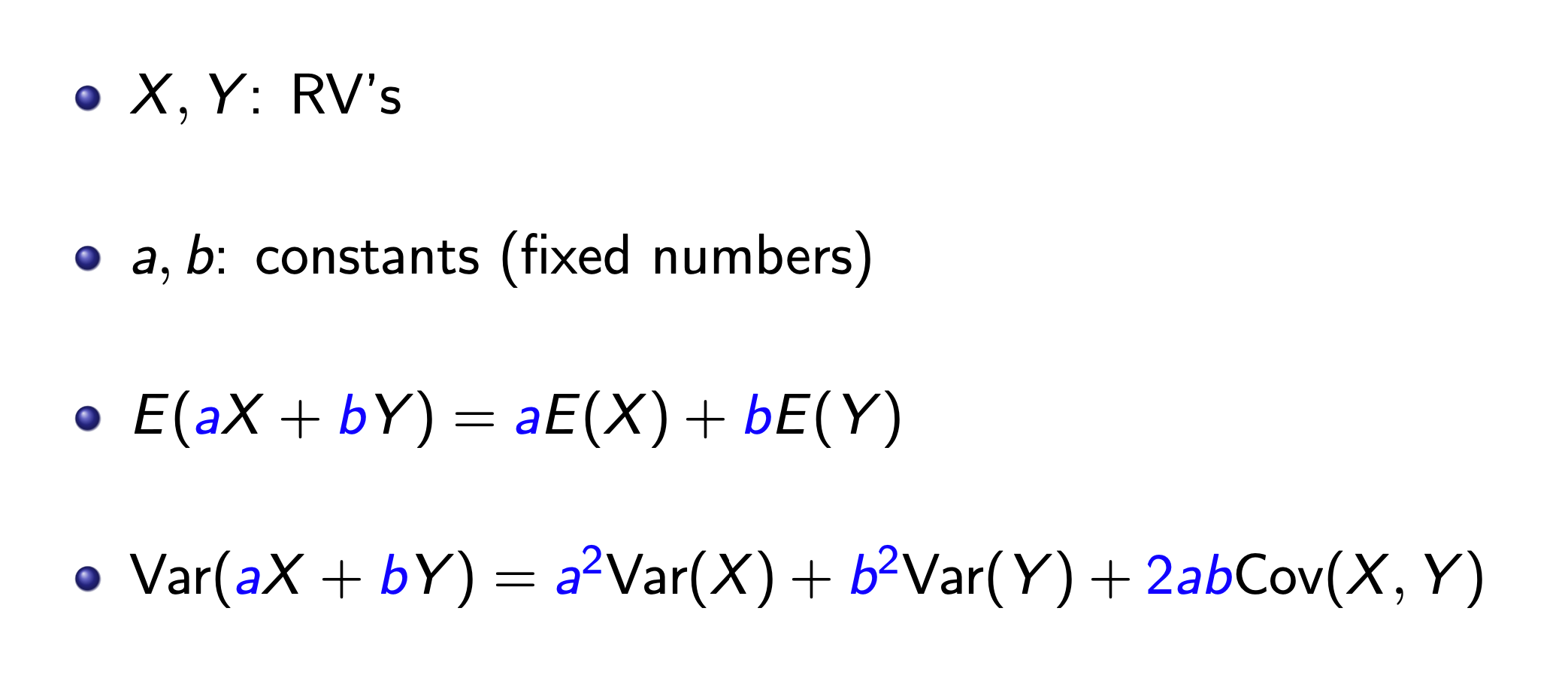Statistics¶
Materials¶
Tables¶
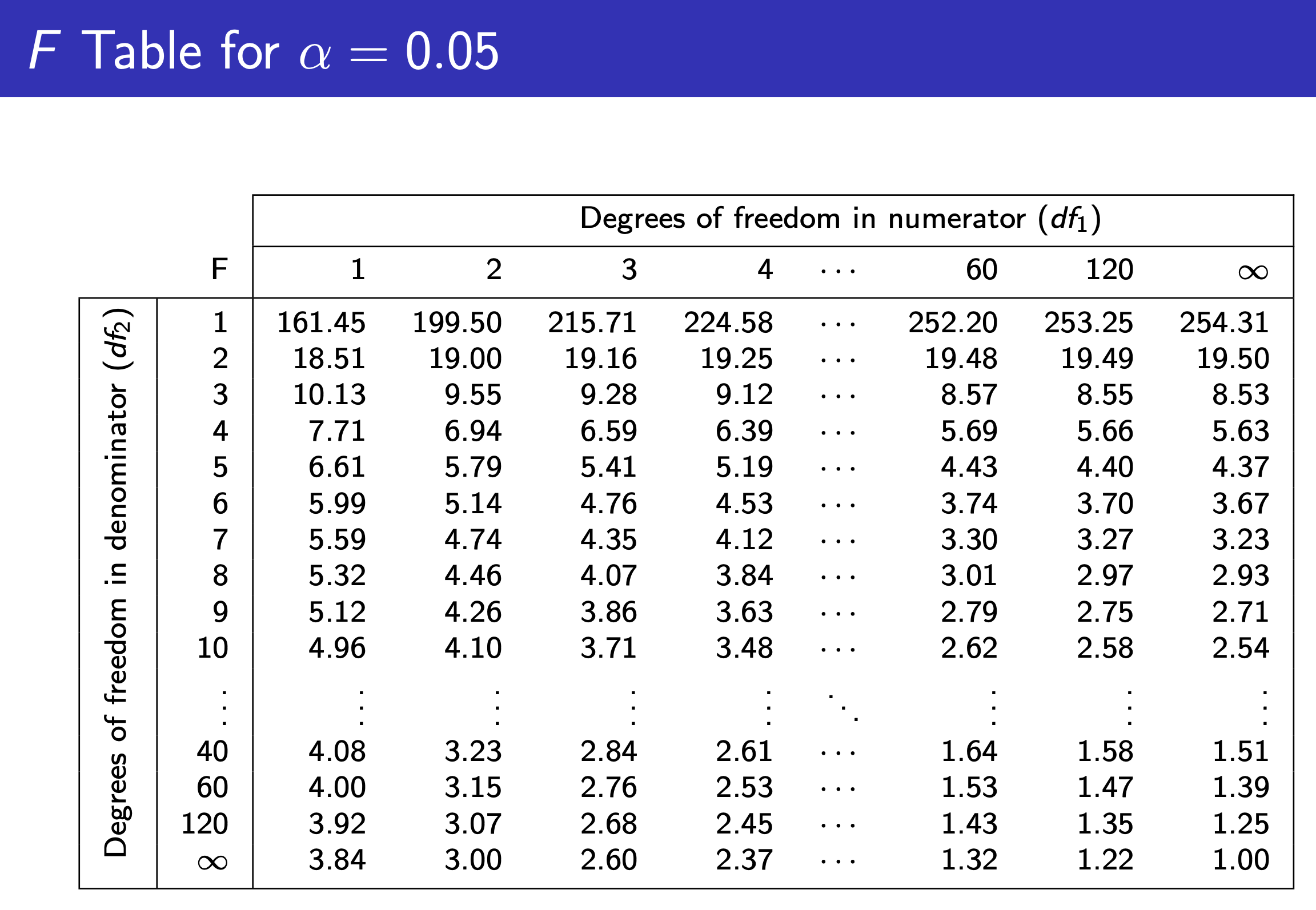
Z Table¶
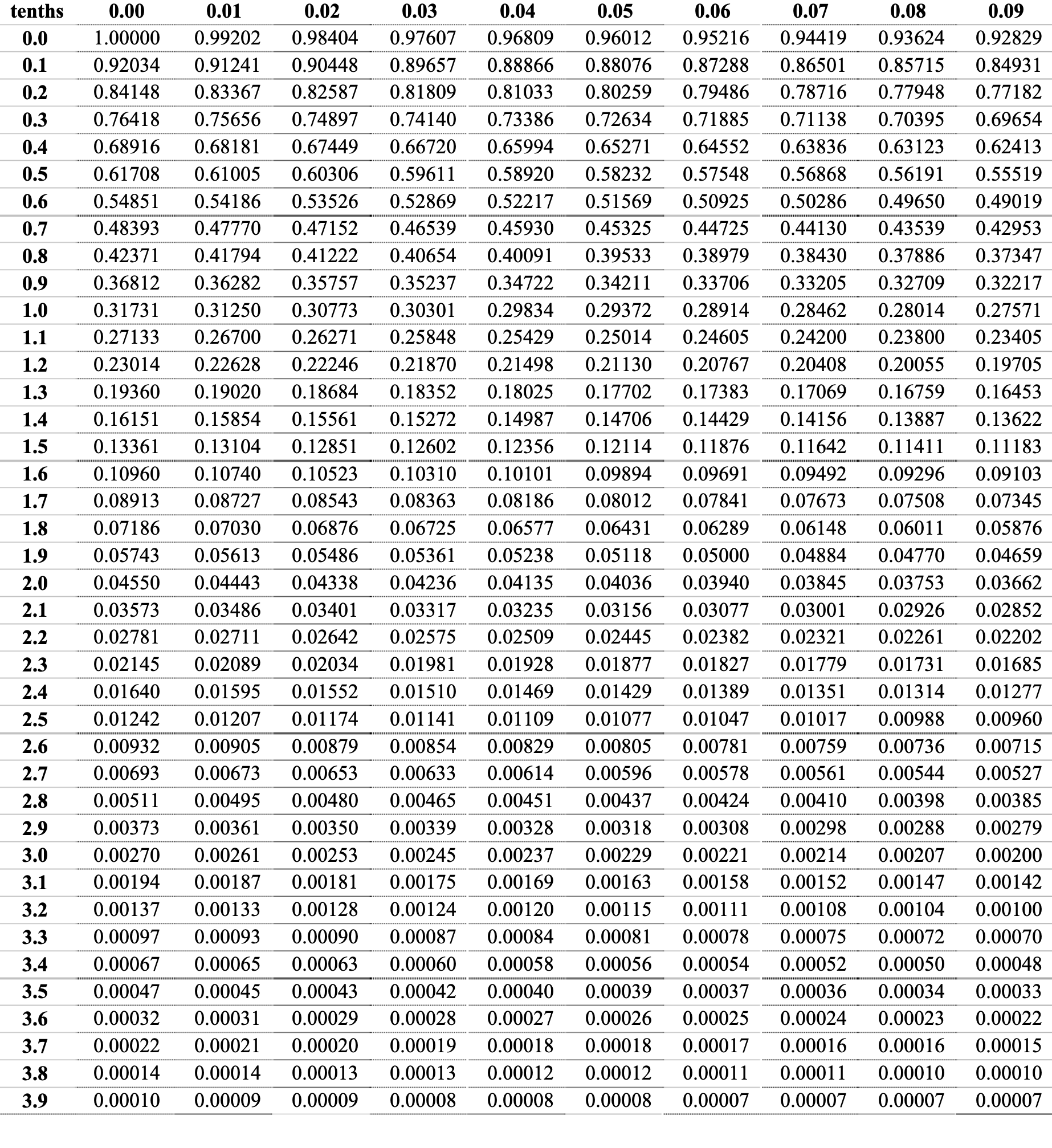
T Table¶
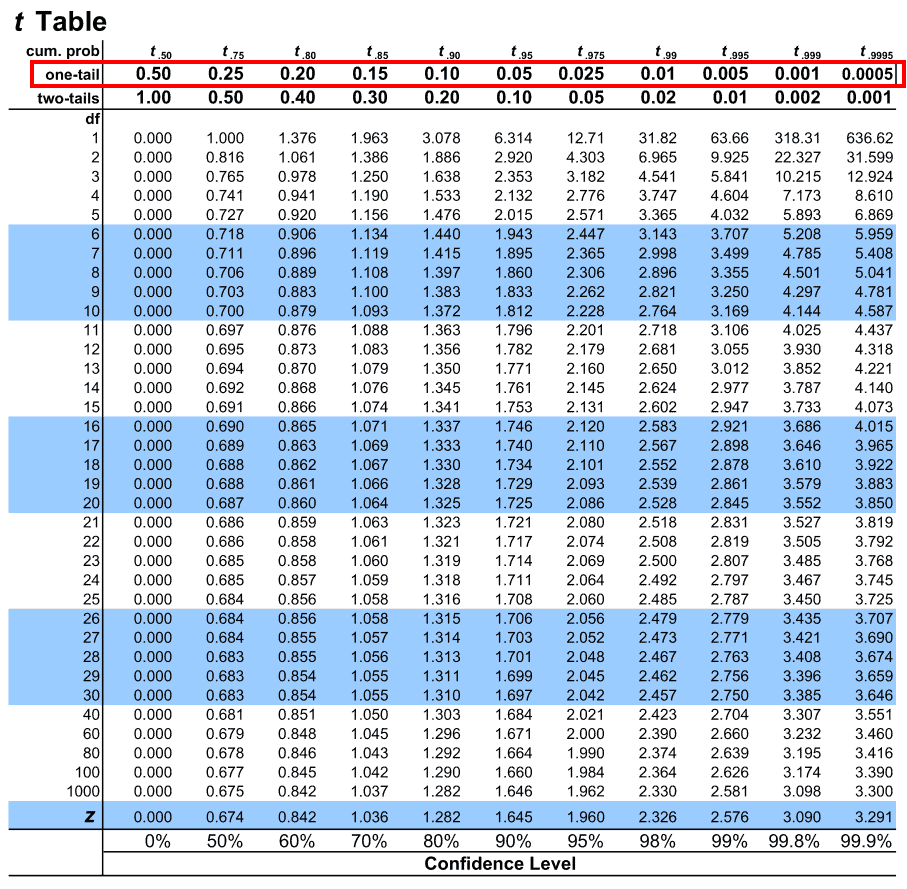
F Table¶
Notation¶
- \(p\) = population
- \(\hat{p}\) = sample
Intro¶
Explanatory & Response variable¶
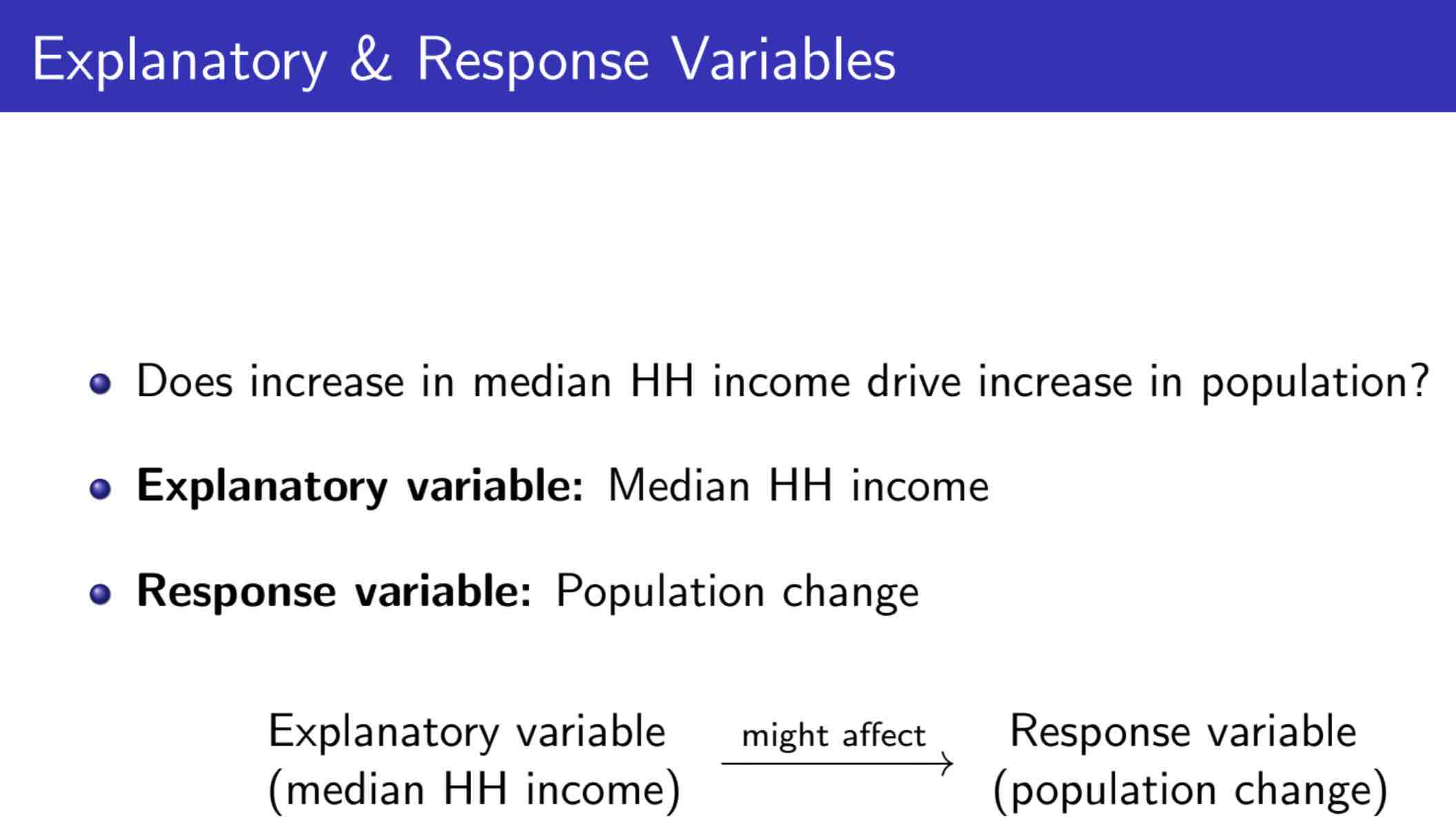
Variables¶
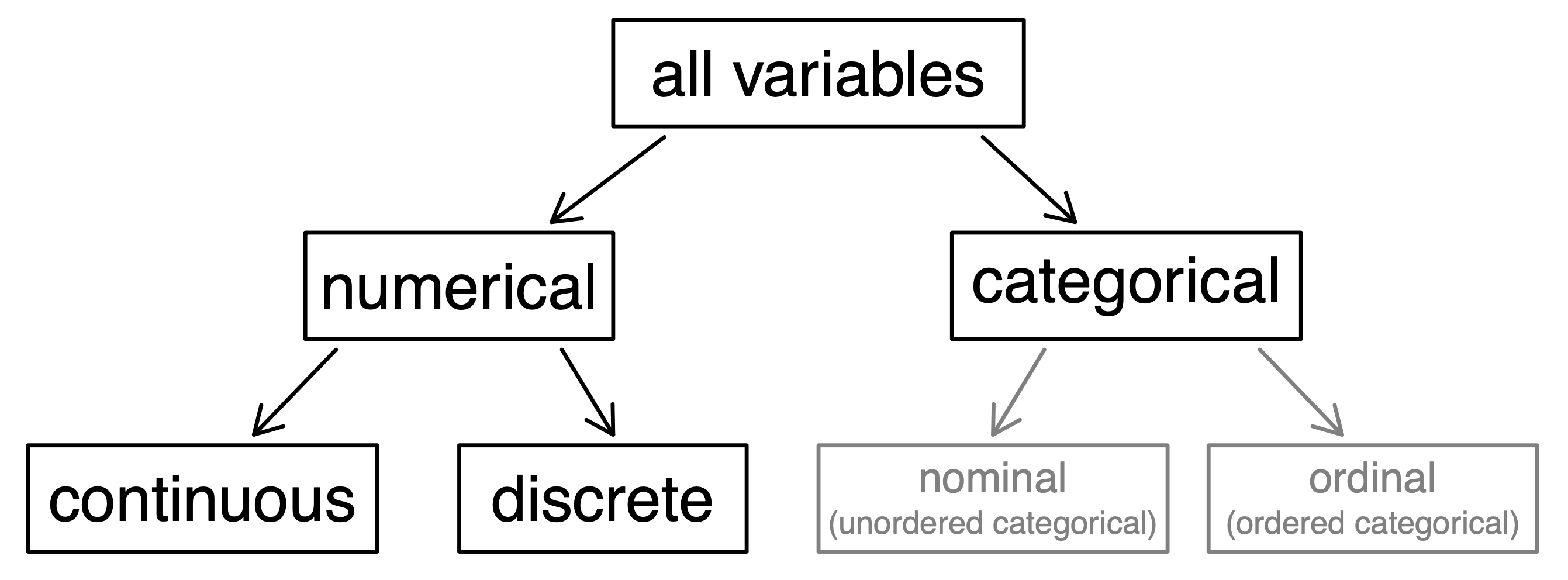
- numeric
- discrete
- continious
- categorical
- ordinal
- can be sorted
- e.g. A, B, C ...
- not ordinal
- ordinal
Sampling¶
- simple random sampling
- stratified sampling
- group into stratas -> sample within each strata (sample unit: case)
- each strata has its charactersitcs
- cluster sampling
- divide into clusters -> sample clusters (sample unit: cluster)
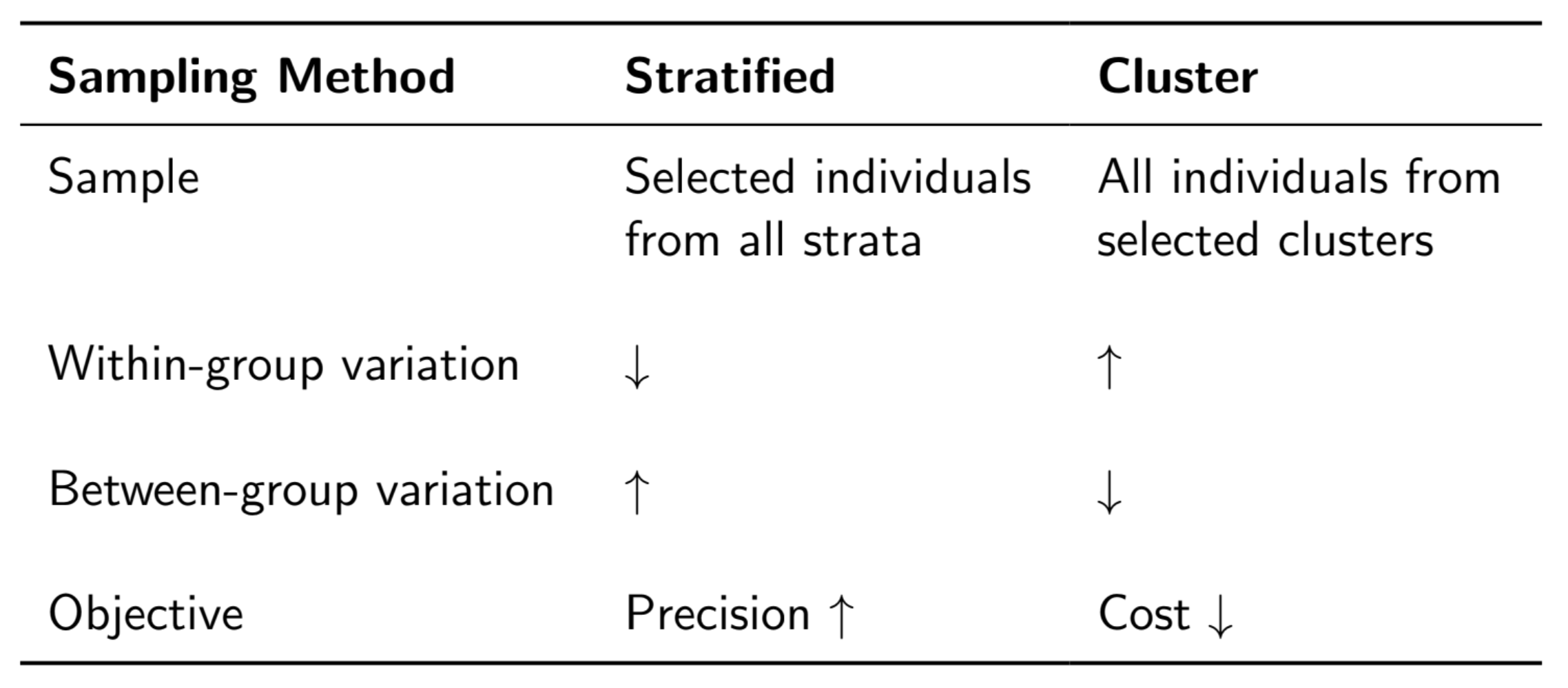
- multistage sampling
- divide into clusters -> sample clusters -> sample within each selected cluster
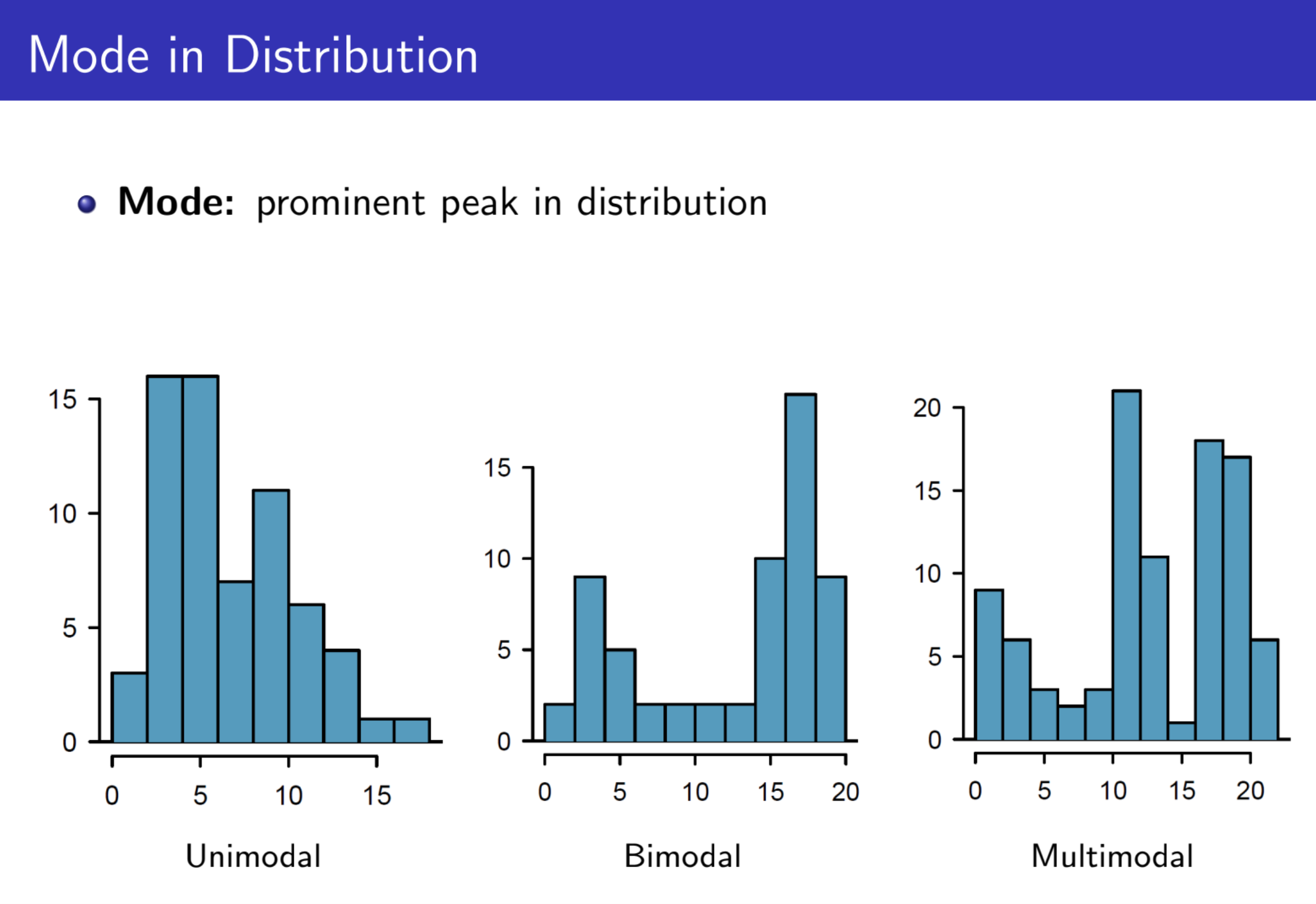
Distribution Mode¶
How are local maxima distributed?
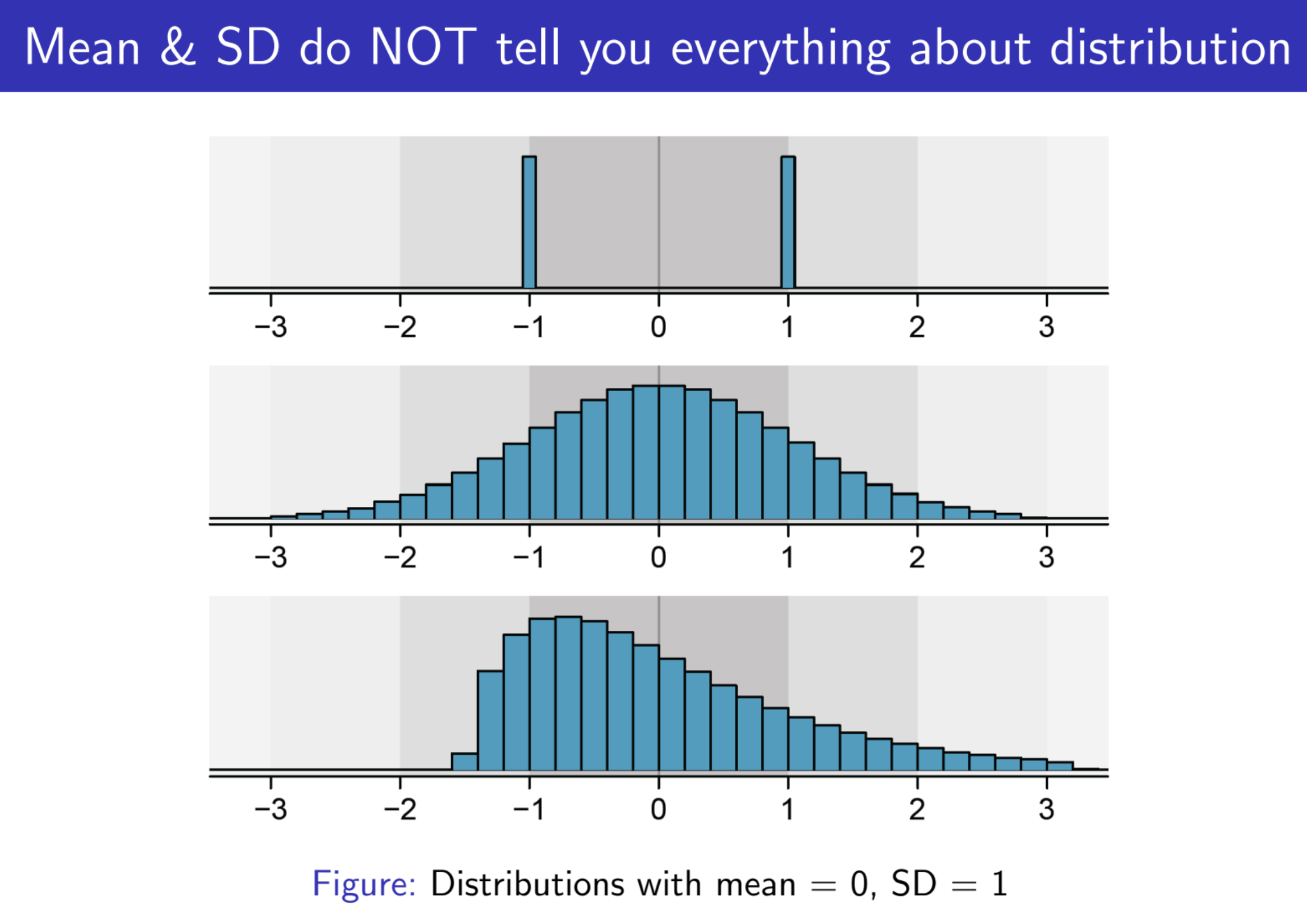
Mean & Variance¶
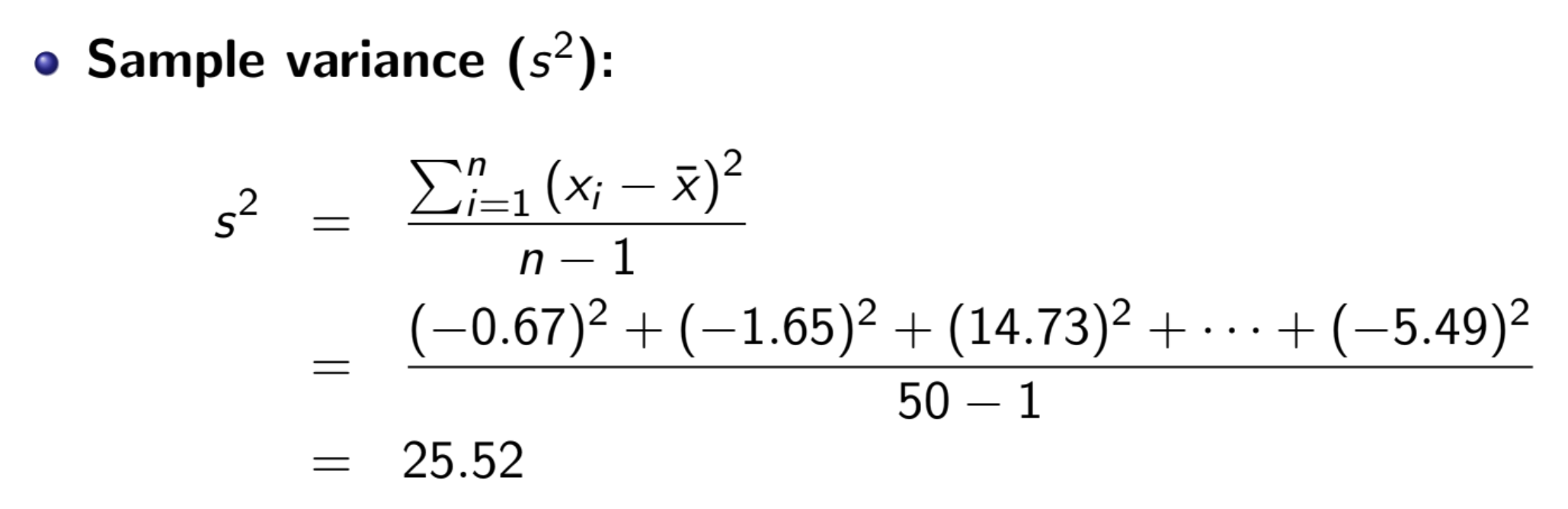
Same mean & variance may stem from very different distributions
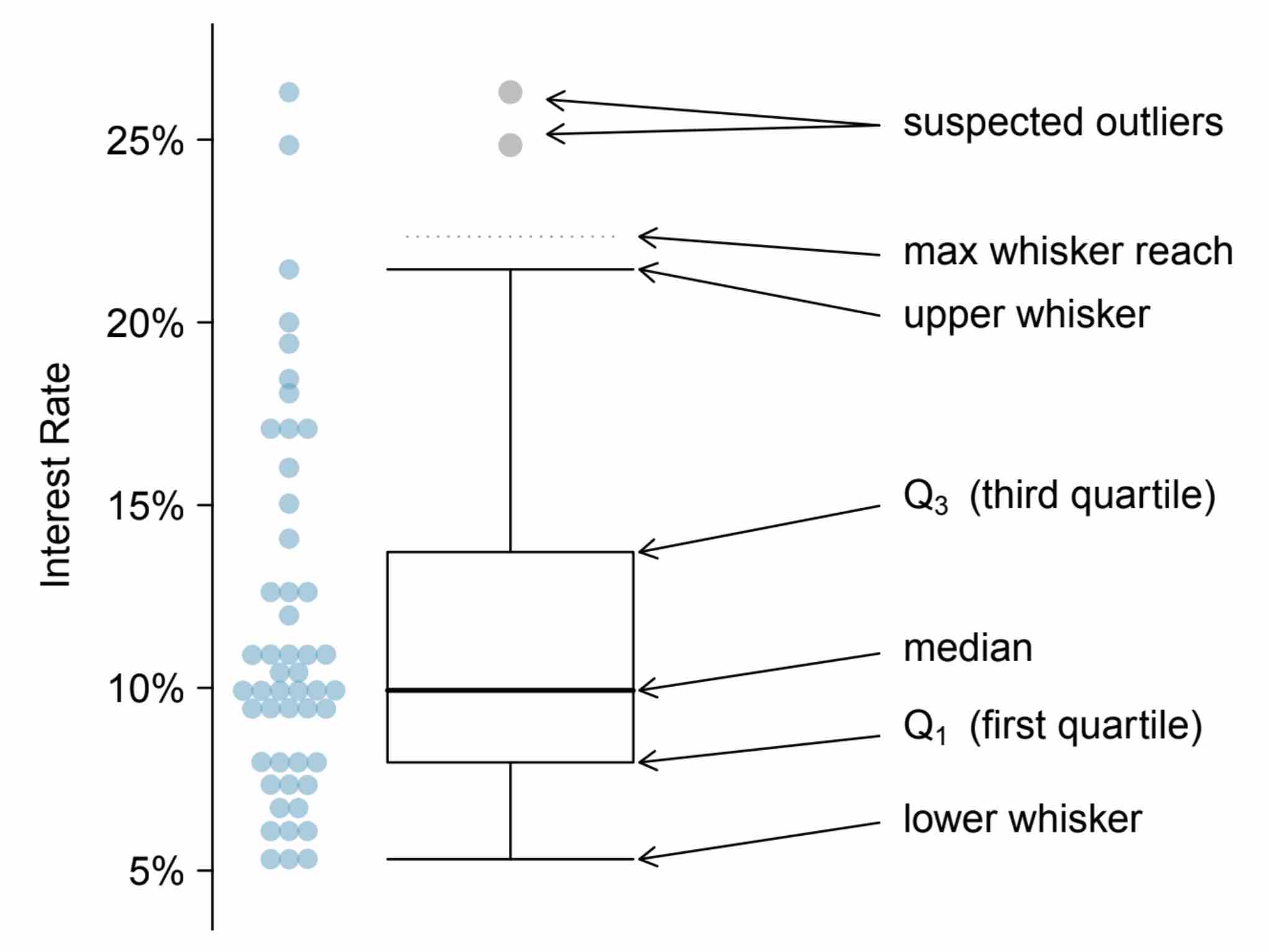
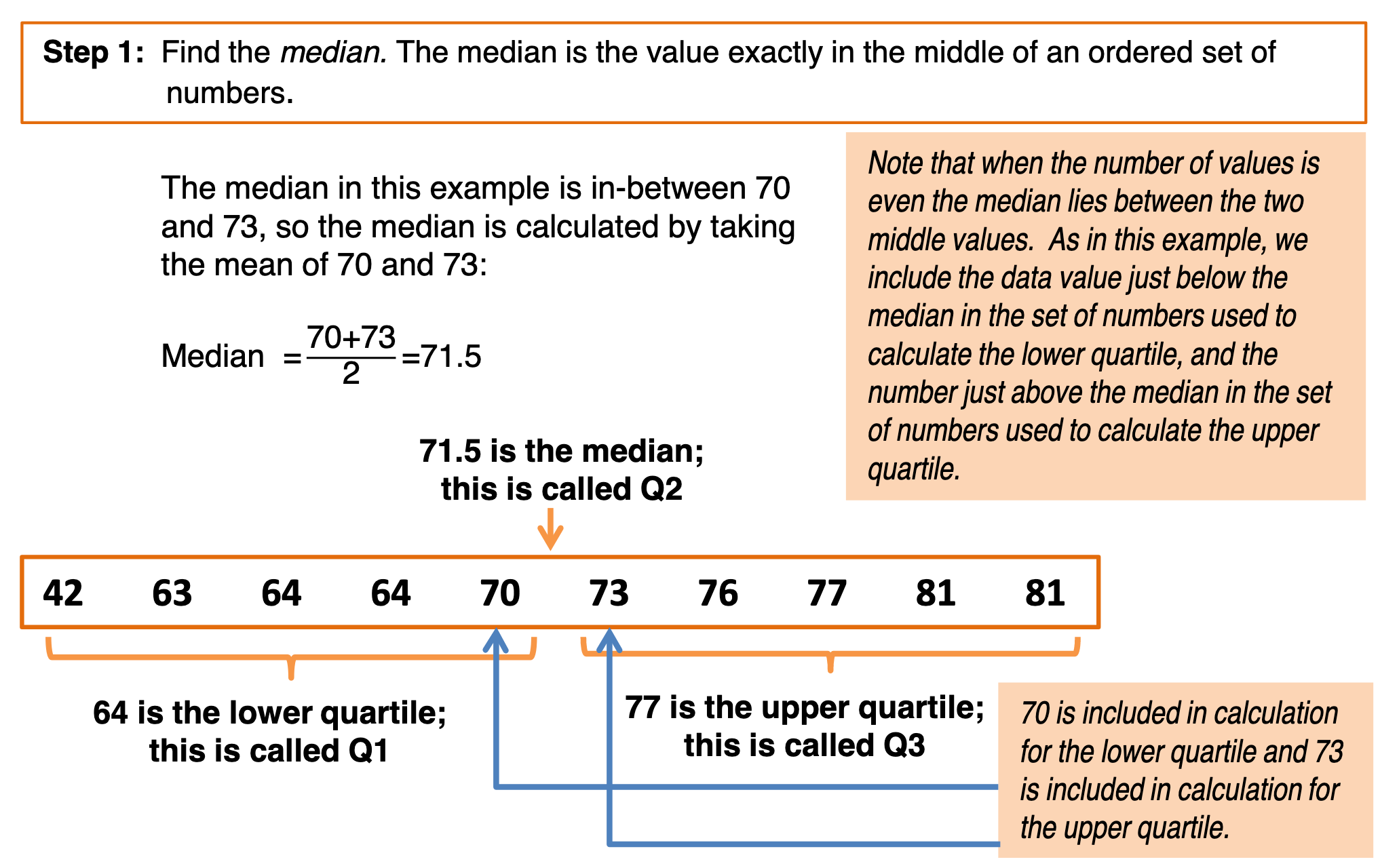
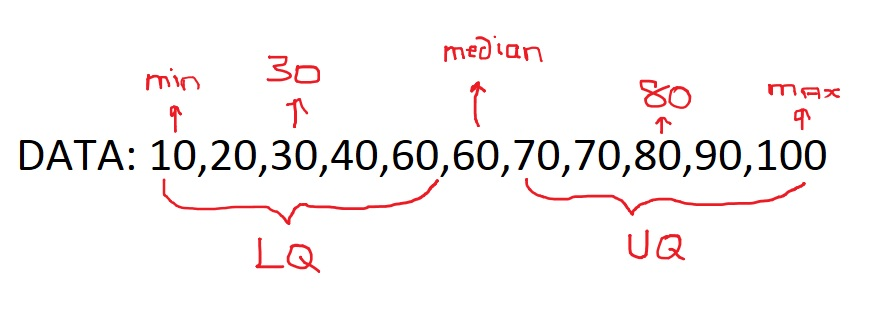
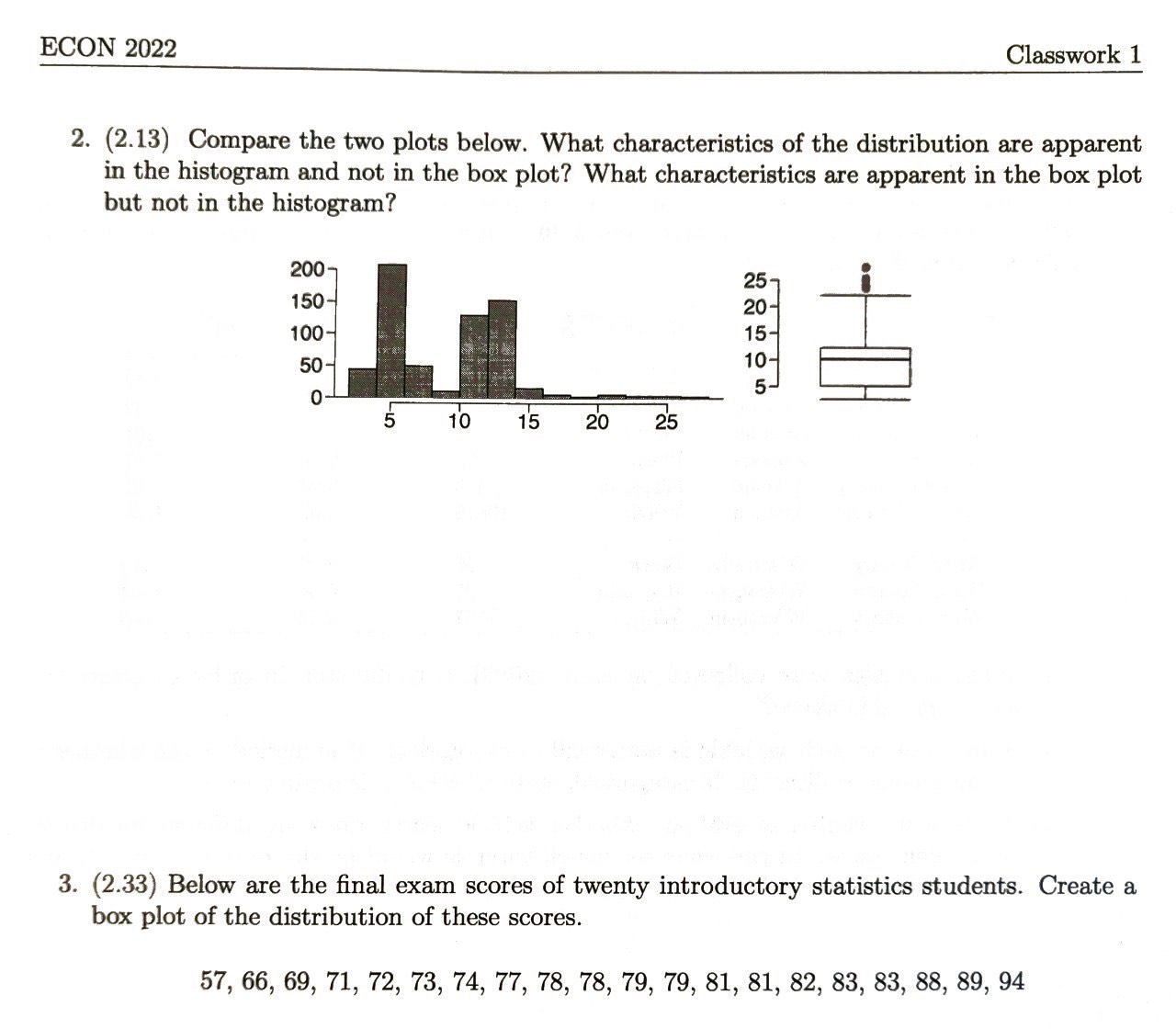
Box Plot¶
- median = middle number
- 2 number -> average
- Q1 = middle number in upper half
- median has 2 number -> middle between min & closest median
- Q3 = middle number in lower half
- IQR = Q3-Q1
- upper whisker = min(max, Q3 + 1.5 x IQR)
- lower whisker = max(min, Q1 - 1.5 x IQR)
- outliers = those ouside of upper & lower whisker

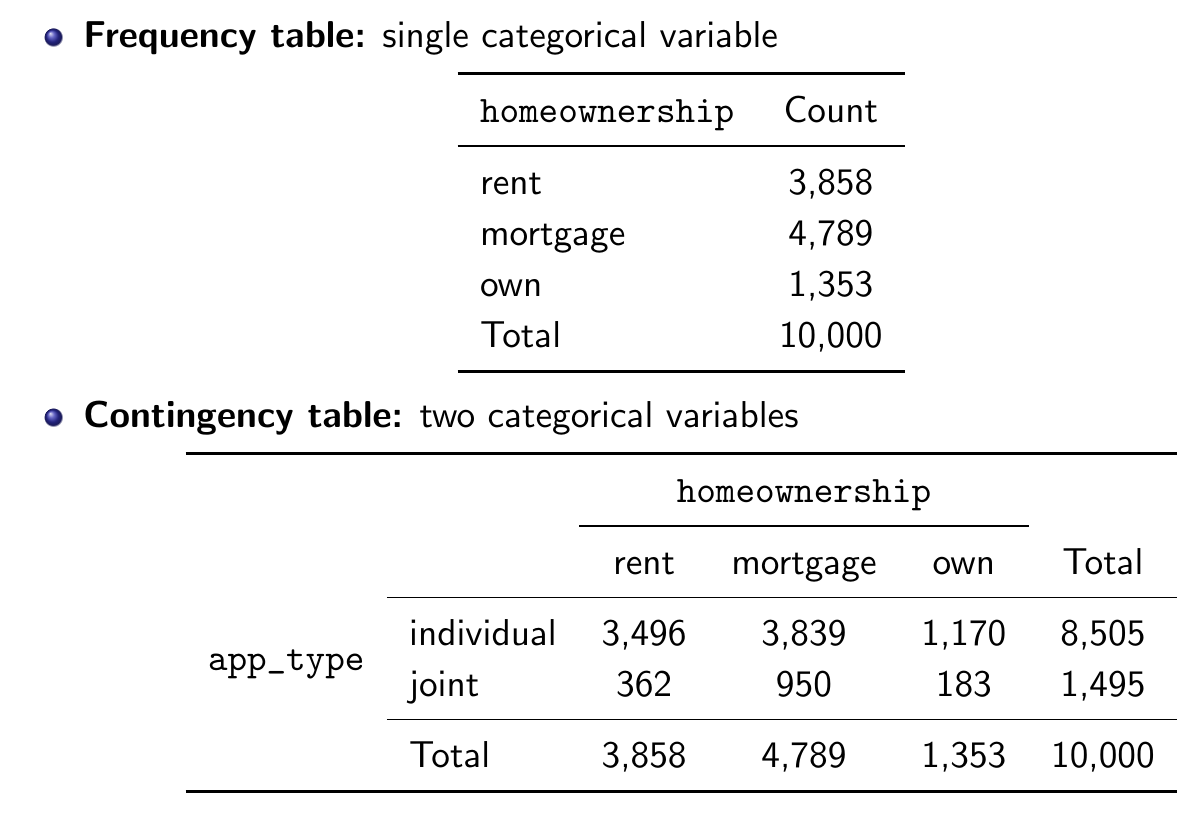
Tables¶
- Frequency table
- Contingency table
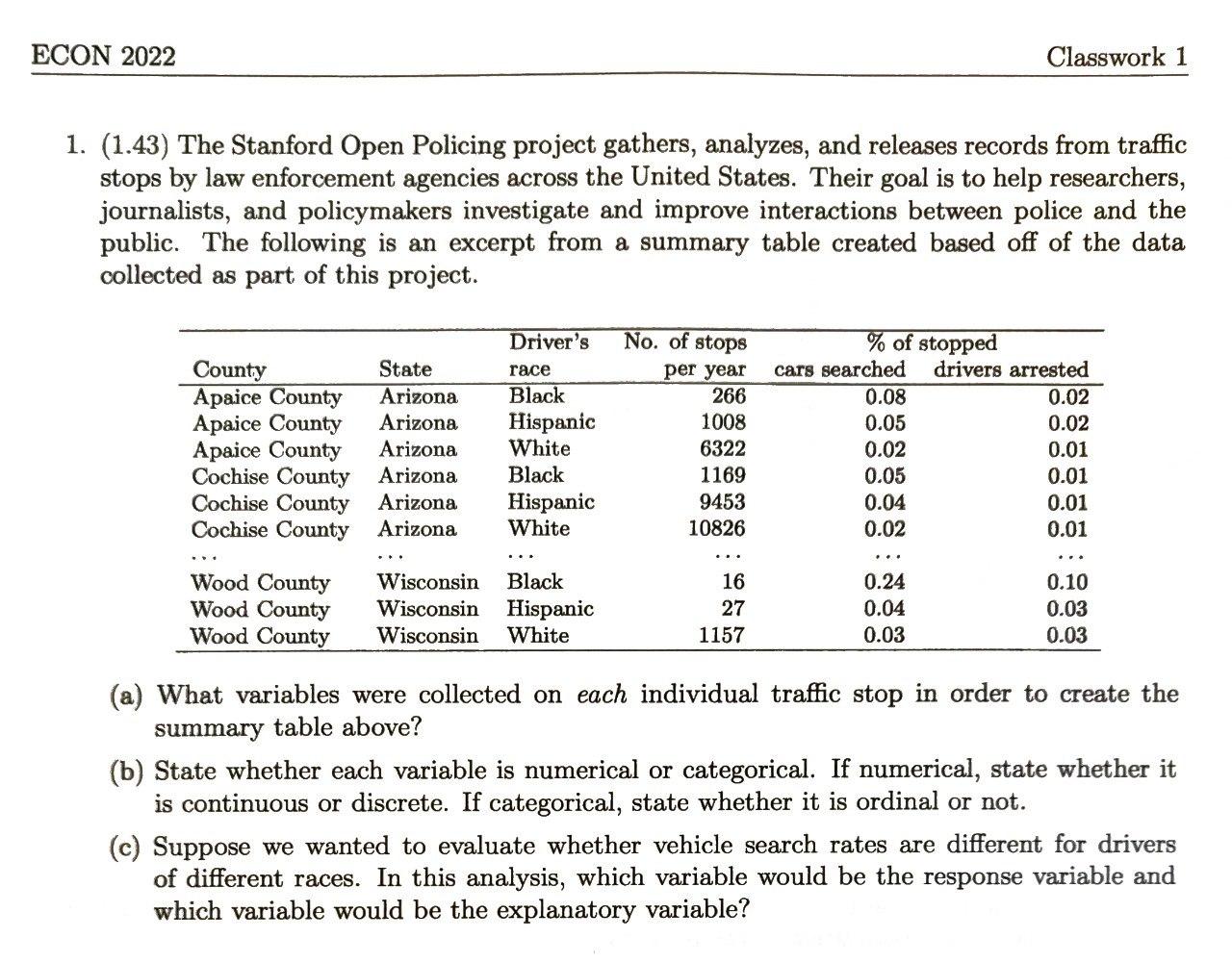
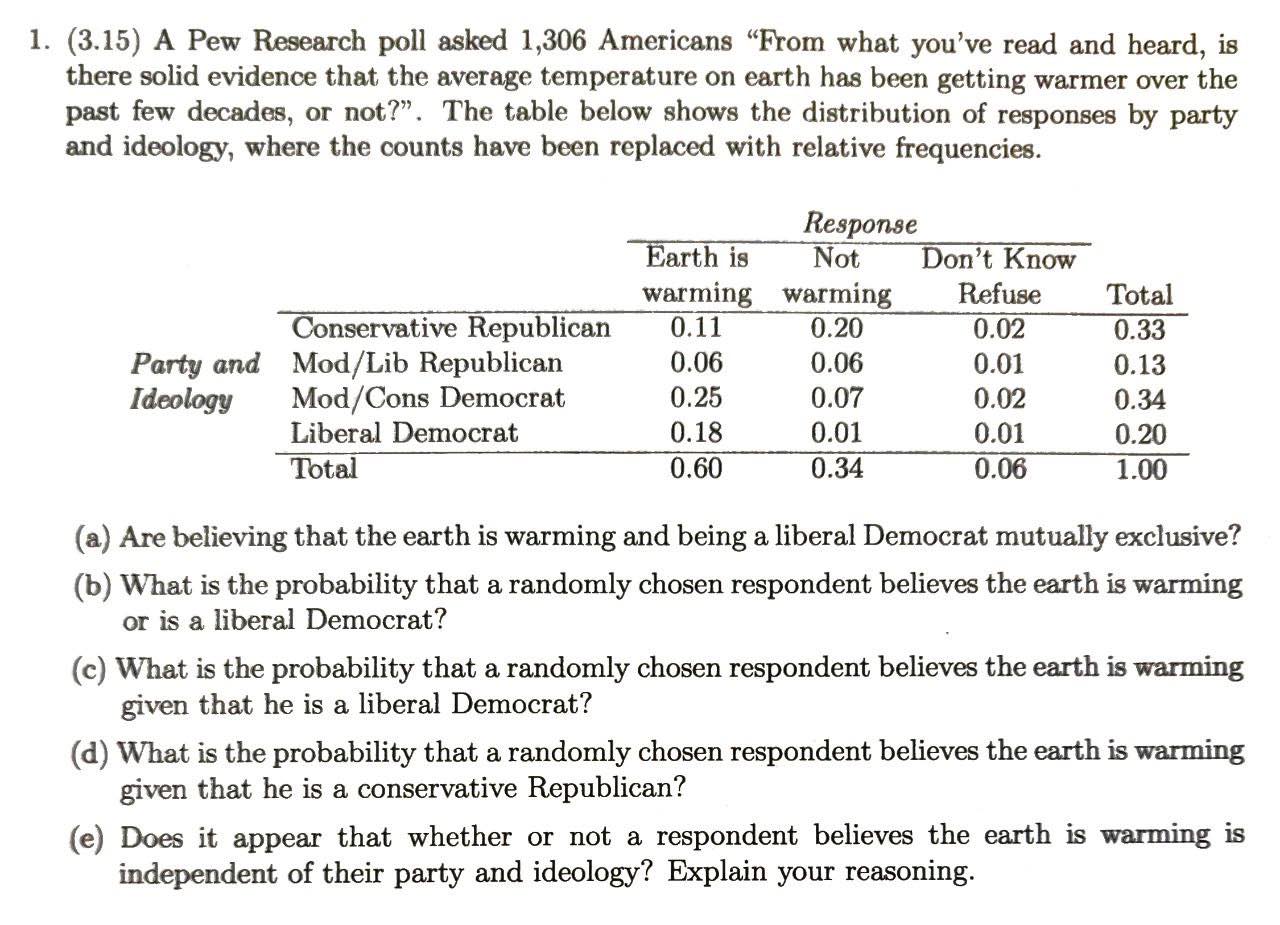
Problems¶
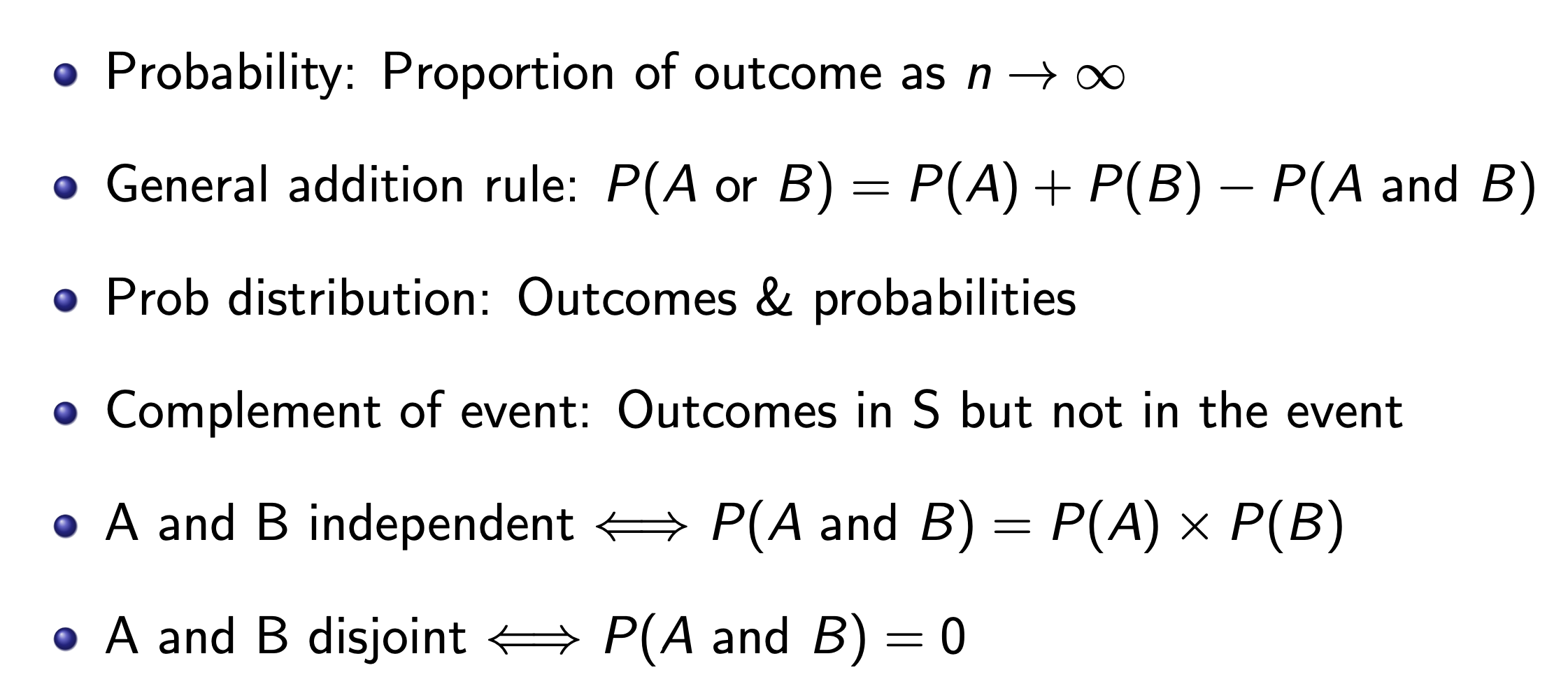
Probability¶
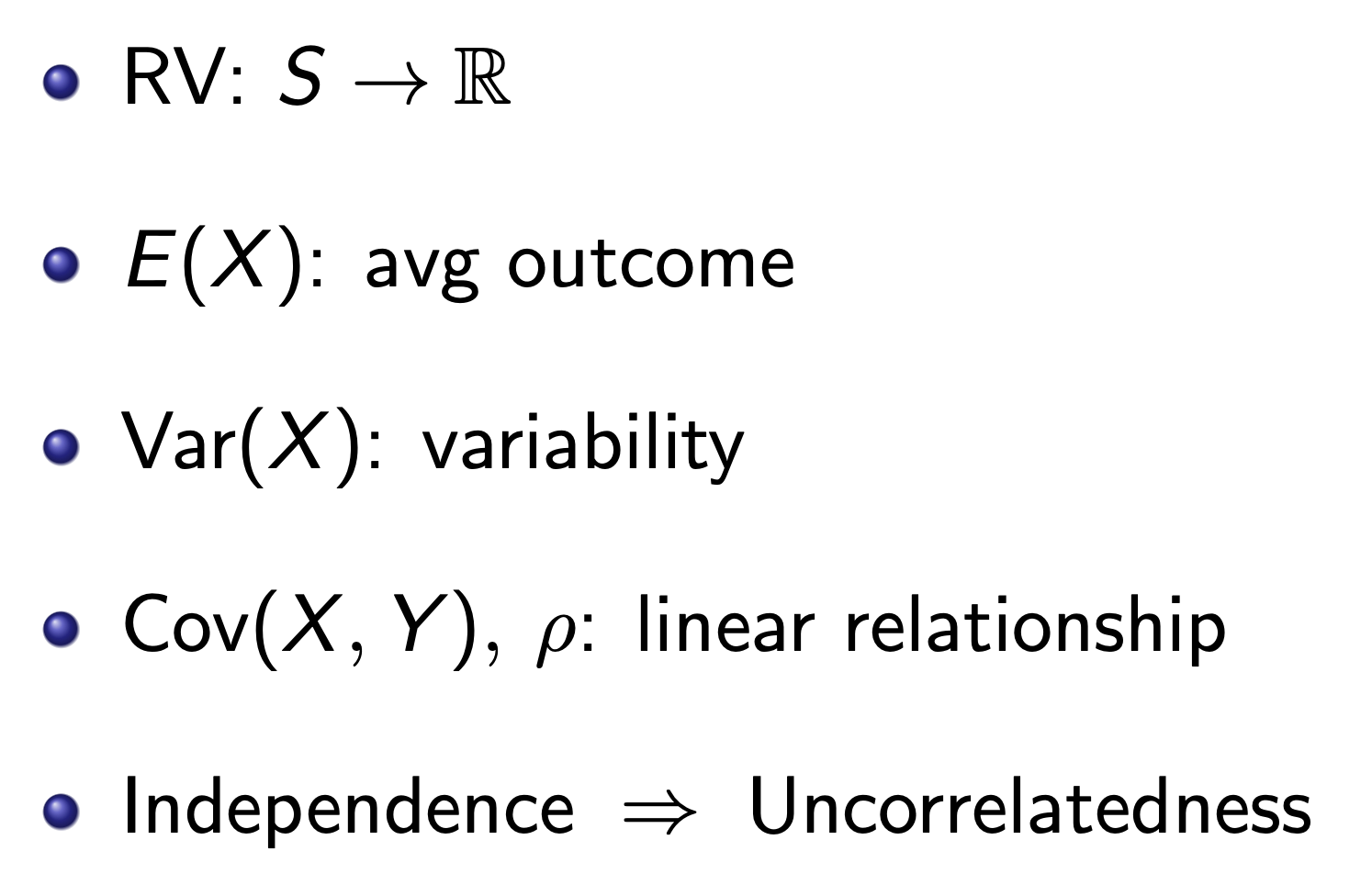
Random Variables¶
- sample space -> number
Rules¶
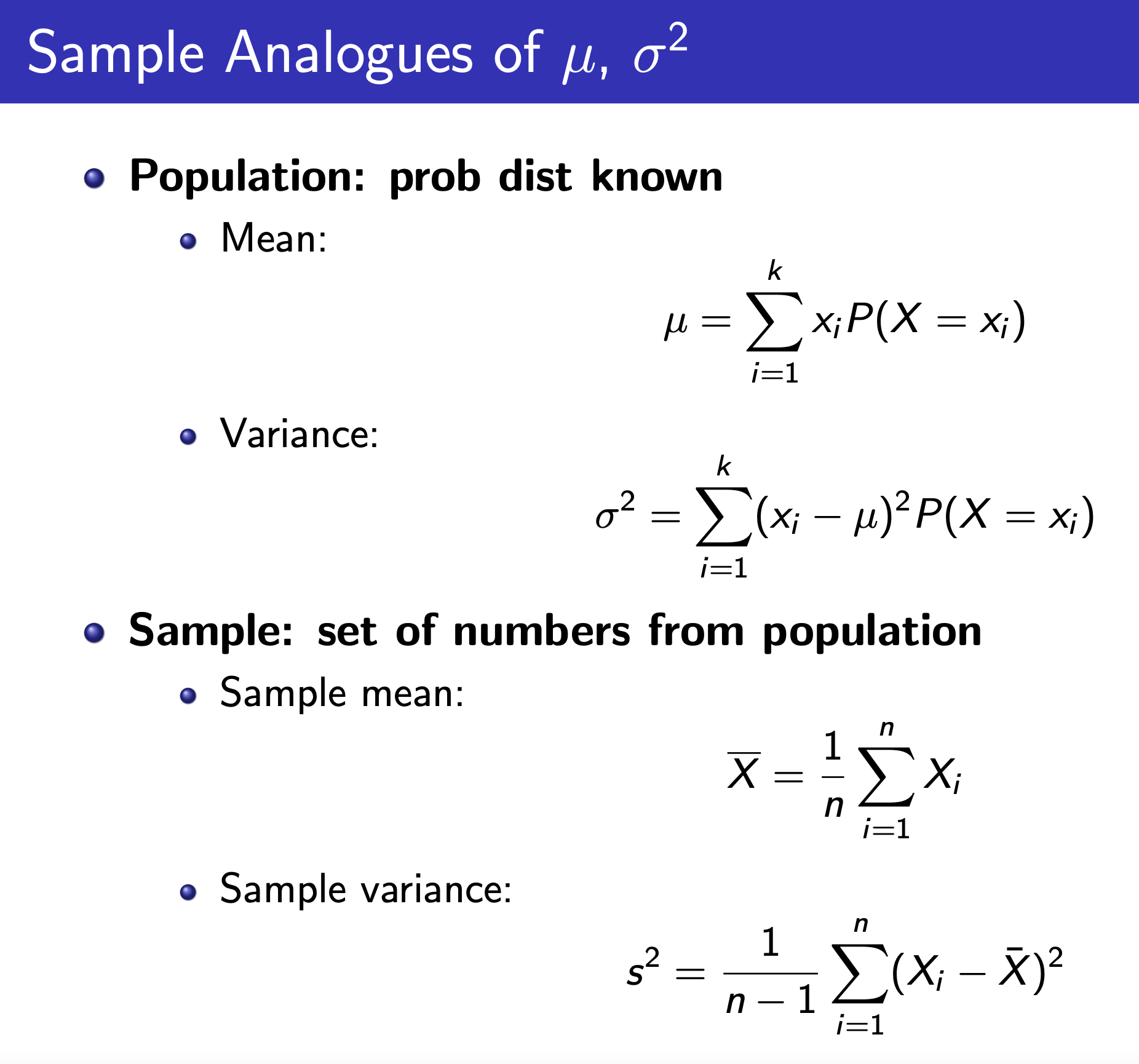
Variance vs. Sample Variance¶
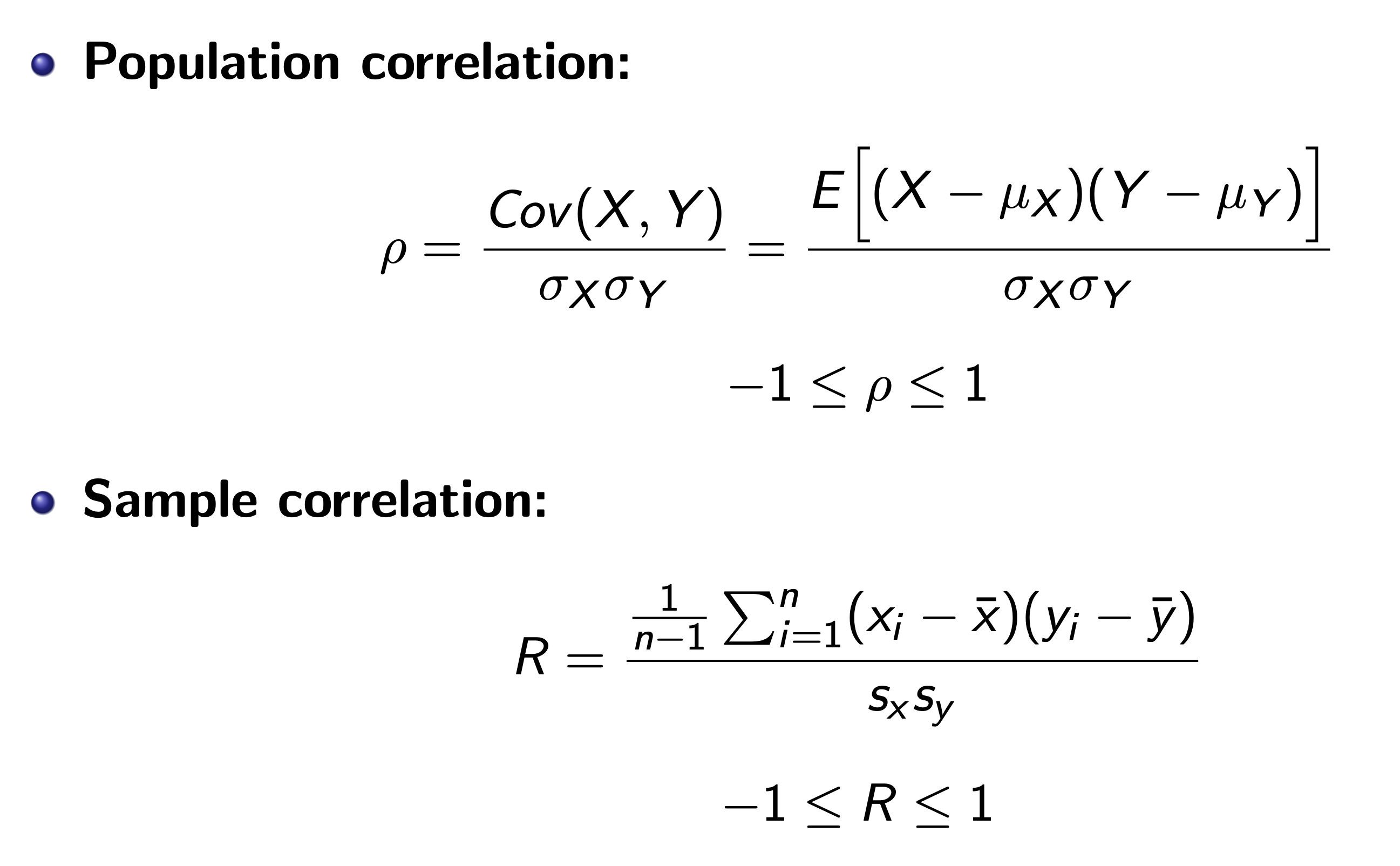
Correlation¶
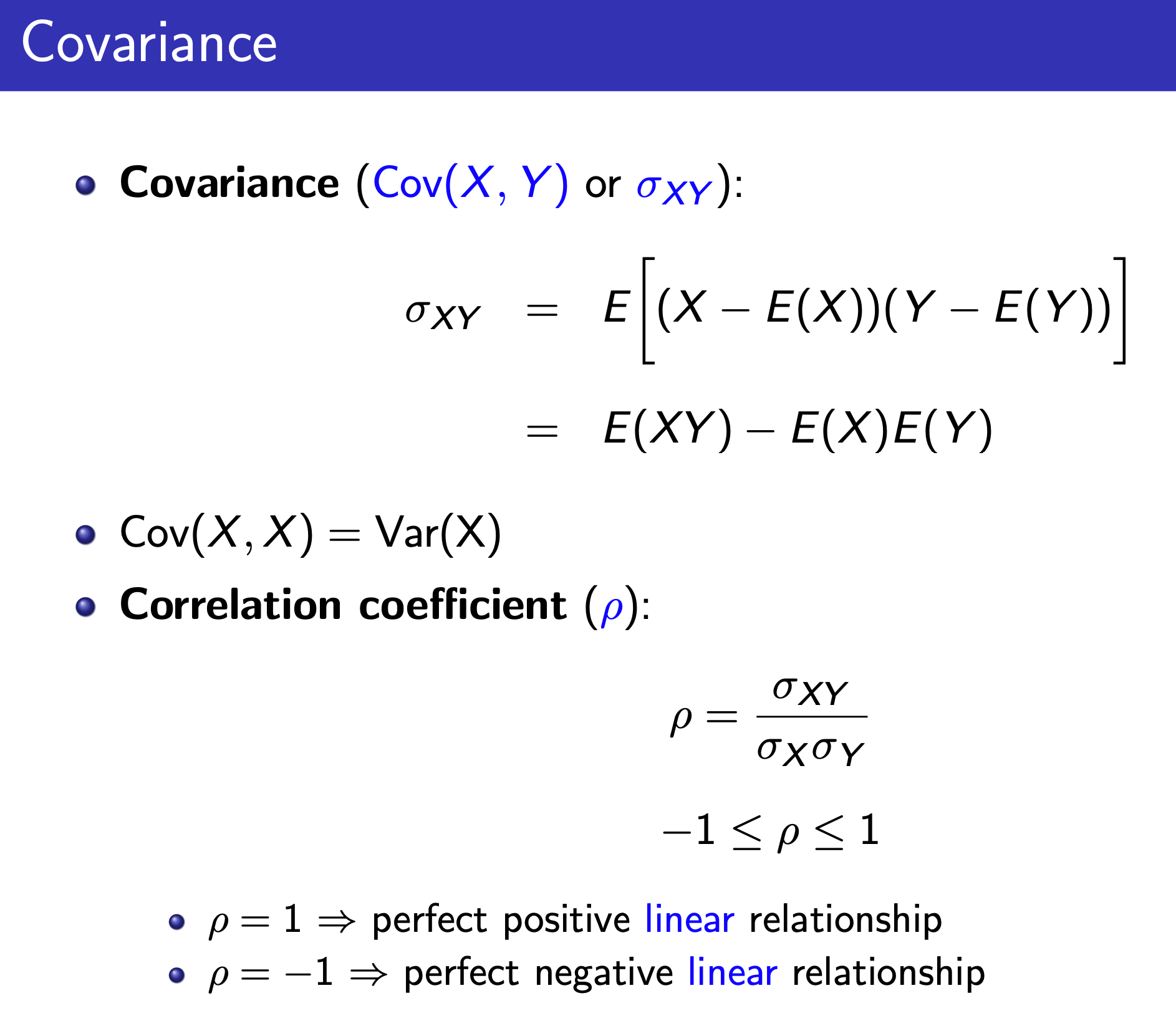
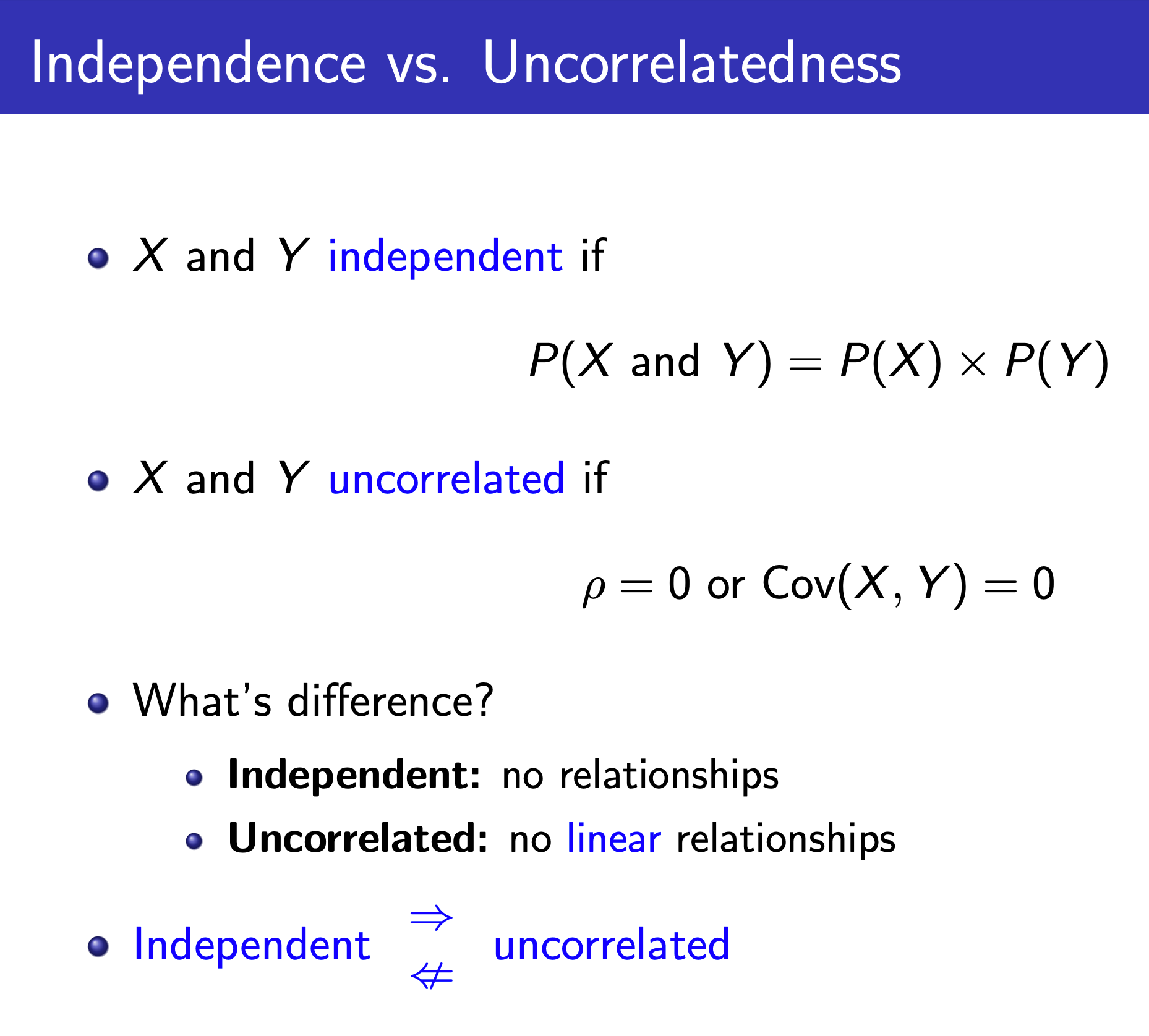
Problems¶



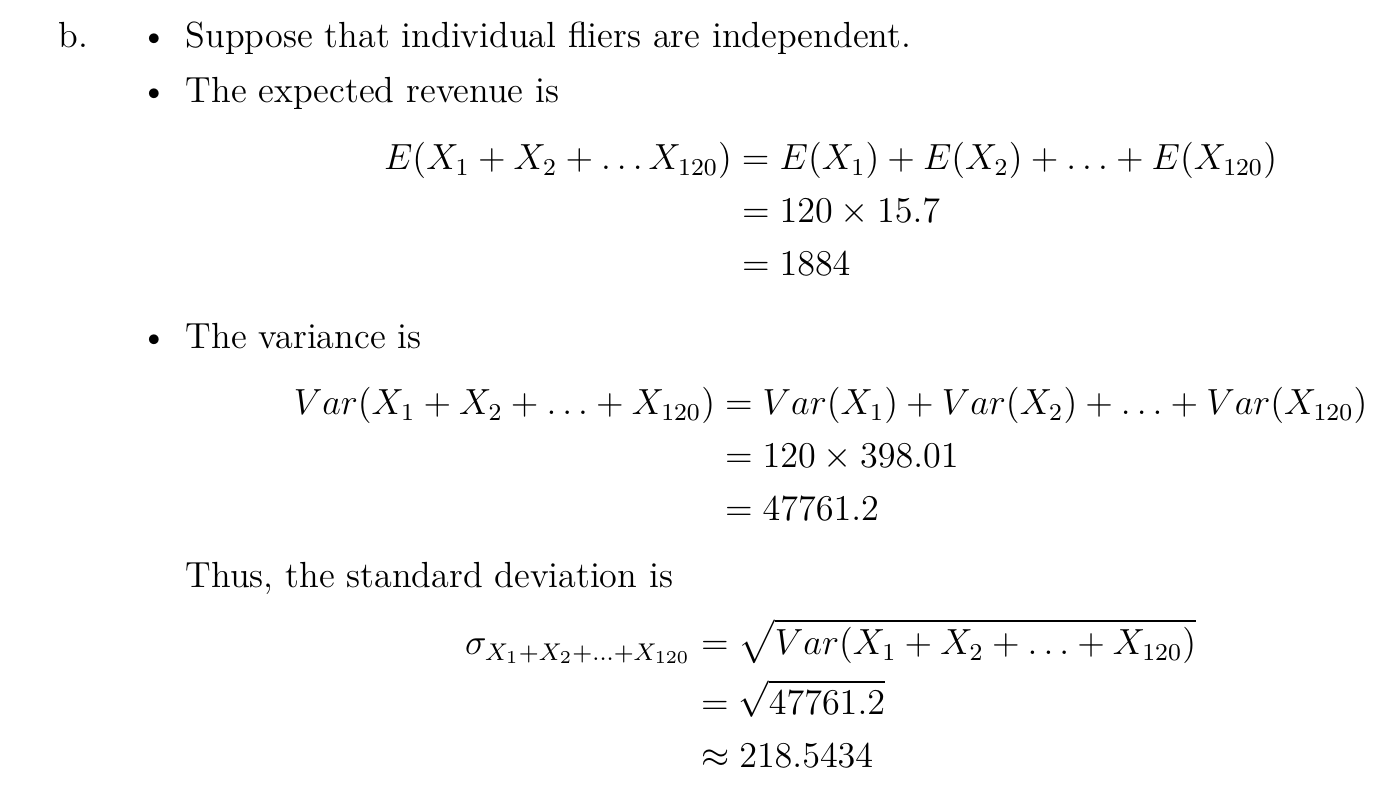
Distribution¶
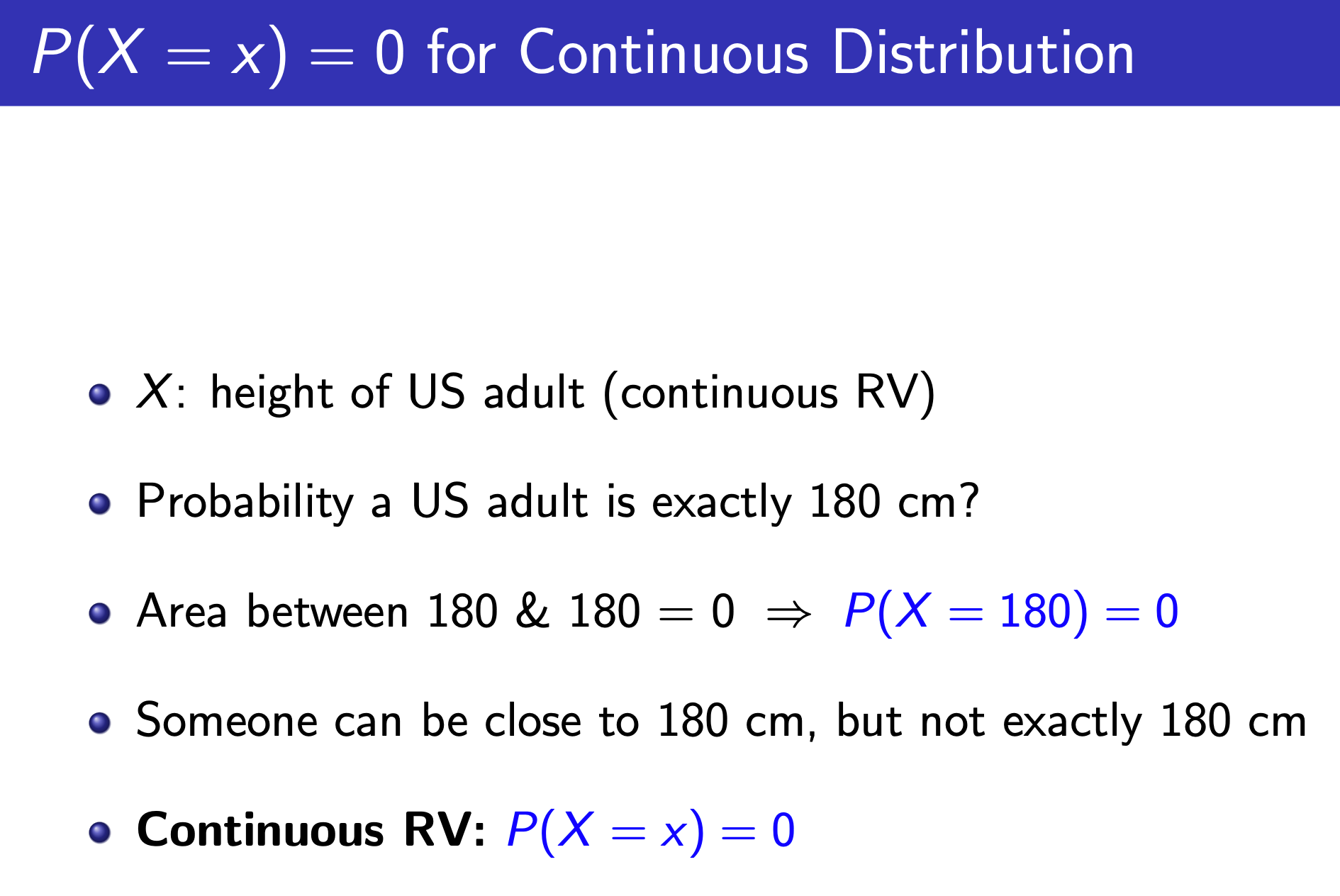
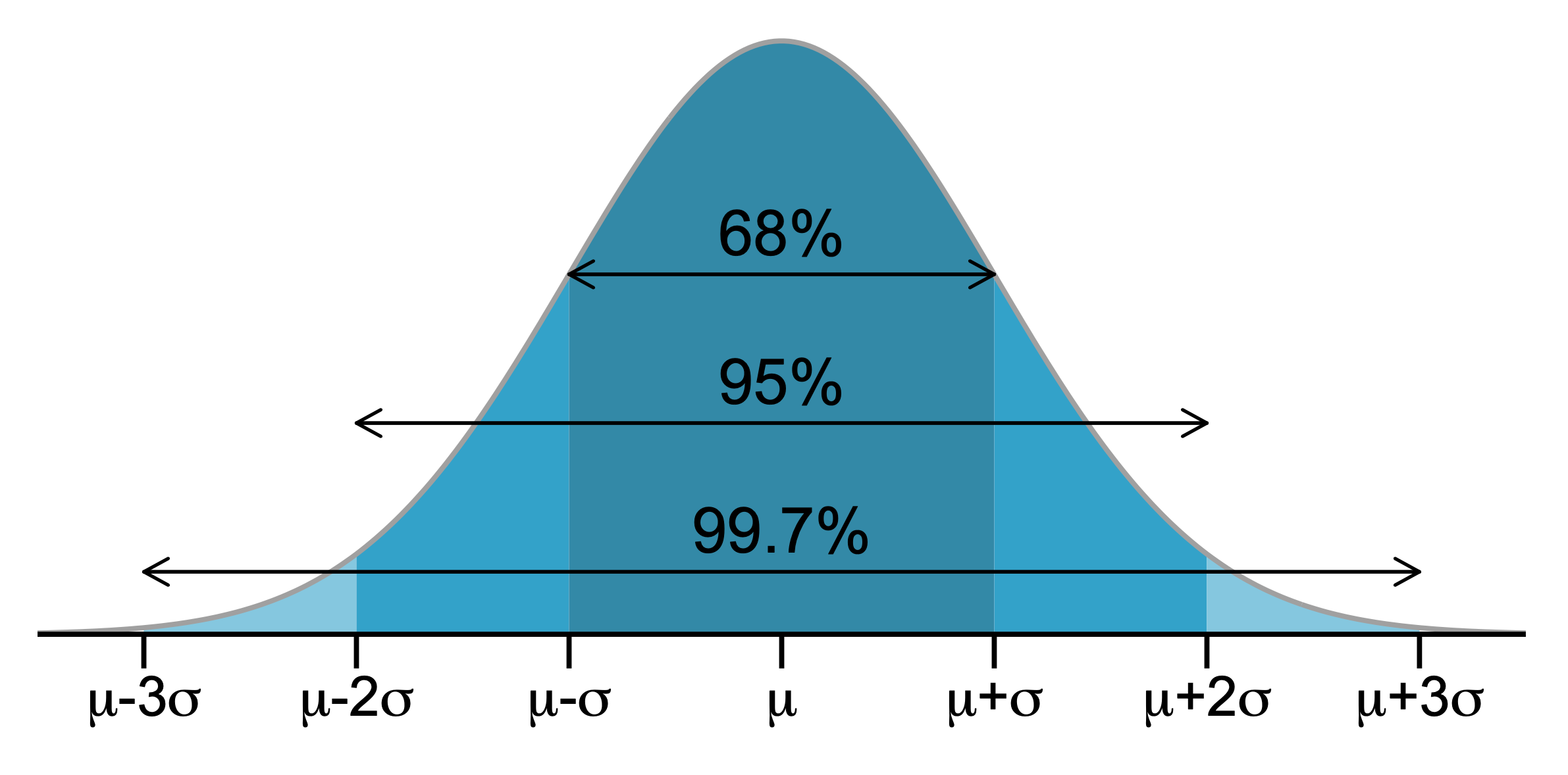
Normal¶
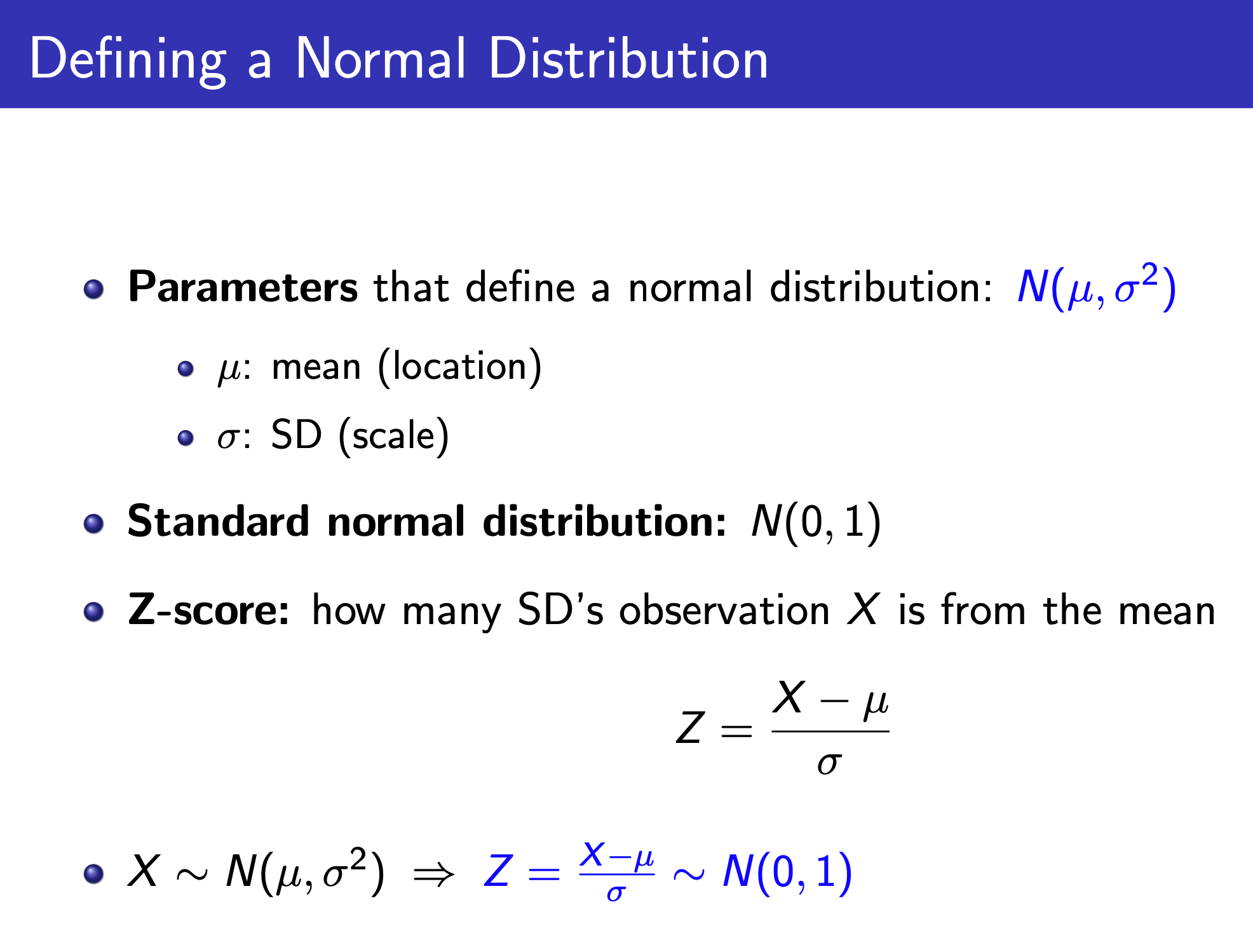
Use z-score to standardize
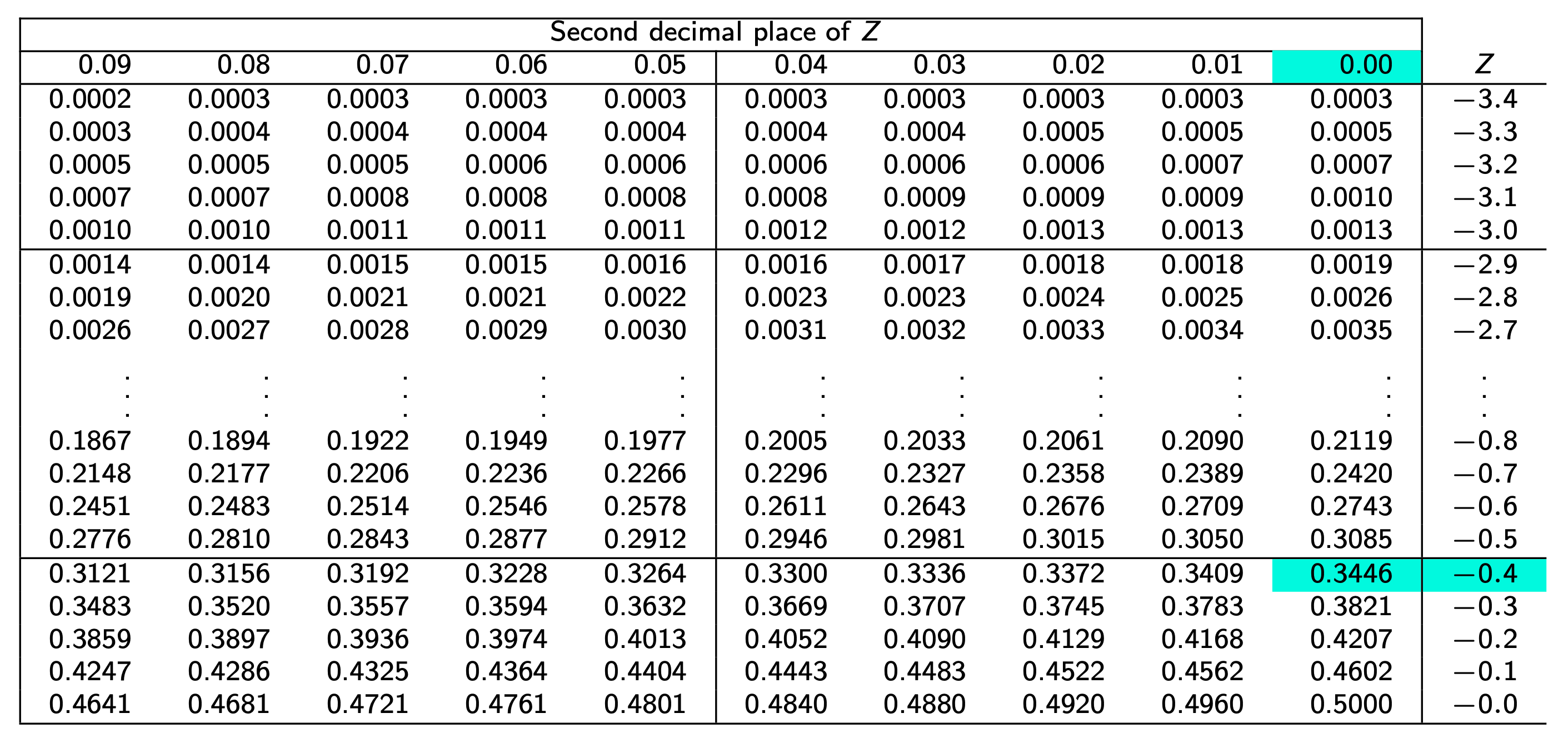
fx-991 es to find probability given z score
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bVdQ7OzGvU0
- P(z) -> Area less than z value
- R(z) -> Area greater than z value
- Q(z) -> Area between 0 and z value
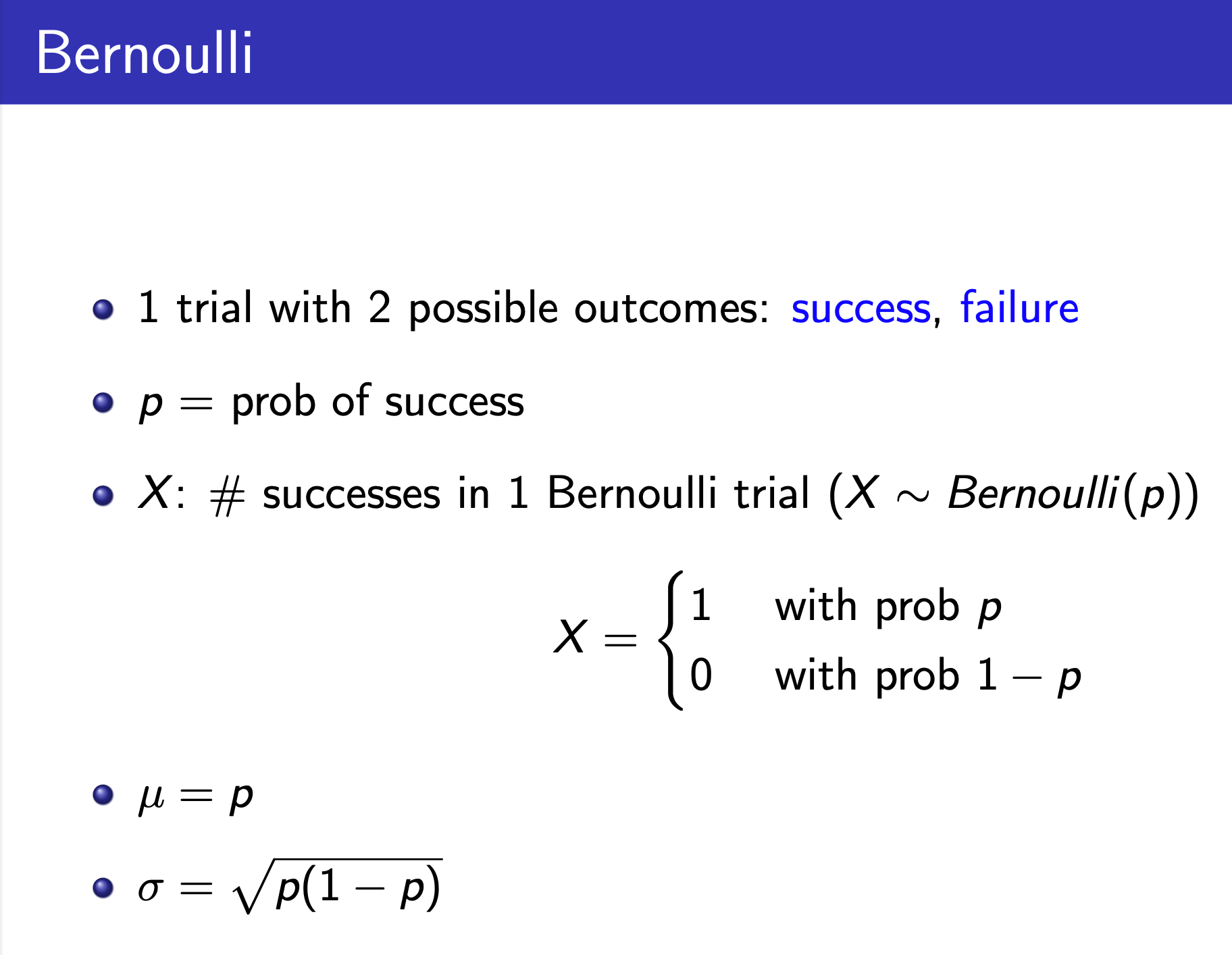
Bernoulli¶
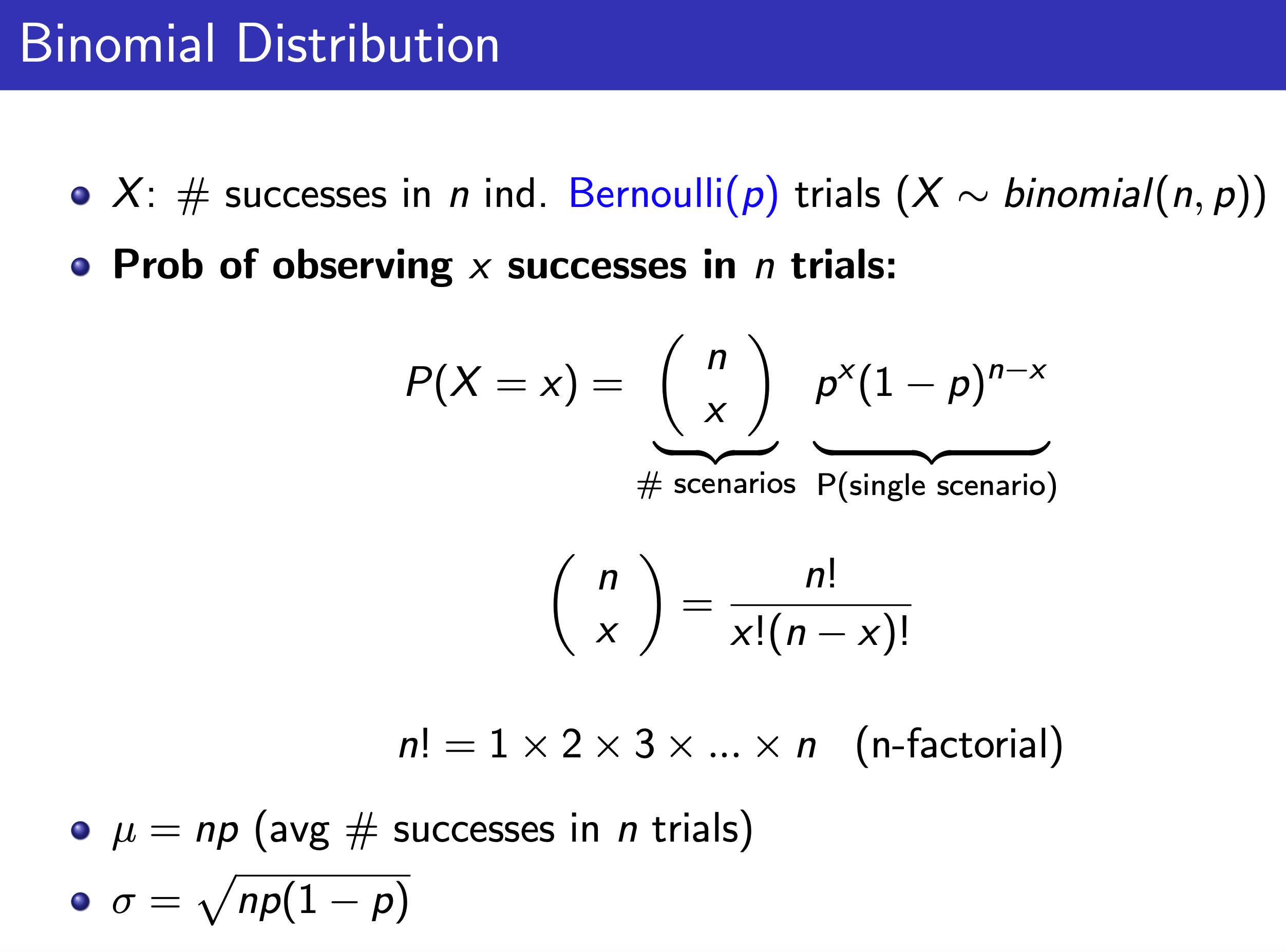
Binomial¶
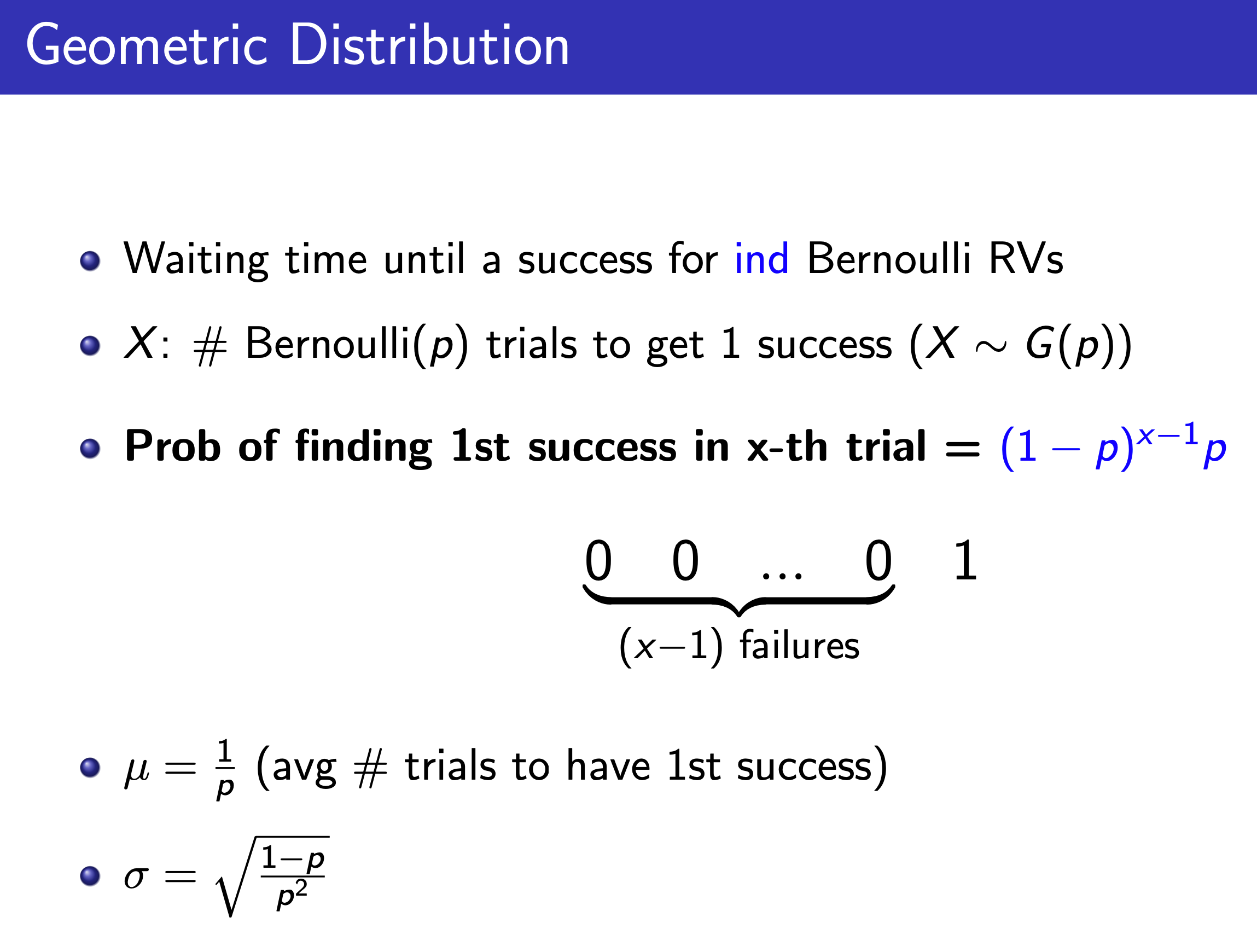
Geometric¶
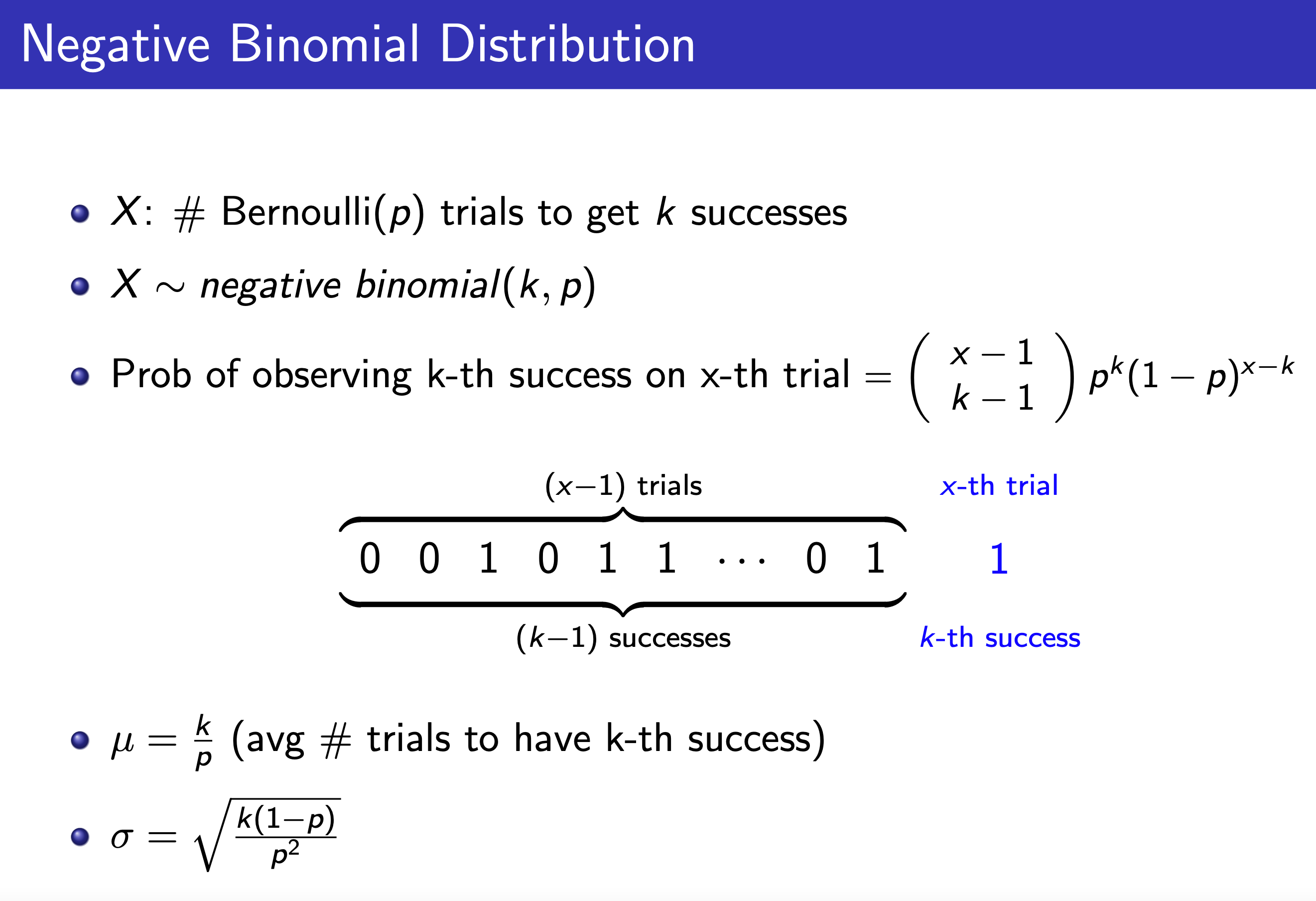
Negative Binomial / Pascal¶
i.e. Pascal
Poisson¶

Problems¶


Foundation of Inference¶
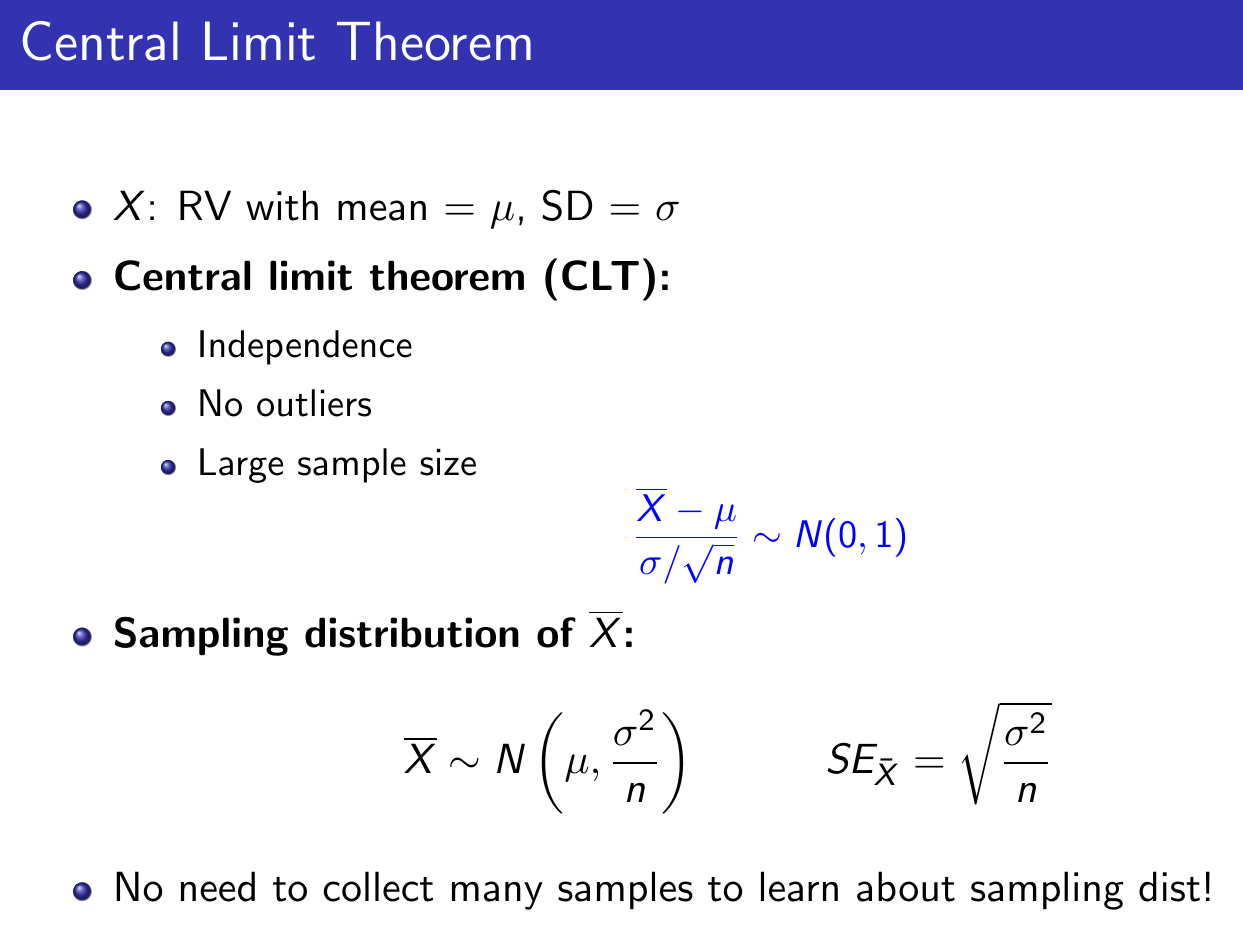
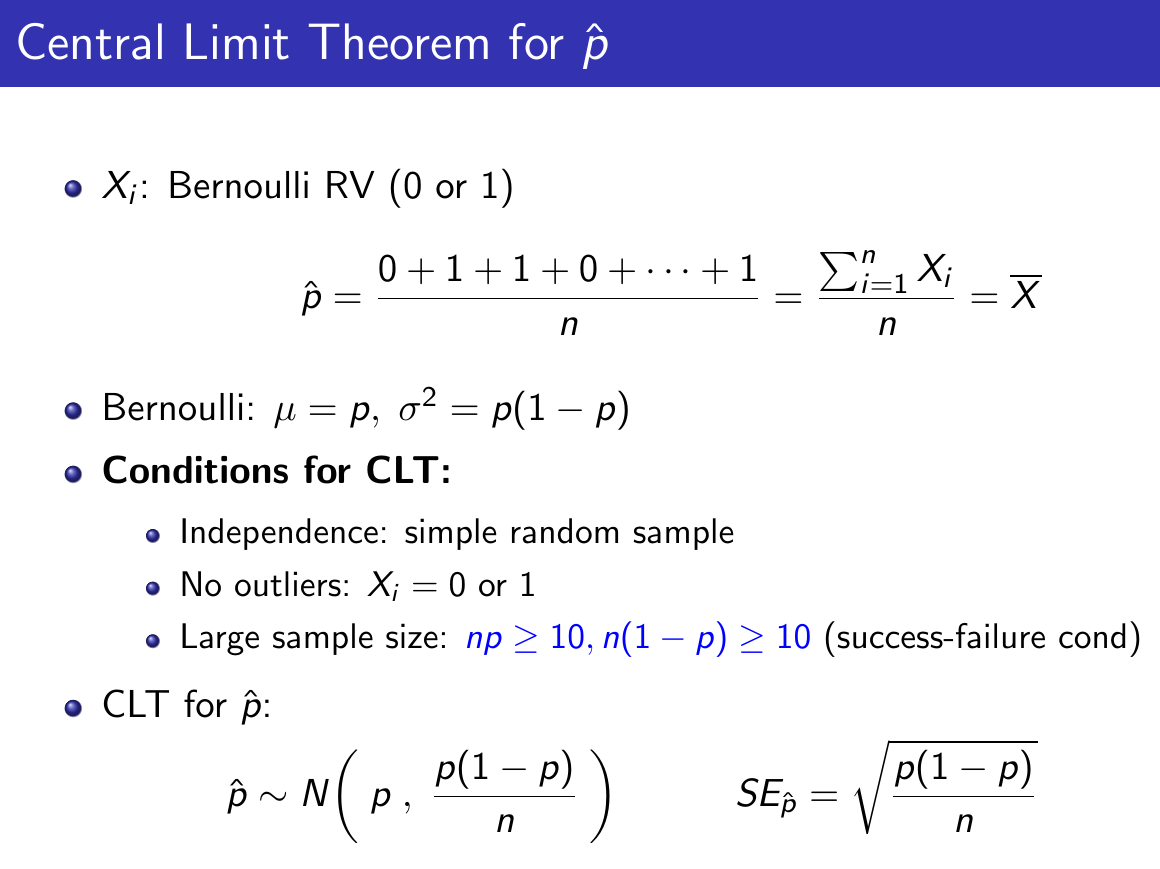
Central Limit Theorem¶

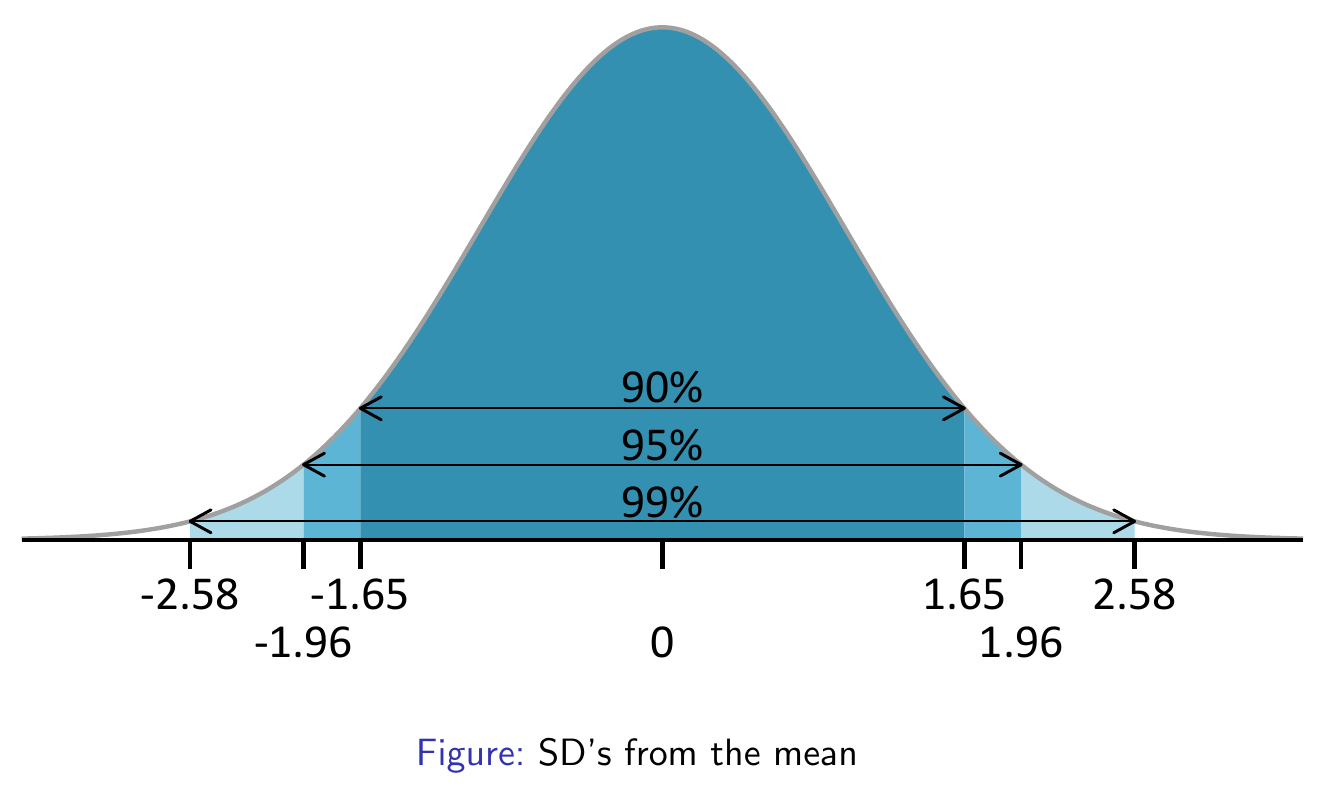
Confidence Interval¶
- Confidence Interval
- 99%: 2.5758 = 2.576 = 2.58
- 95%: 1.9600 = 1.960 = 1.96
- 90%: 1.6449 = 1.645 = 1.65
Hypothesis Testing¶
\(\alpha\) means the critical p value i.e. significance level
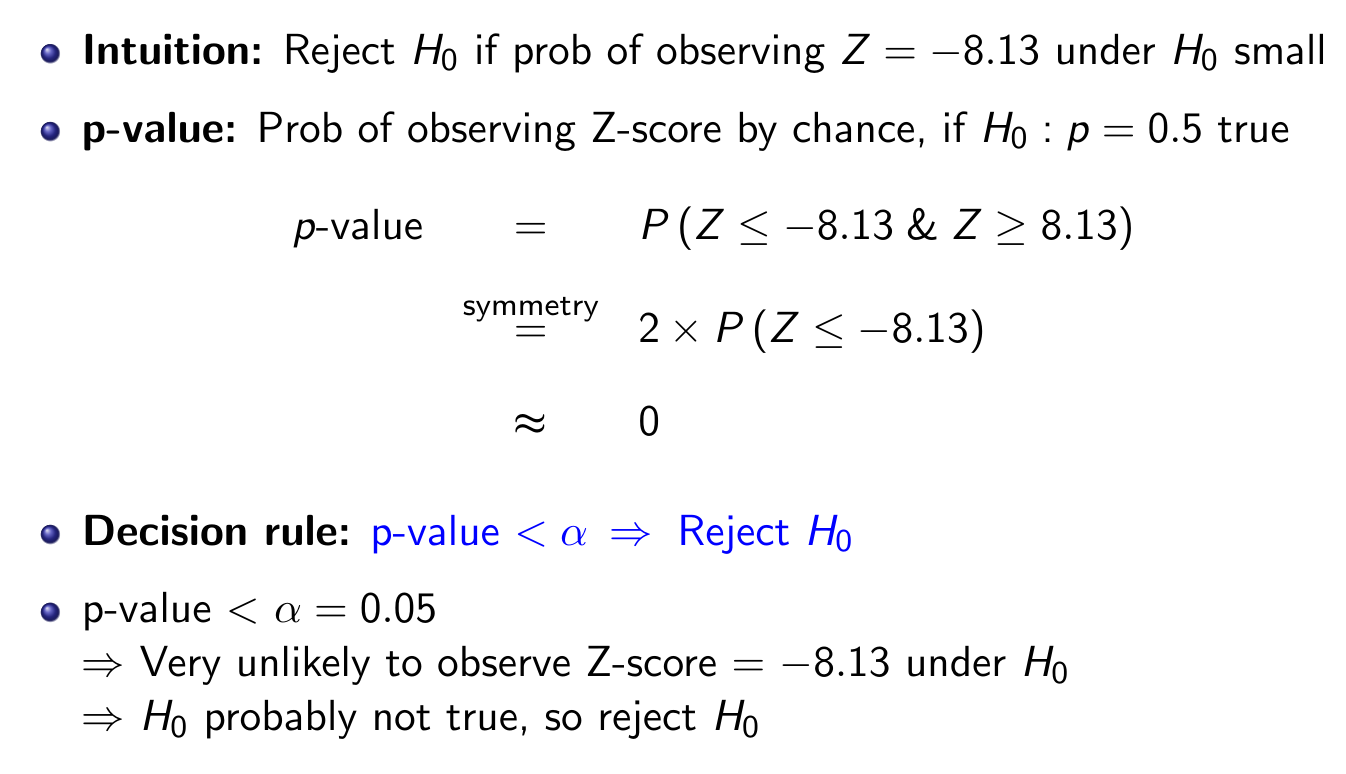
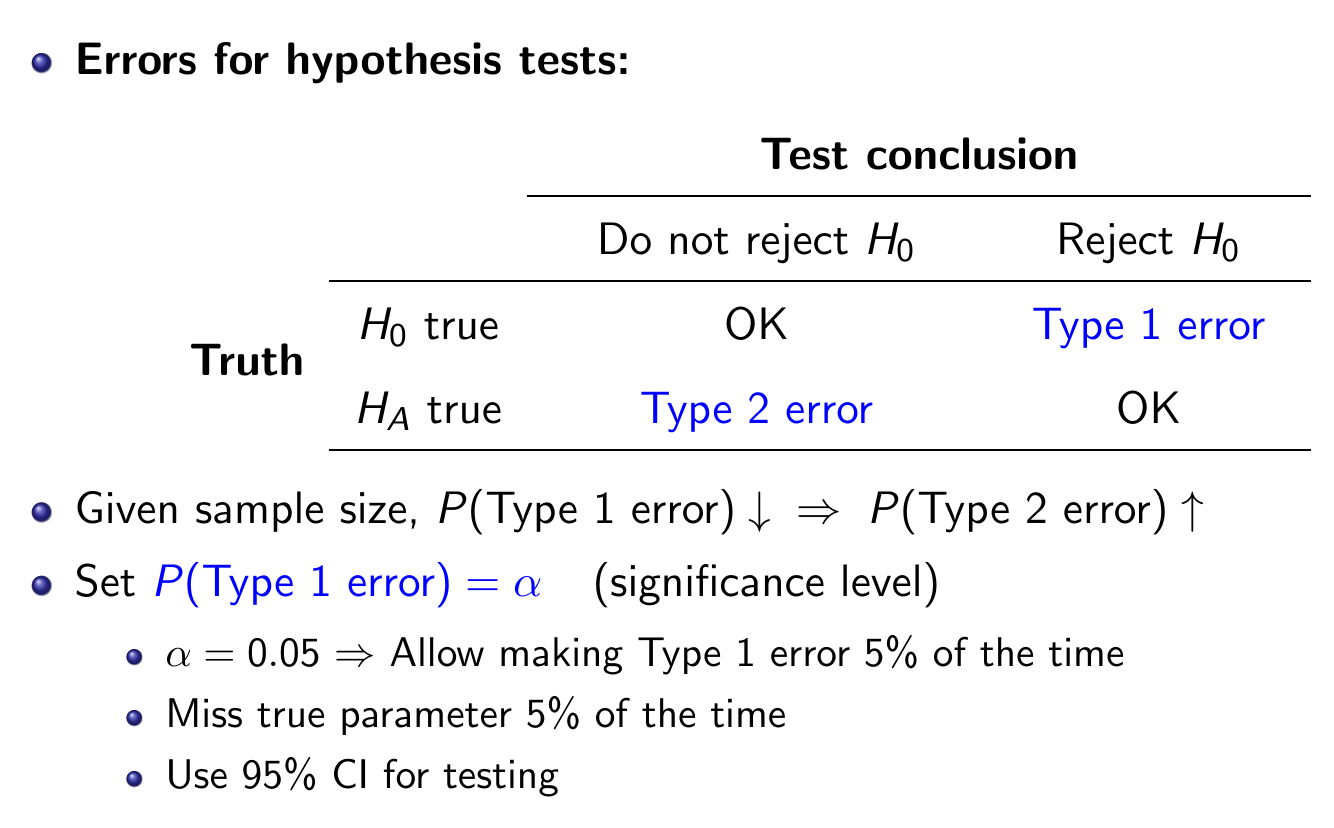
- Type 1 Error = False Positive
- assuming null -> negative, reject null -> positive
- Type 2 Error = False Negative
Remember to use the p stated in \(H_0\) to calculate SE and do hypothesis testing!
e.g.



There is no statistically significant evidence that the fraction of children who are nearsighted is different from 0.08 at the 5% level
Inference for Categorical Data¶
Hypothesis Testing for 1 Porportion¶
Problems¶






Hypothesis Testing for 2 Porportion¶
SE of the difference between 2 porportions
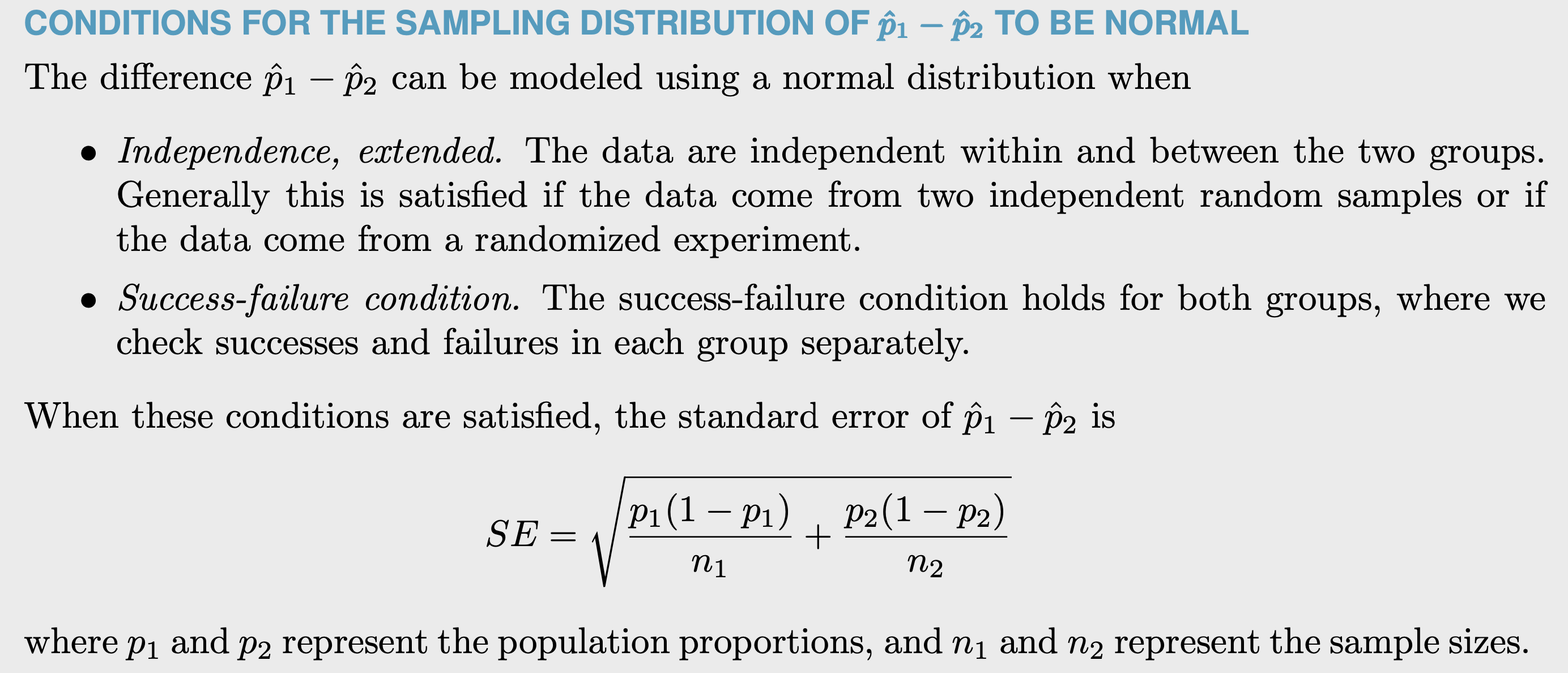
e.g.
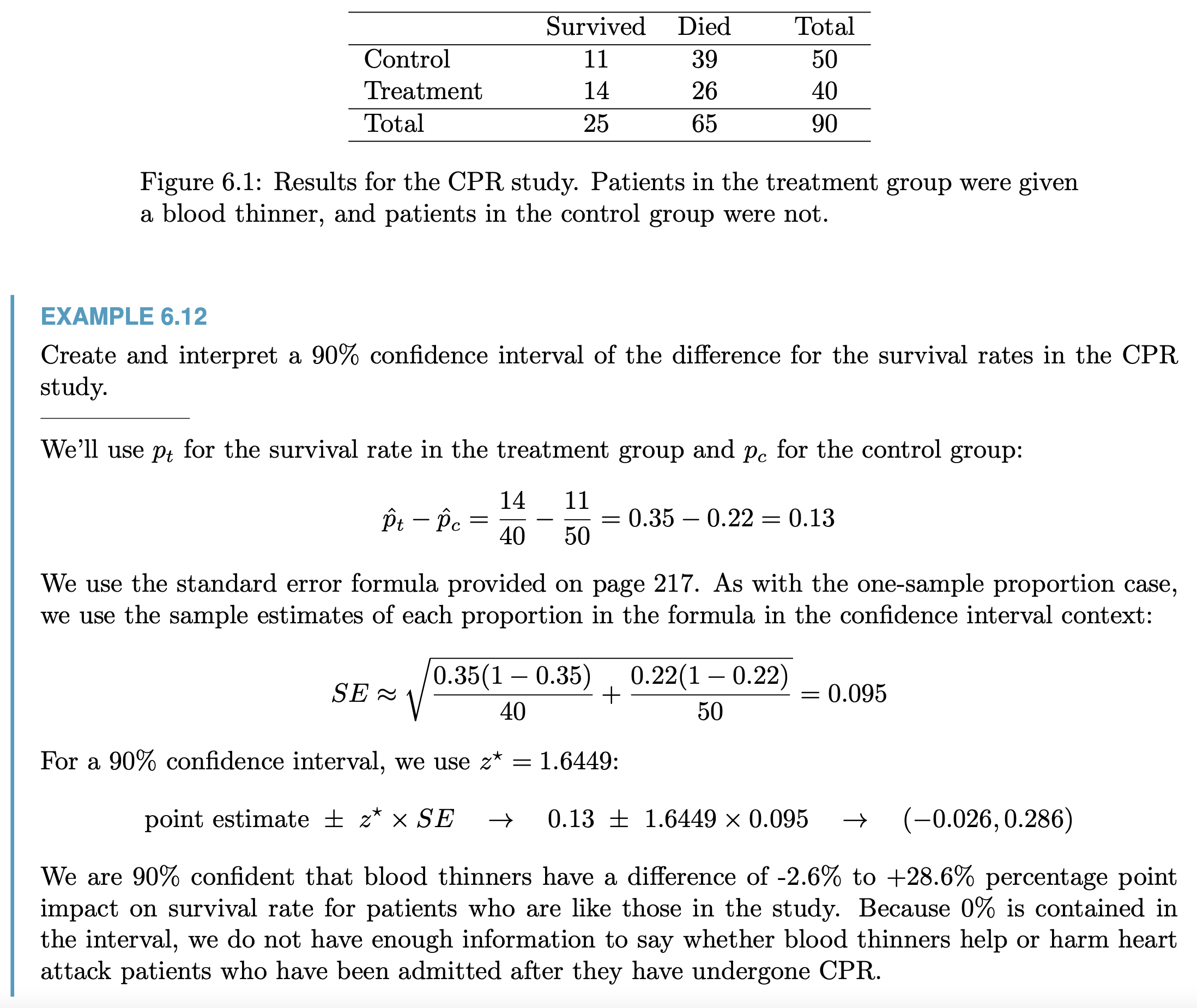
Use p = overall p of the 2 porportions to calculate SE when \(H_0\) is that 2 porportions has the same mean
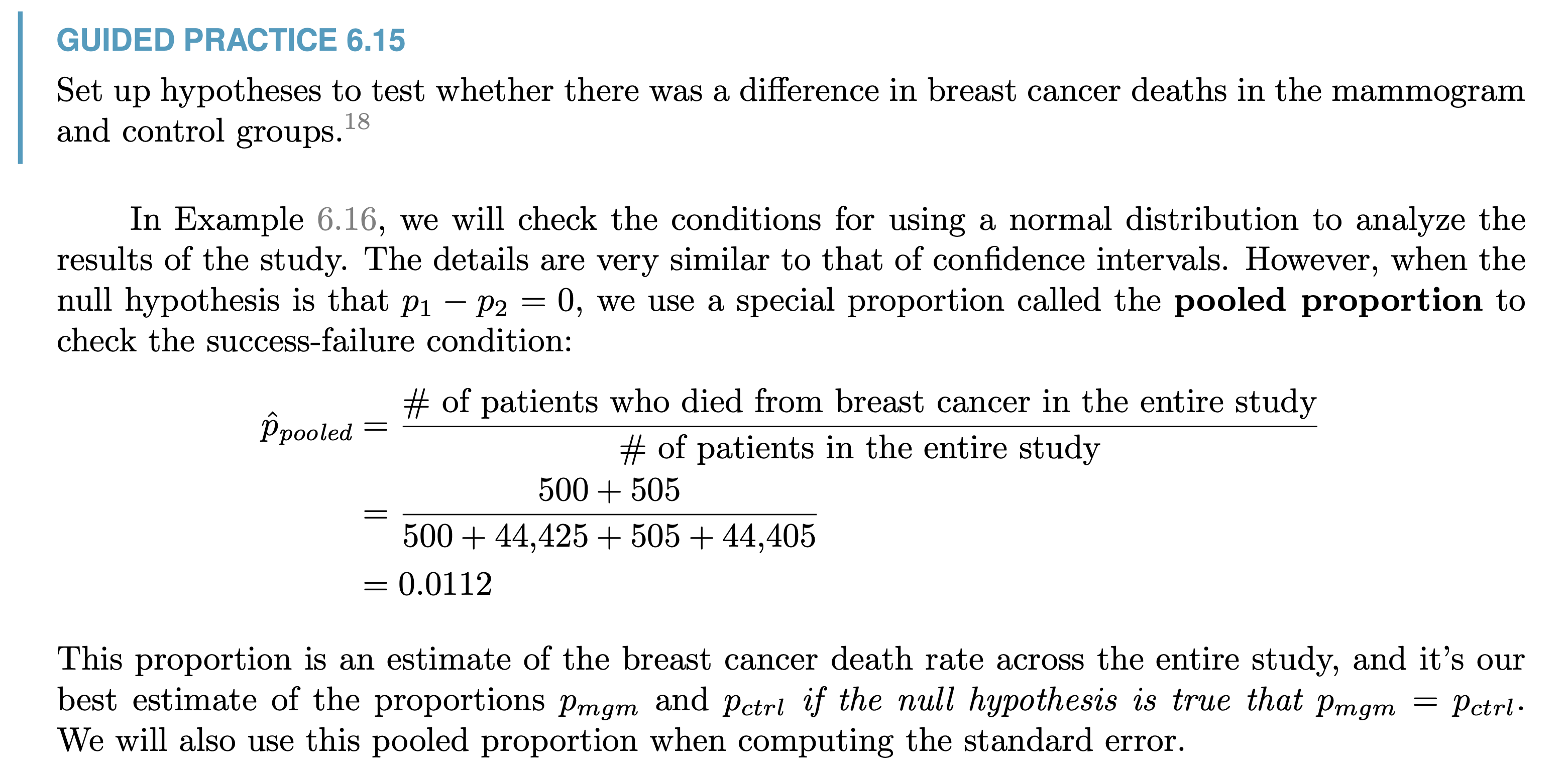
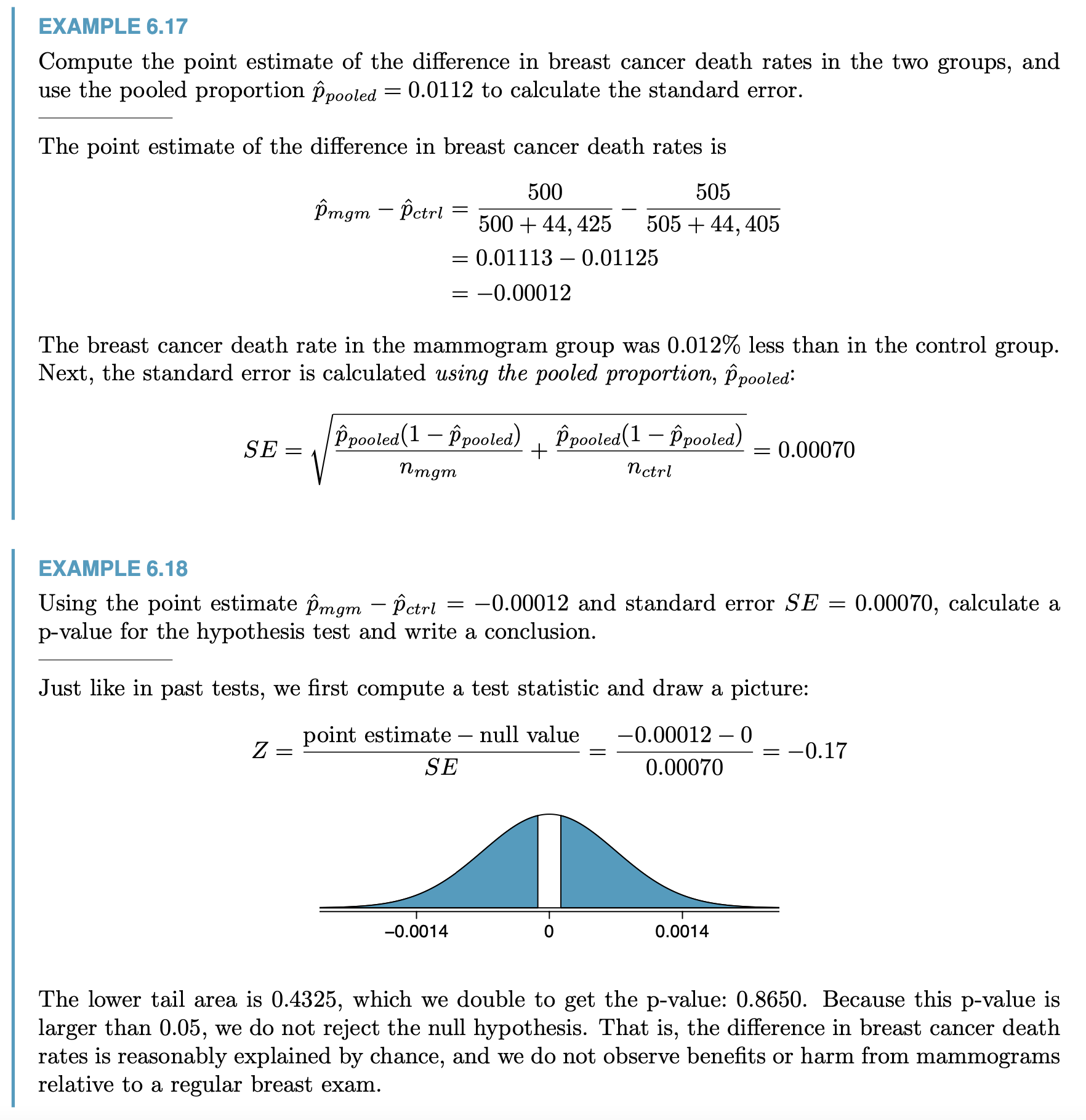
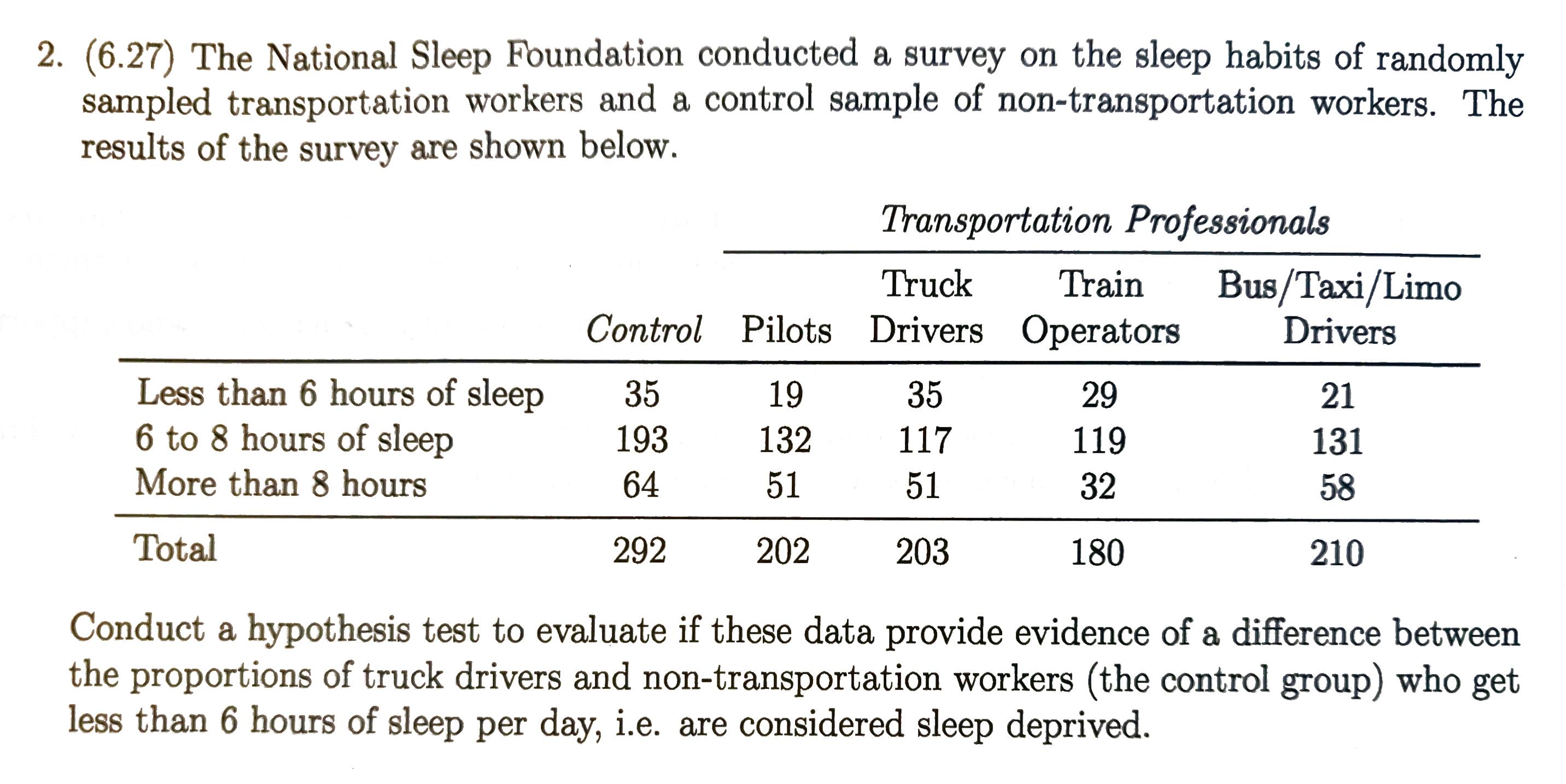
Problems¶

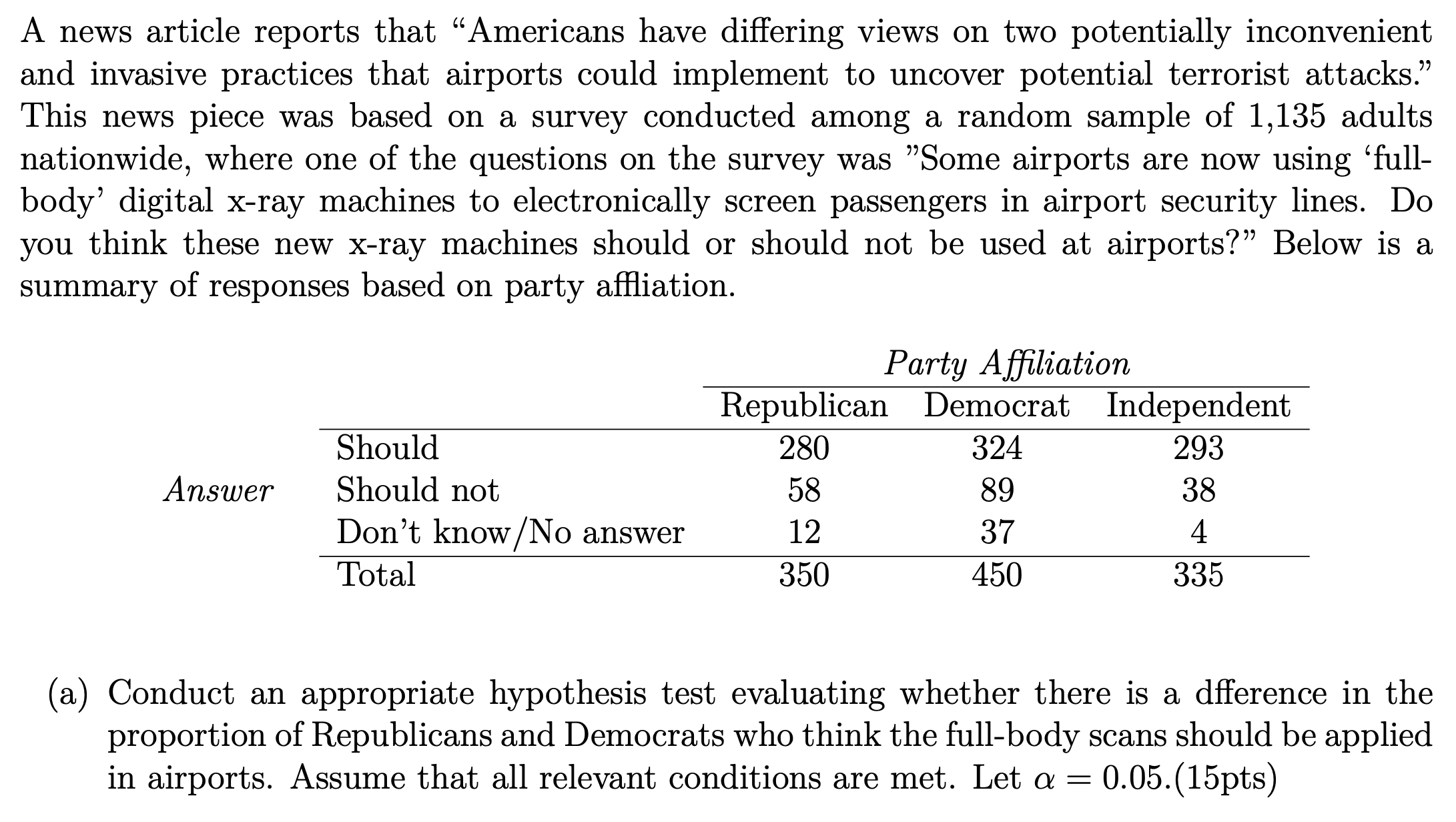

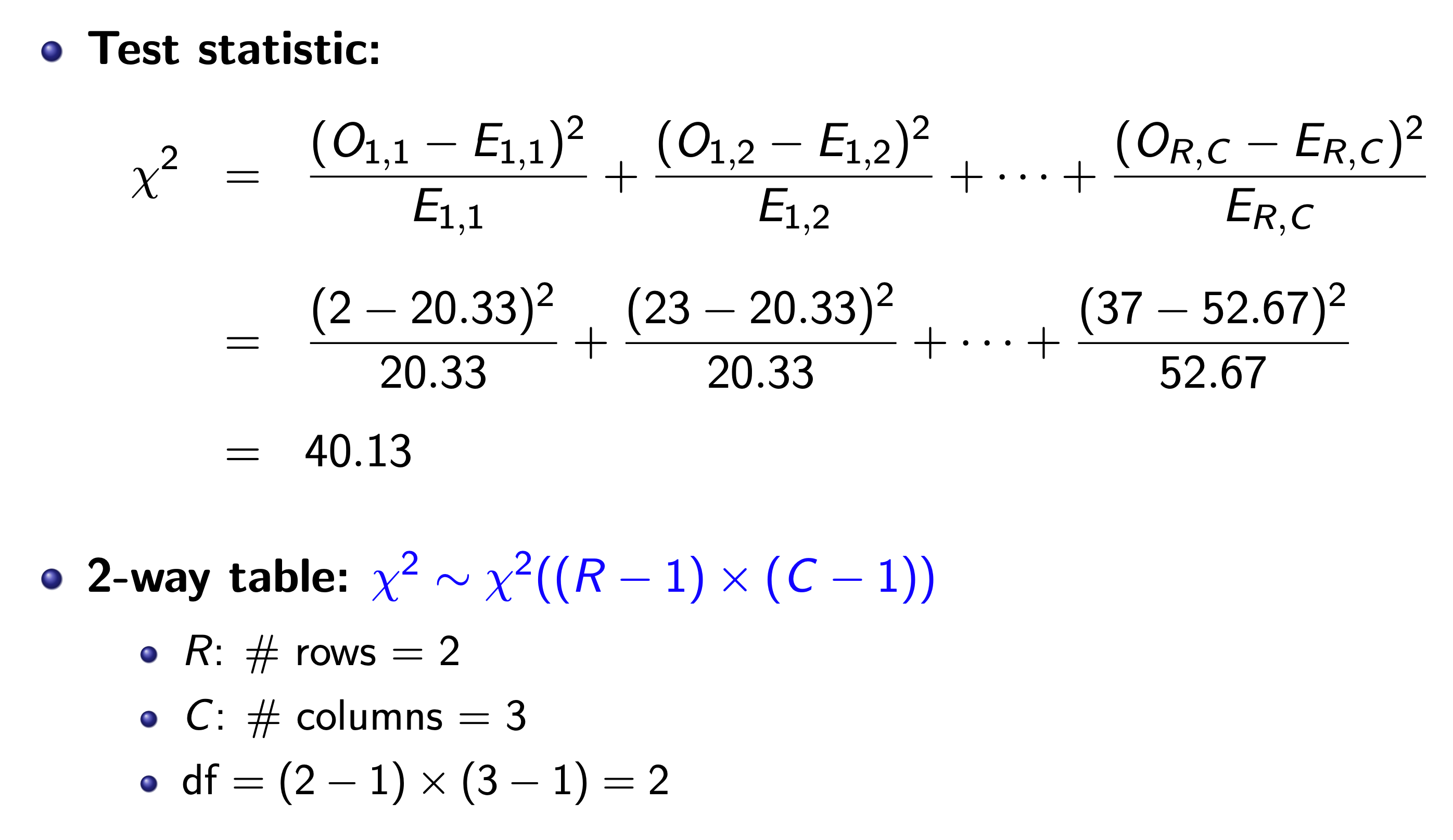
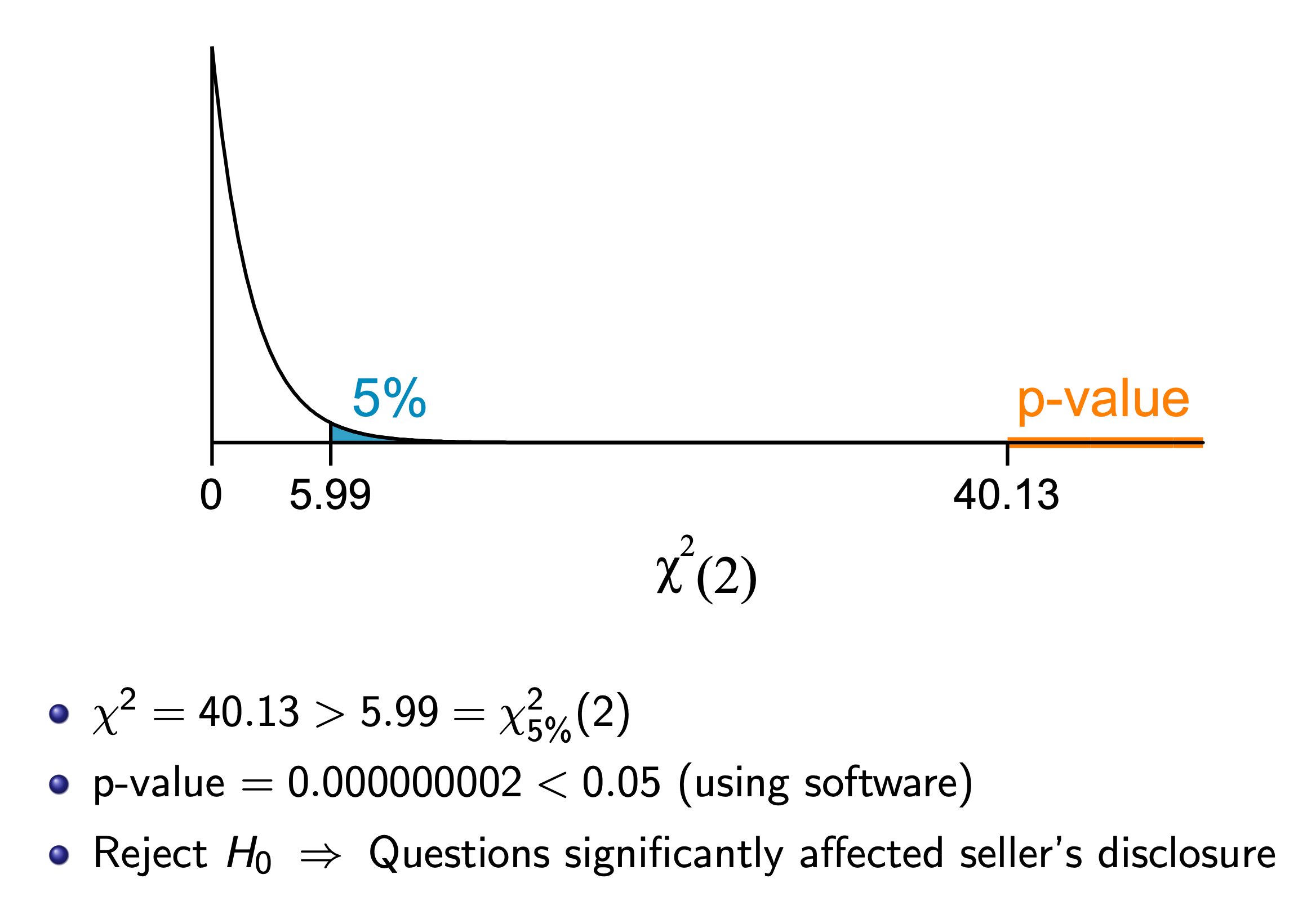
Chi-Square Test¶
One-Way Table¶
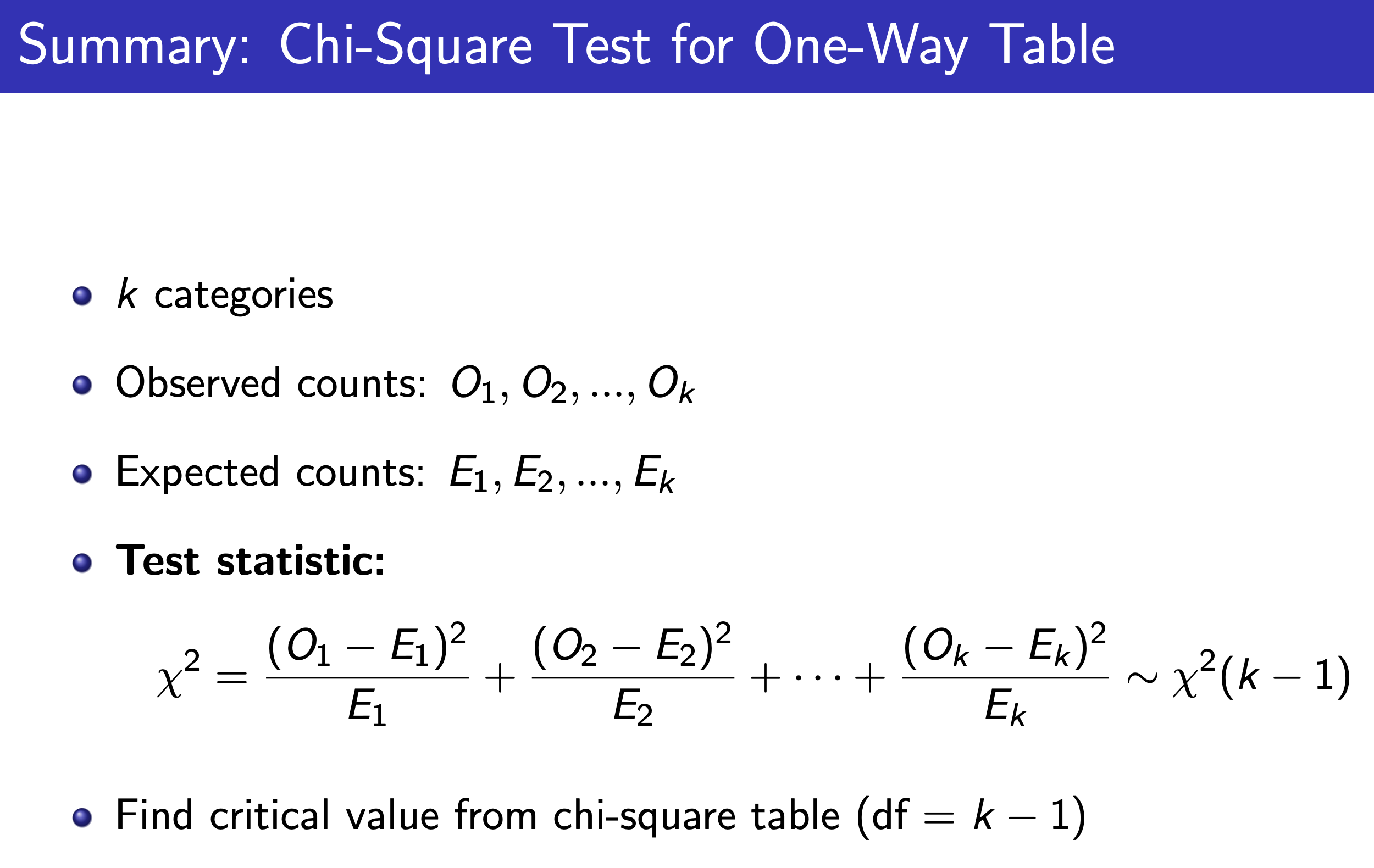
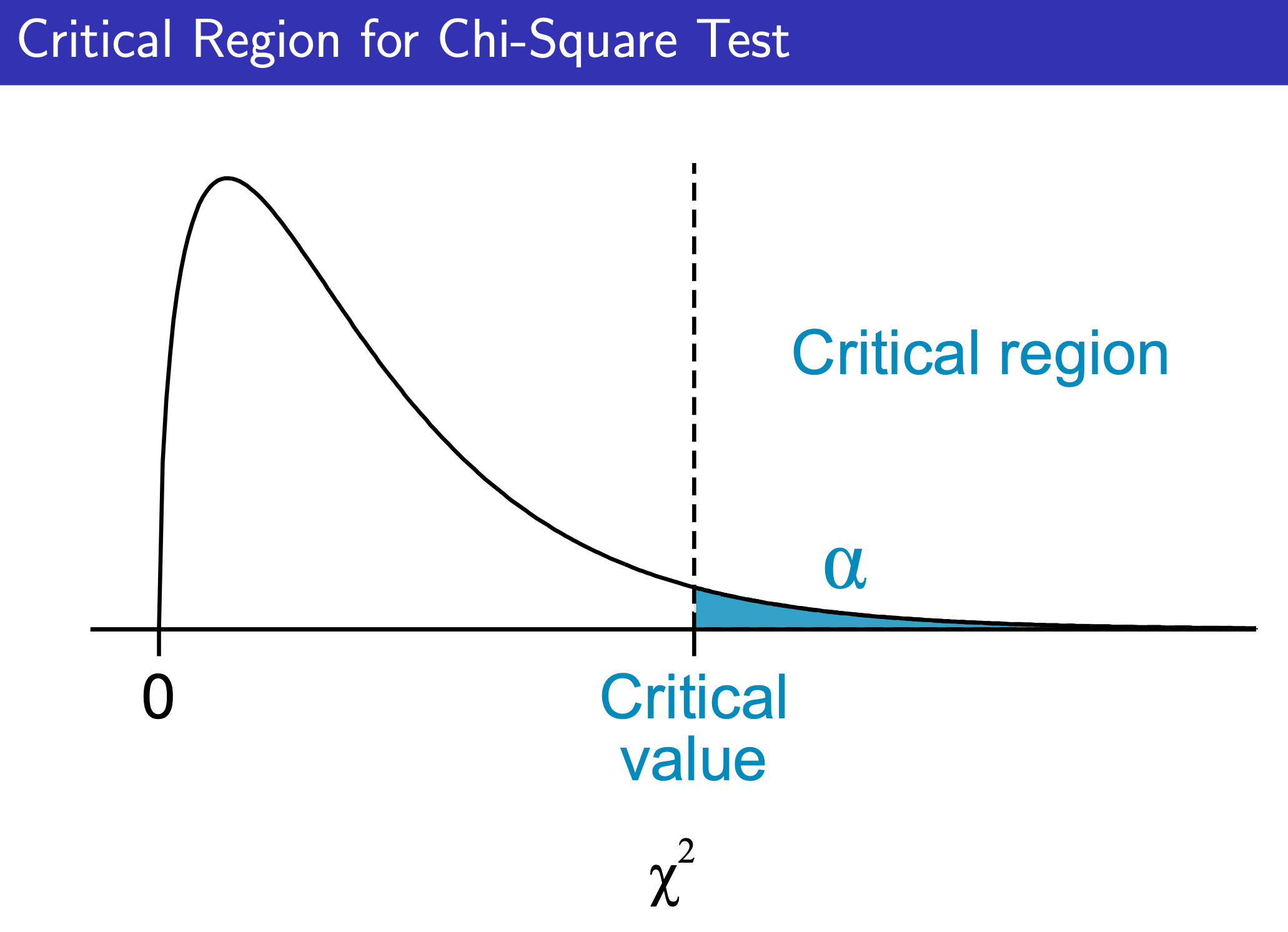
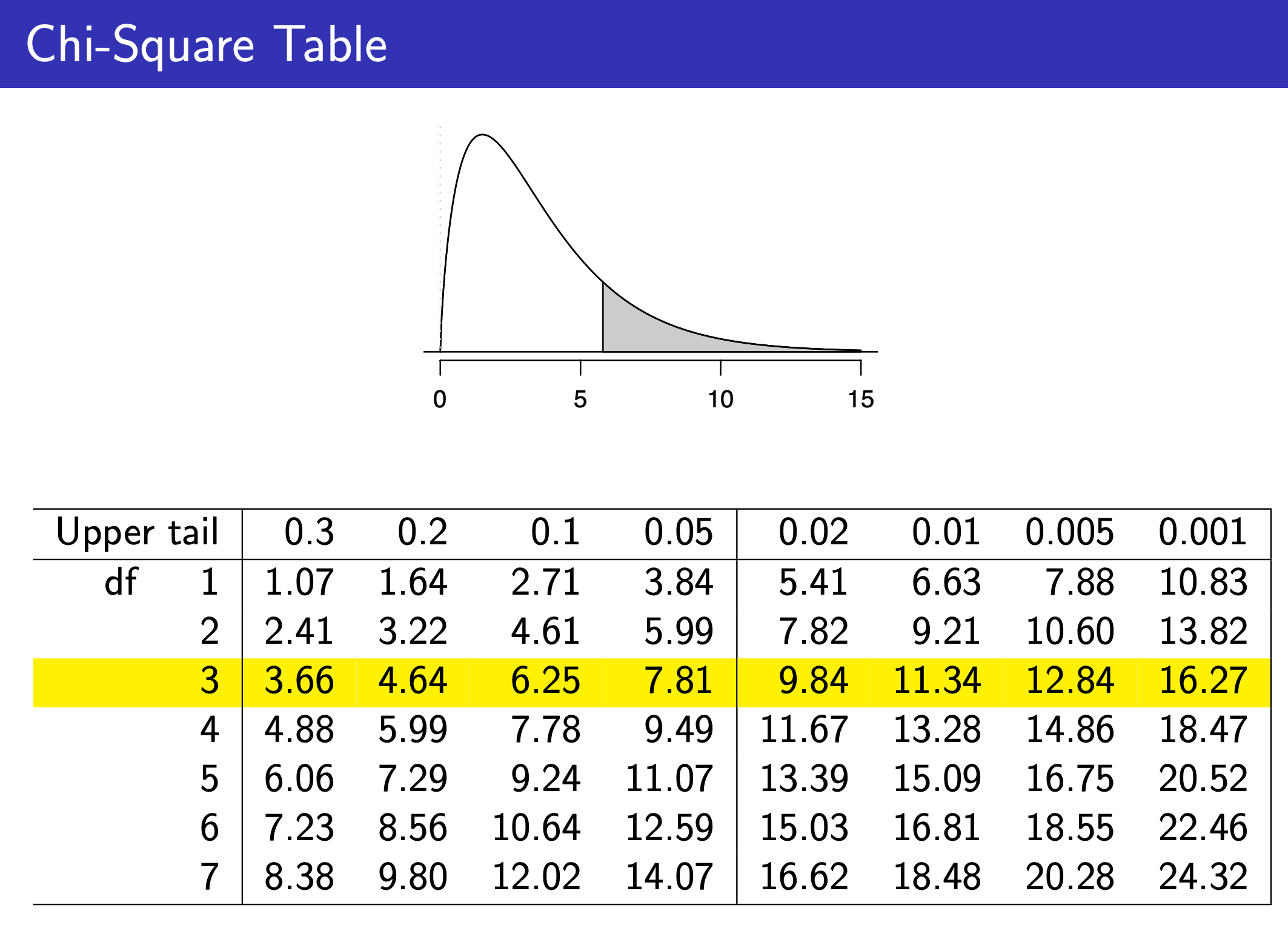
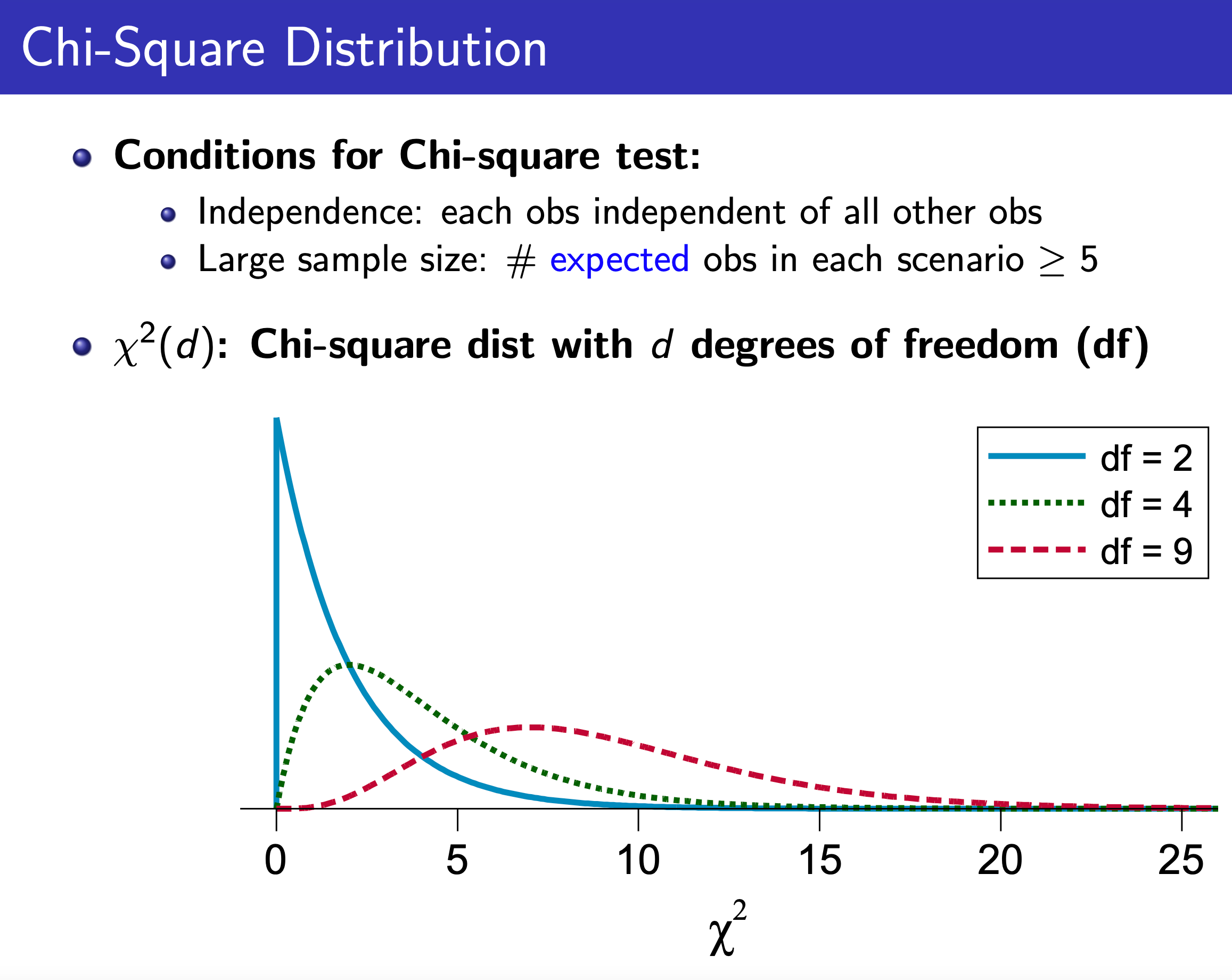
e.g.
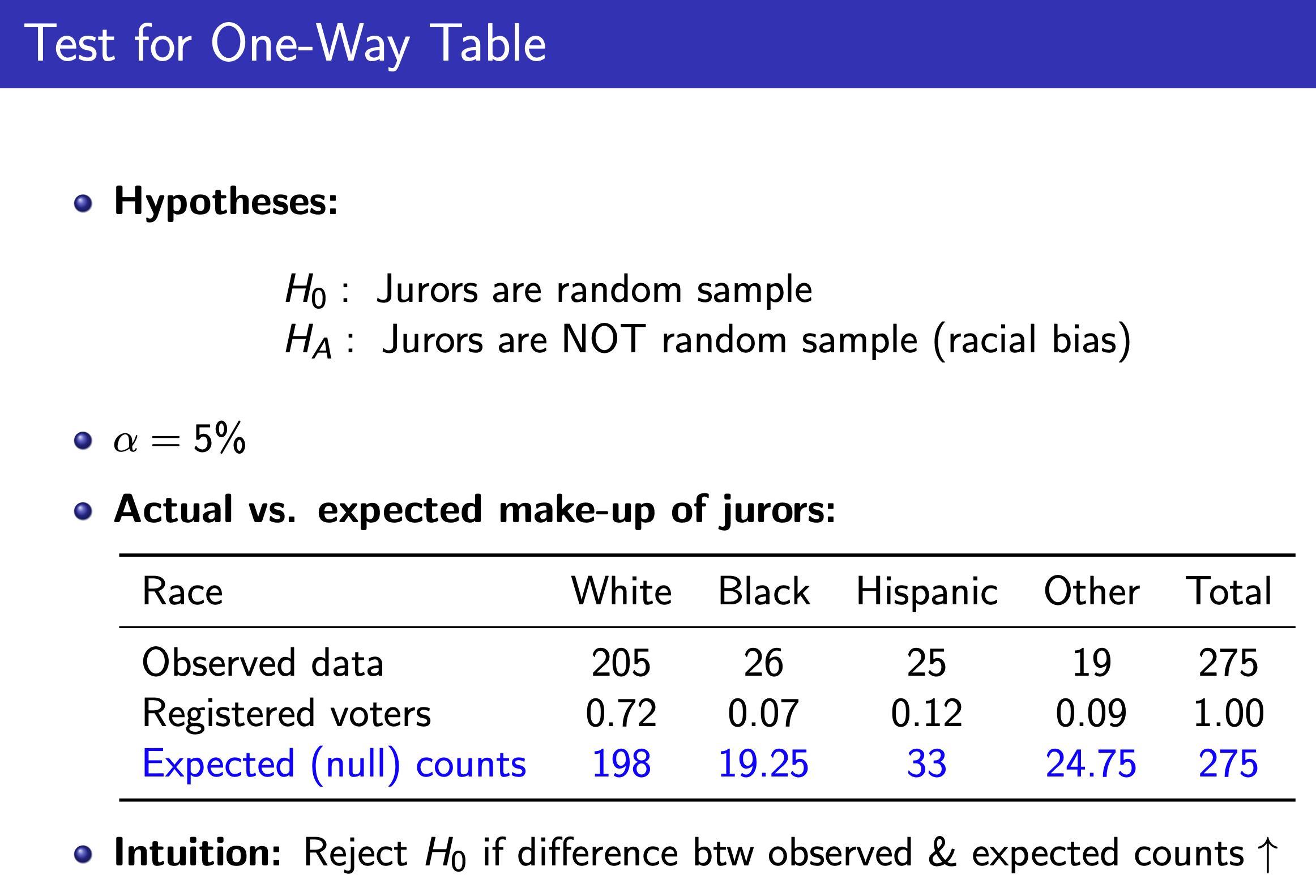
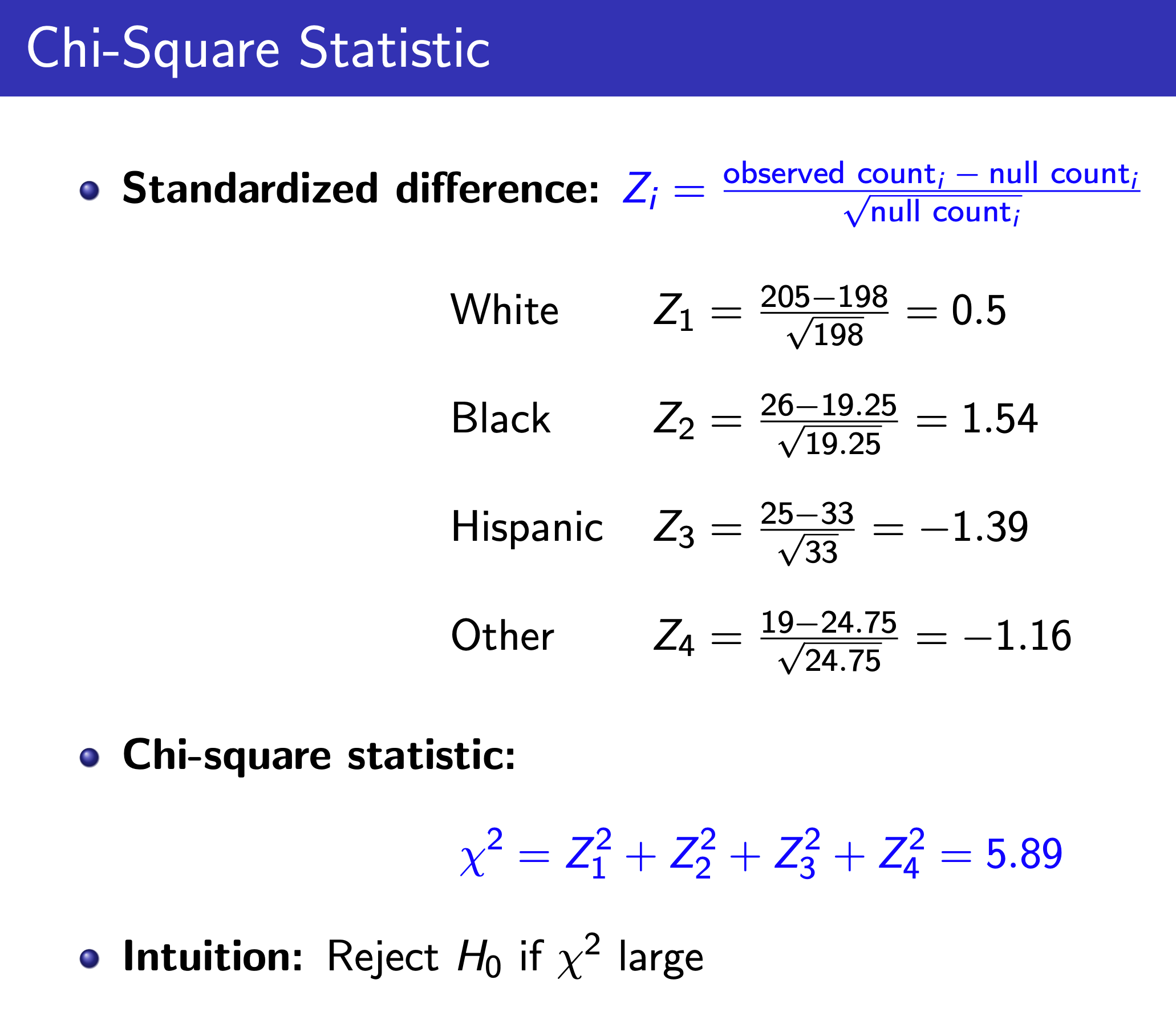
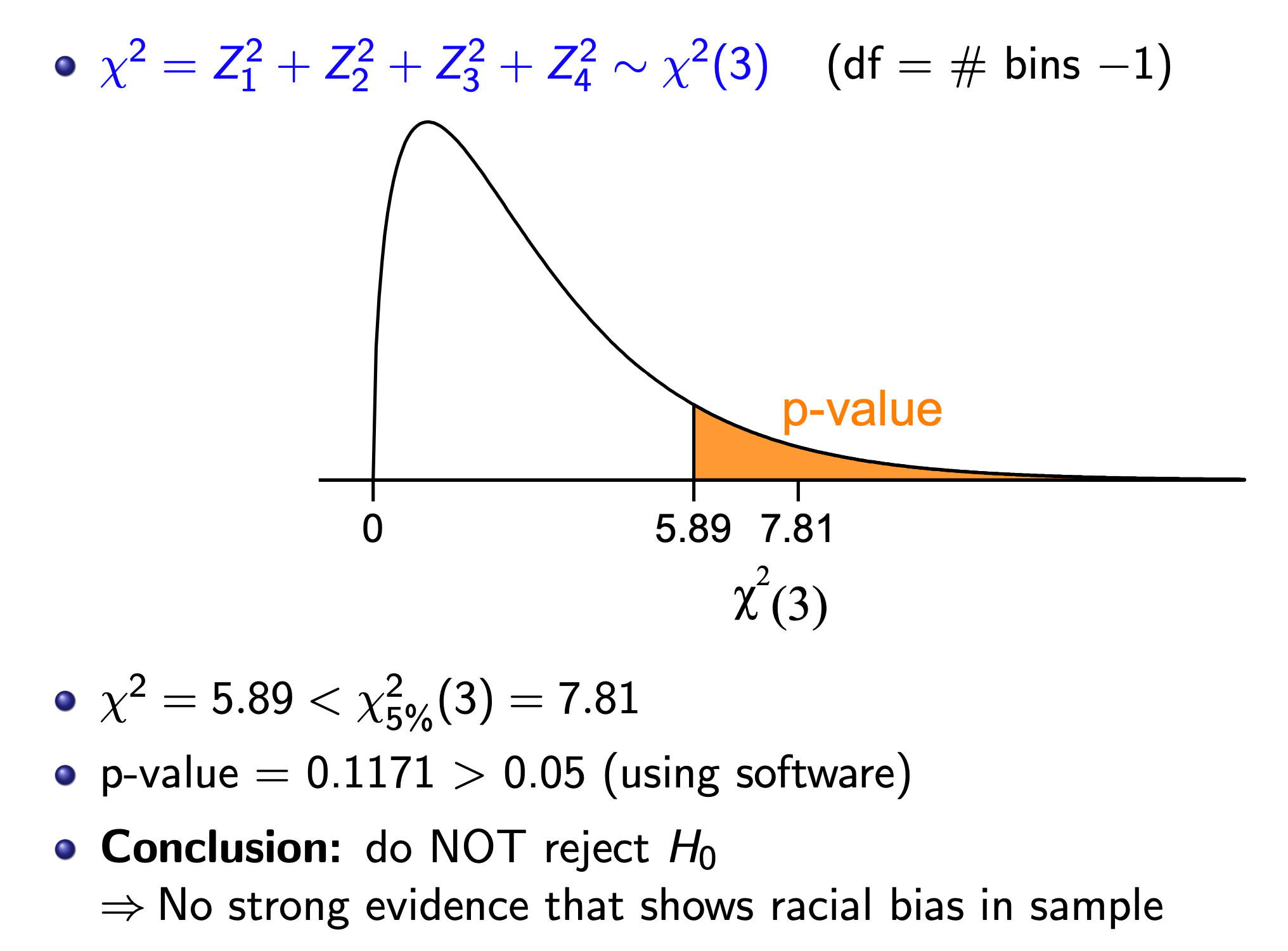
Two-Way Table¶
Each cell is an element, and the caluclate the x square as in one-way table, except df = (# of row - 1)(# of col -1)
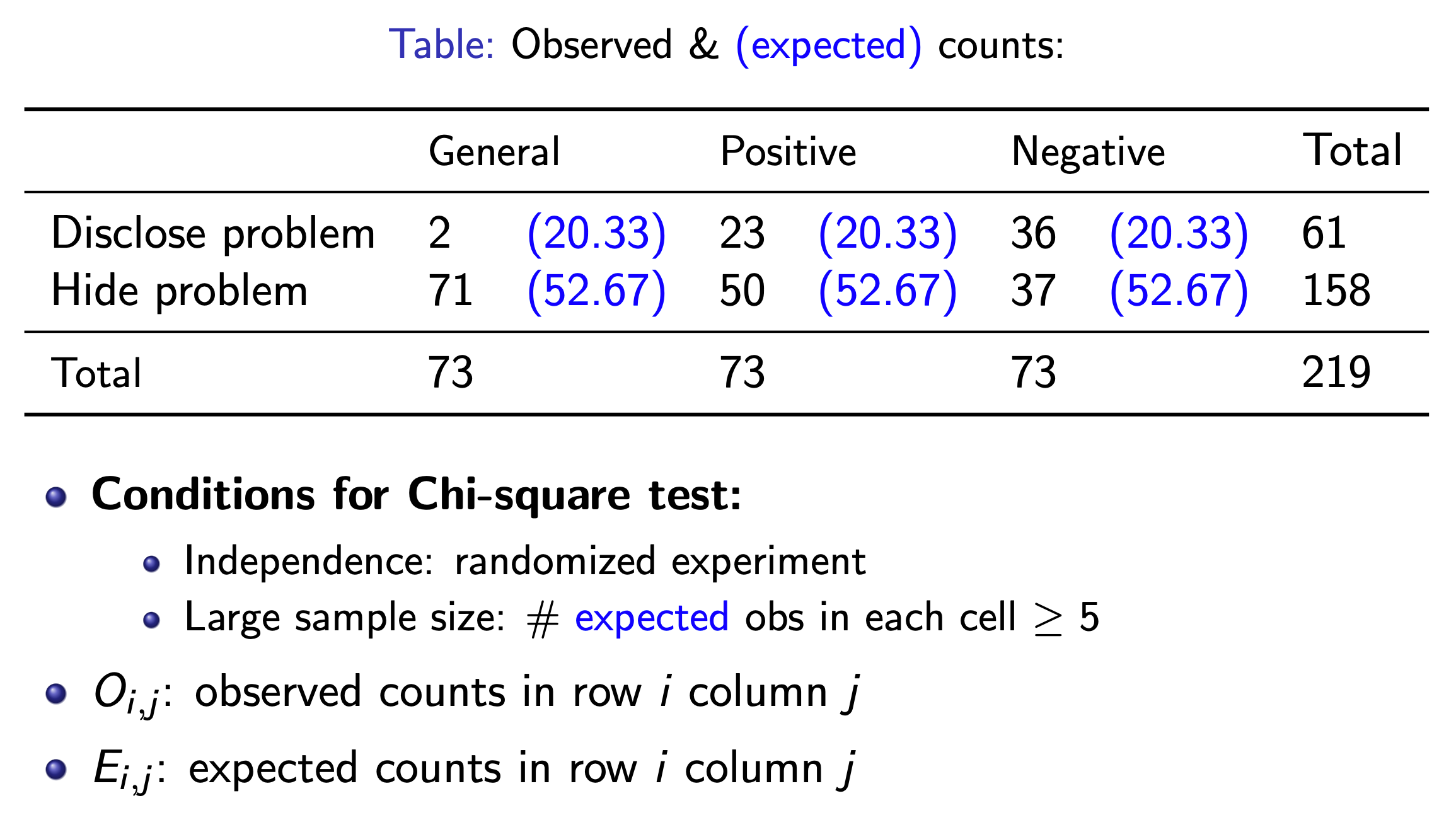
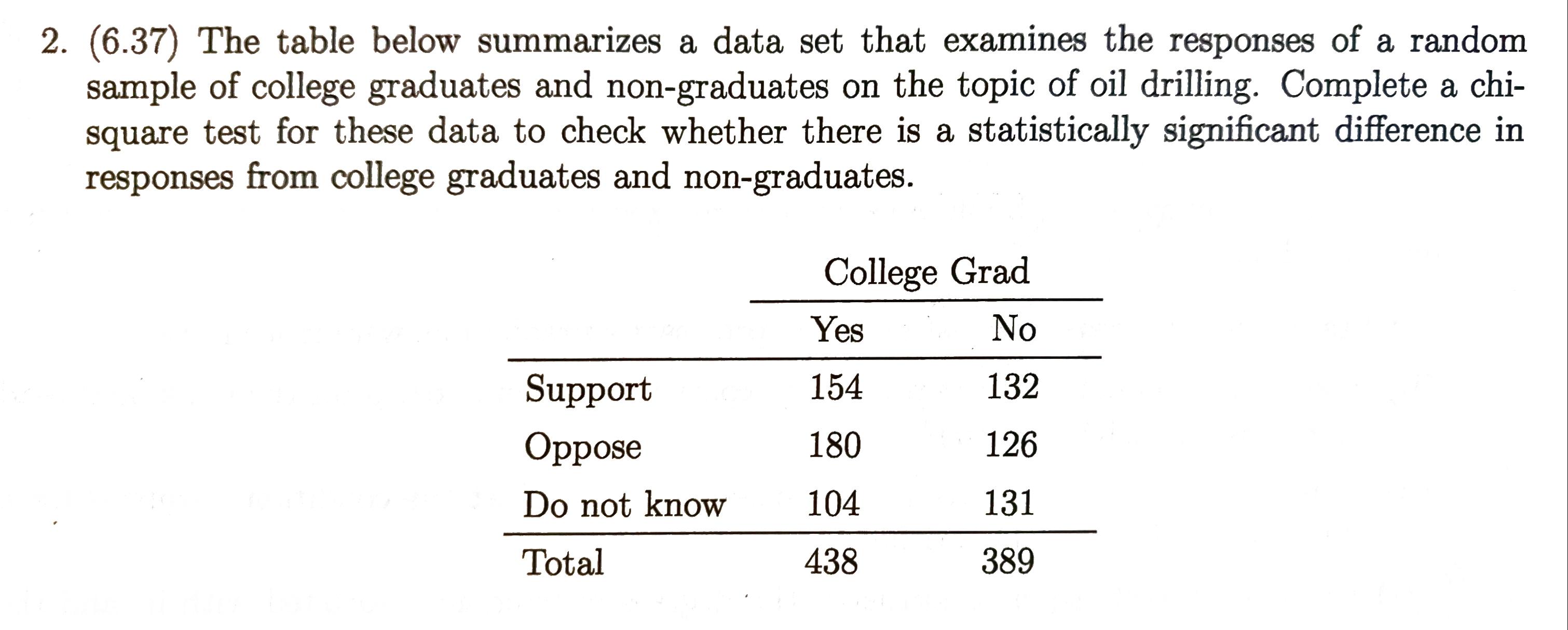
Problems¶

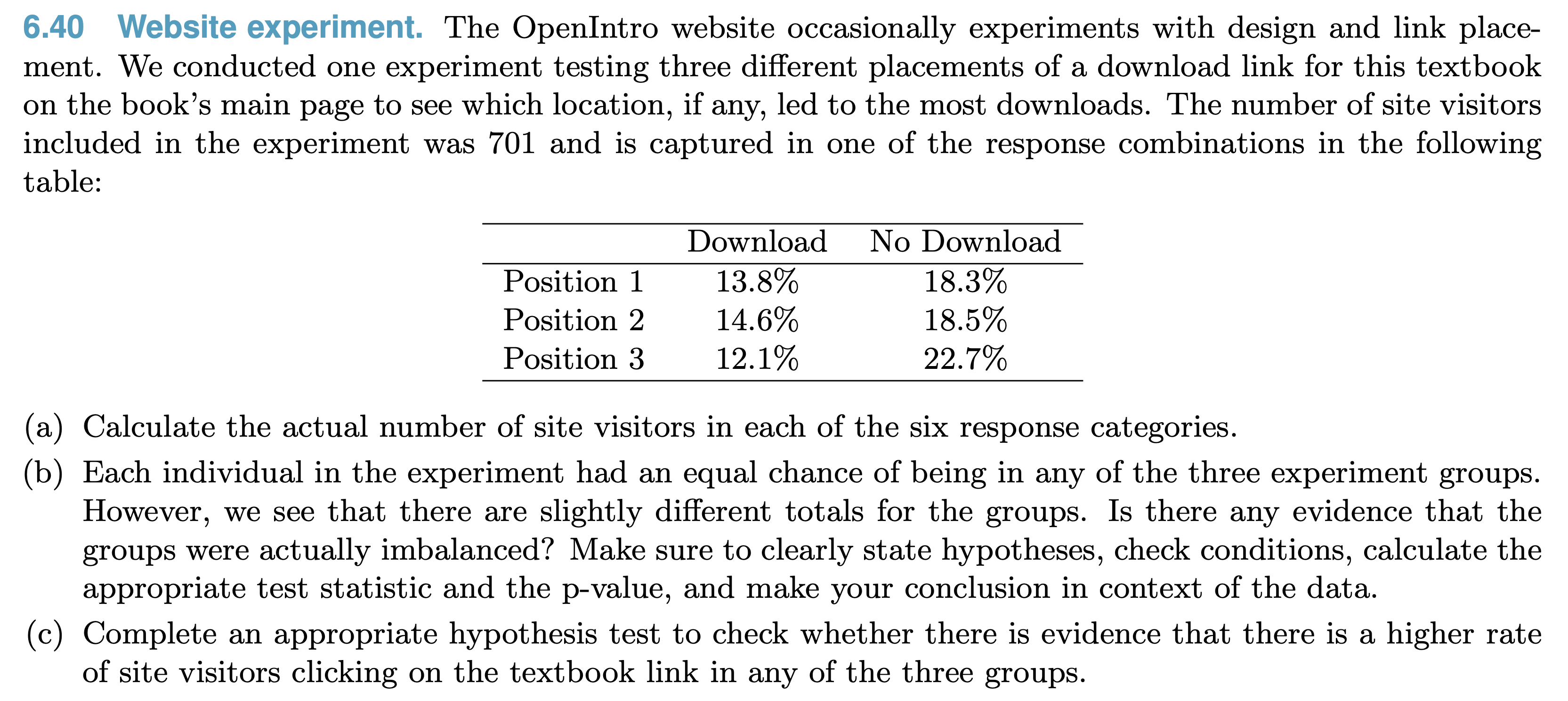




Inference for Numerical Data¶
T test¶
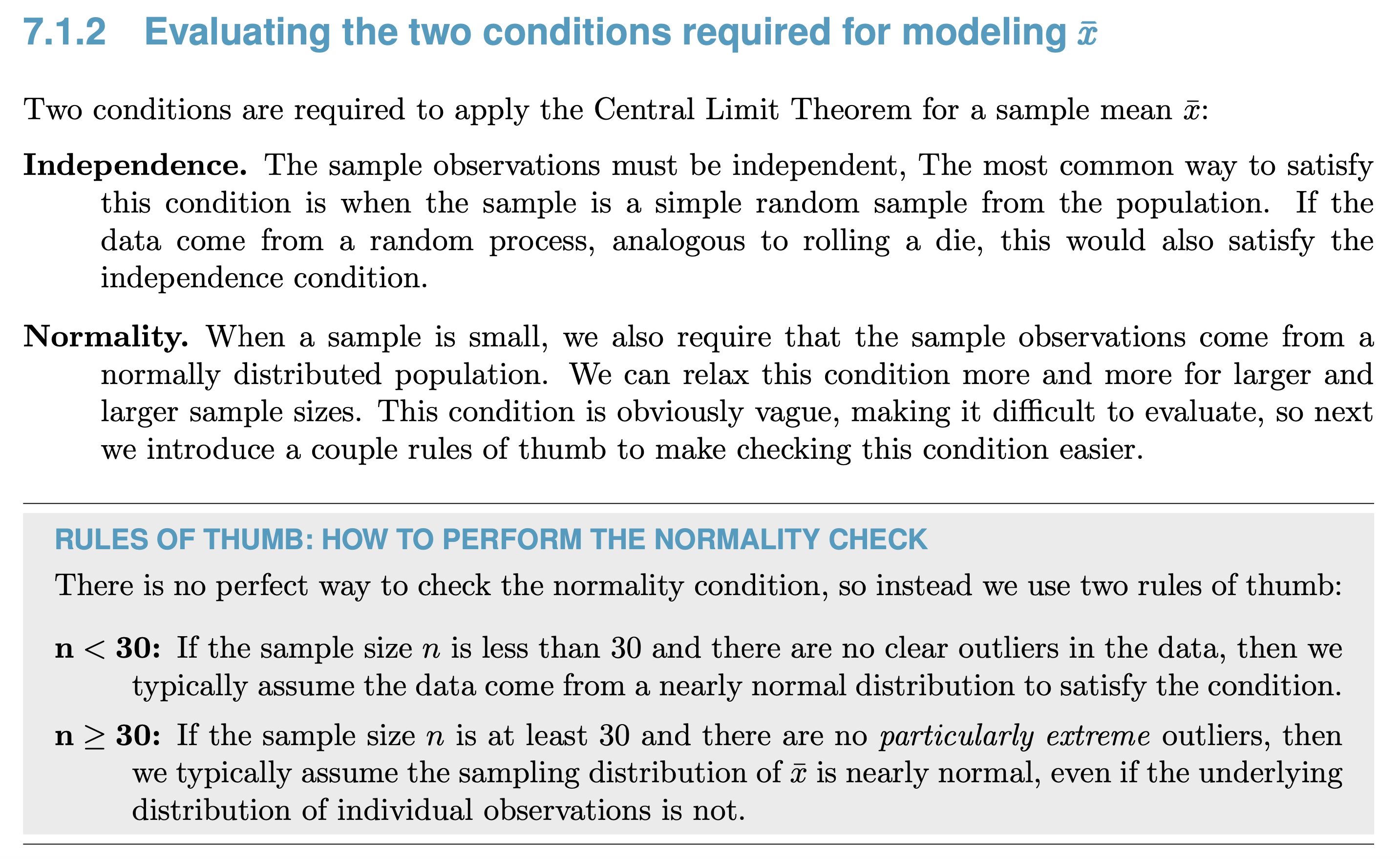
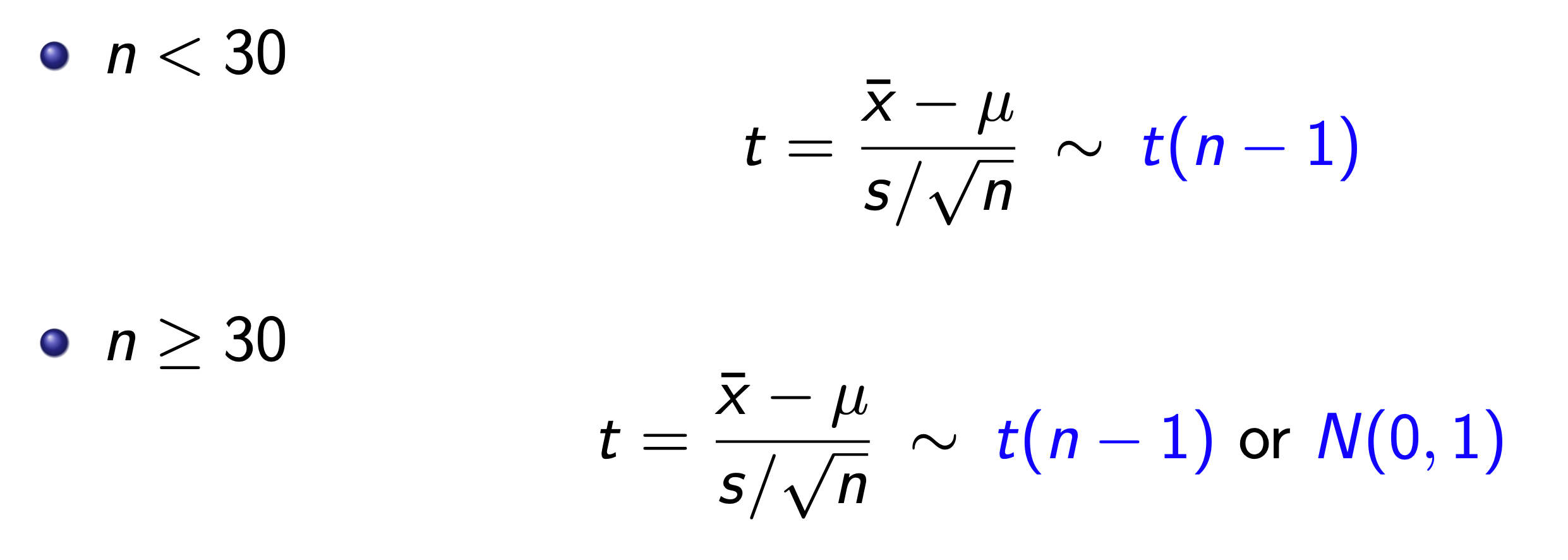

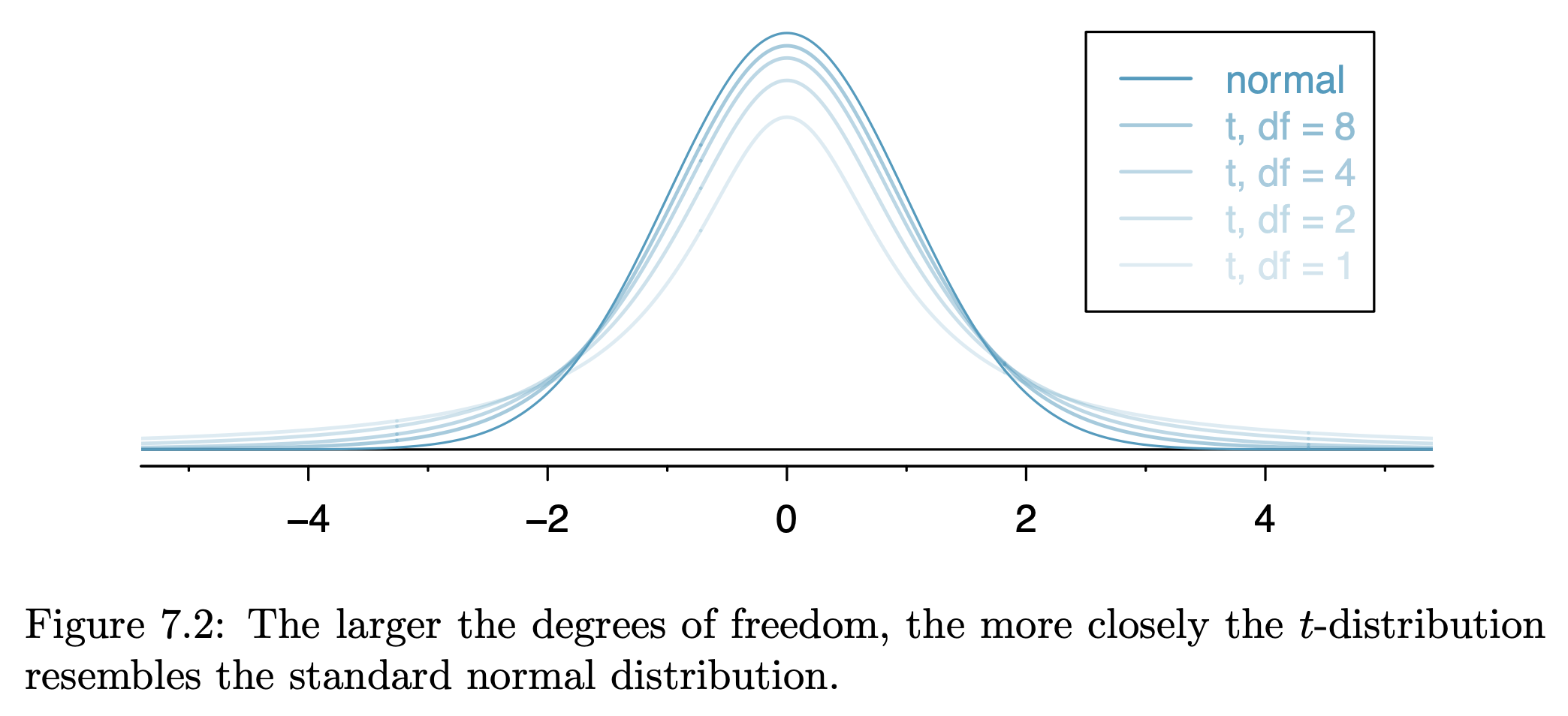
T-Distribution is used when sample size < 30 to solve the problem of sample standard deviation being inaccurate in small samples when using normal distribution to model.
The bigger the degree of freedom = n - 1, the closer it gets to normal distribution.
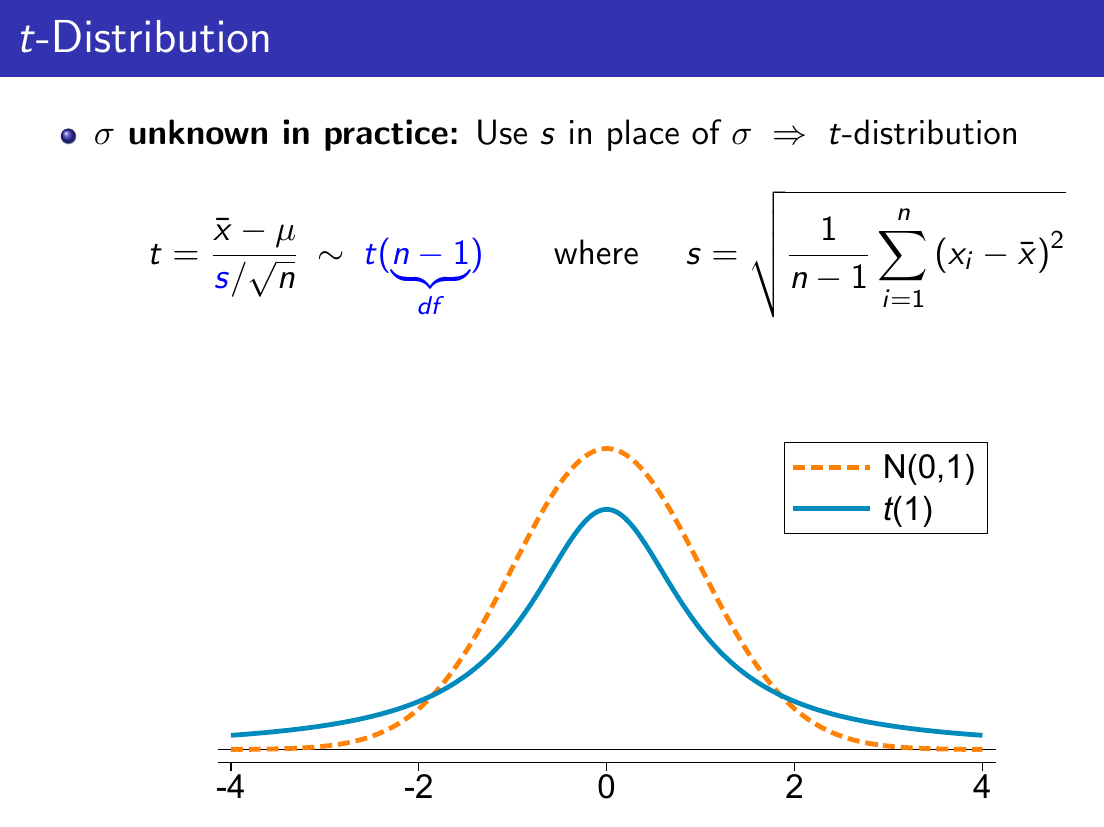
T Table

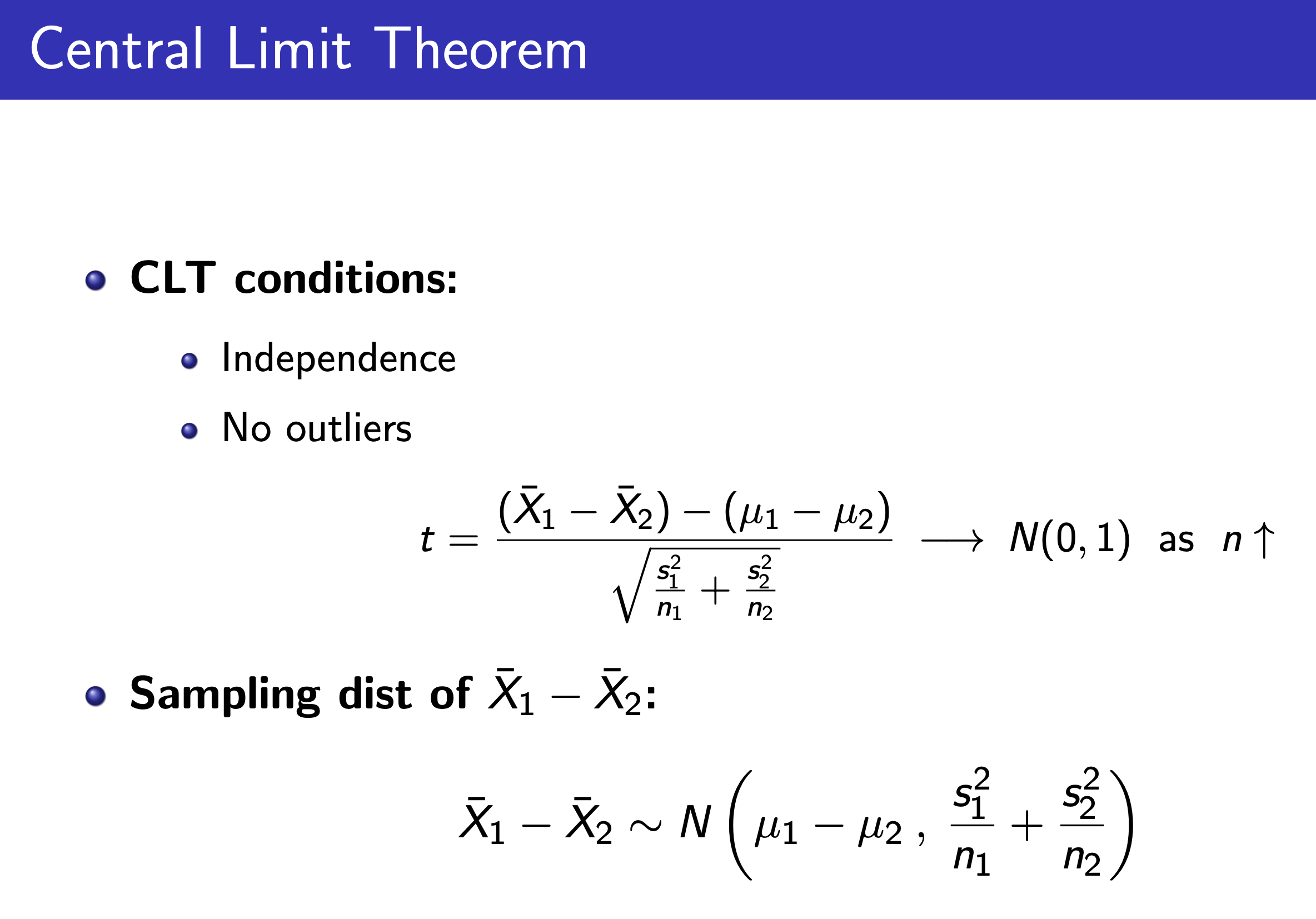
Comparing 2 means
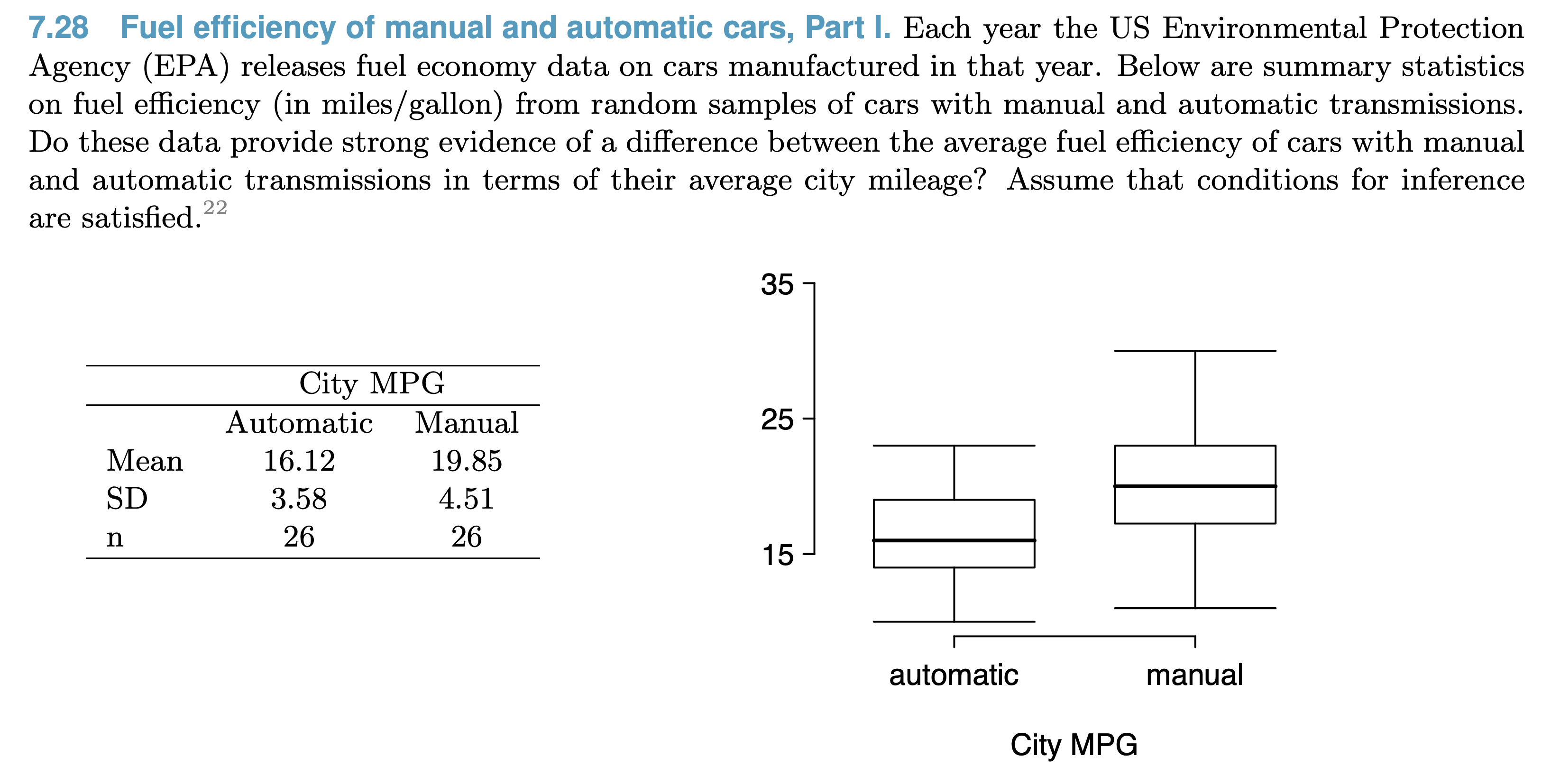
Problem

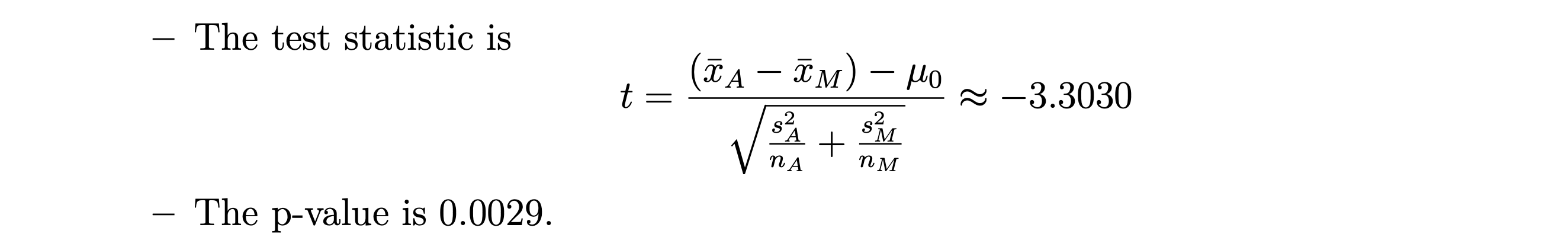
Power of Tests¶
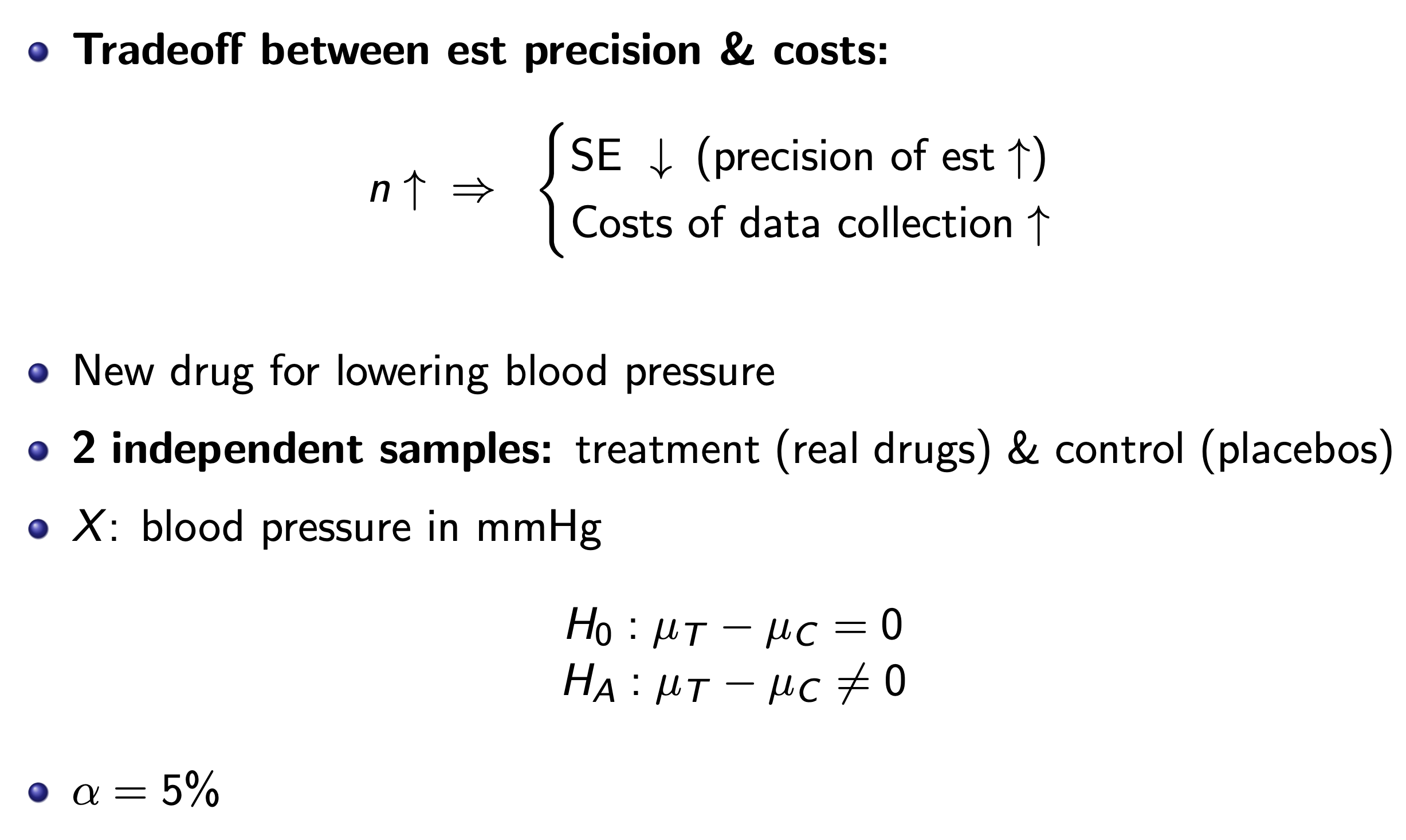
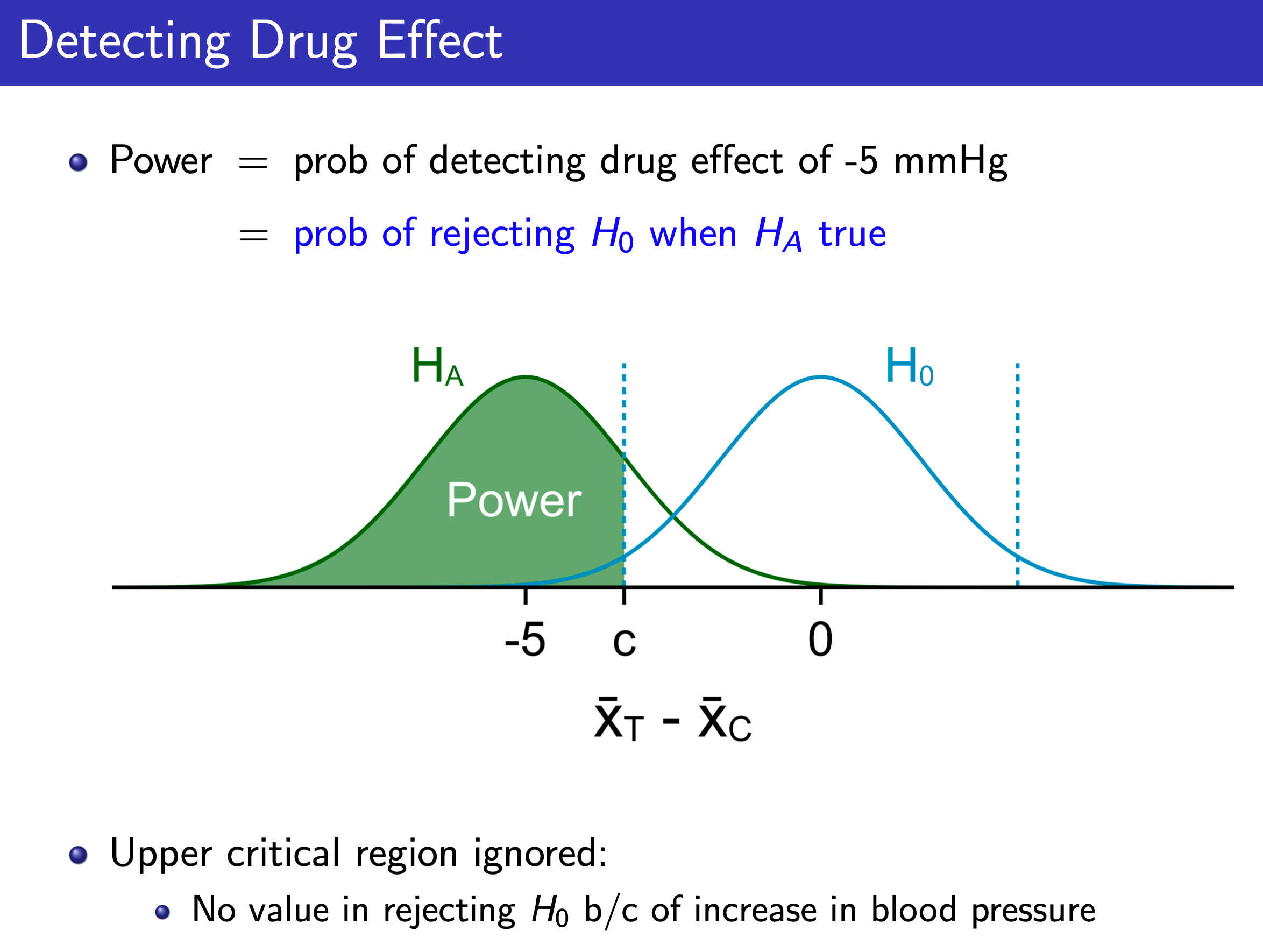
Basically (the Z of power + the Z of the critical value ) x SE = difference of the mean
e.g.
- Given
- sample size of both = \(n\)
- \(\mu\)
- SD
- difference of mean = 0.5
- \(\alpha\) = 5%
- P(Z<-1.96) = 2.5%
- power = 80%
- P(Z<0.8416) = 80%
- Sol
- SE=\(\sqrt{\dfrac{SD^2}{n}+\dfrac{SD^2}{n}}\)
- (1.96+0.8416)xSE = 0.5
- See graph
Problem



Comparing Means¶
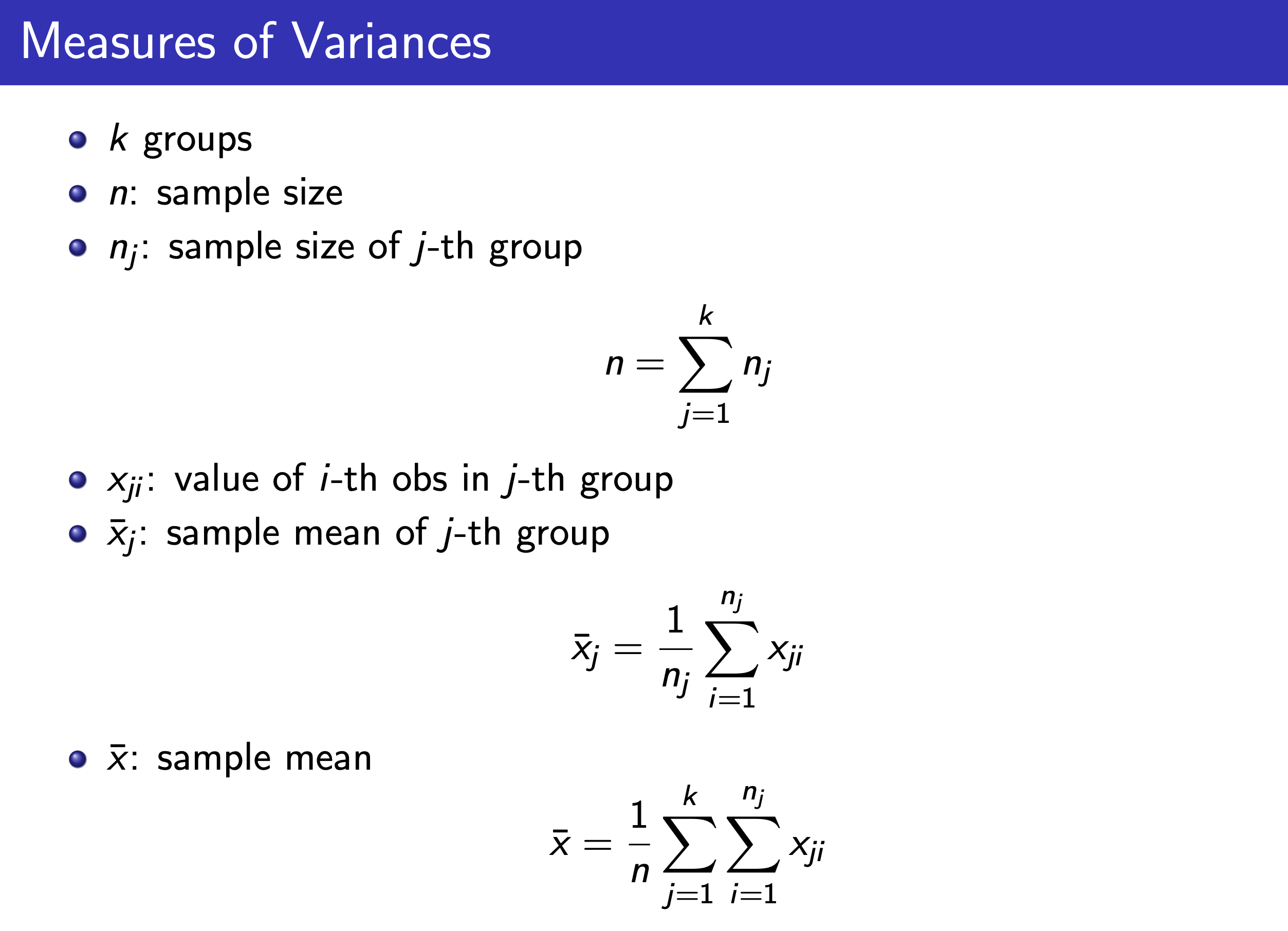
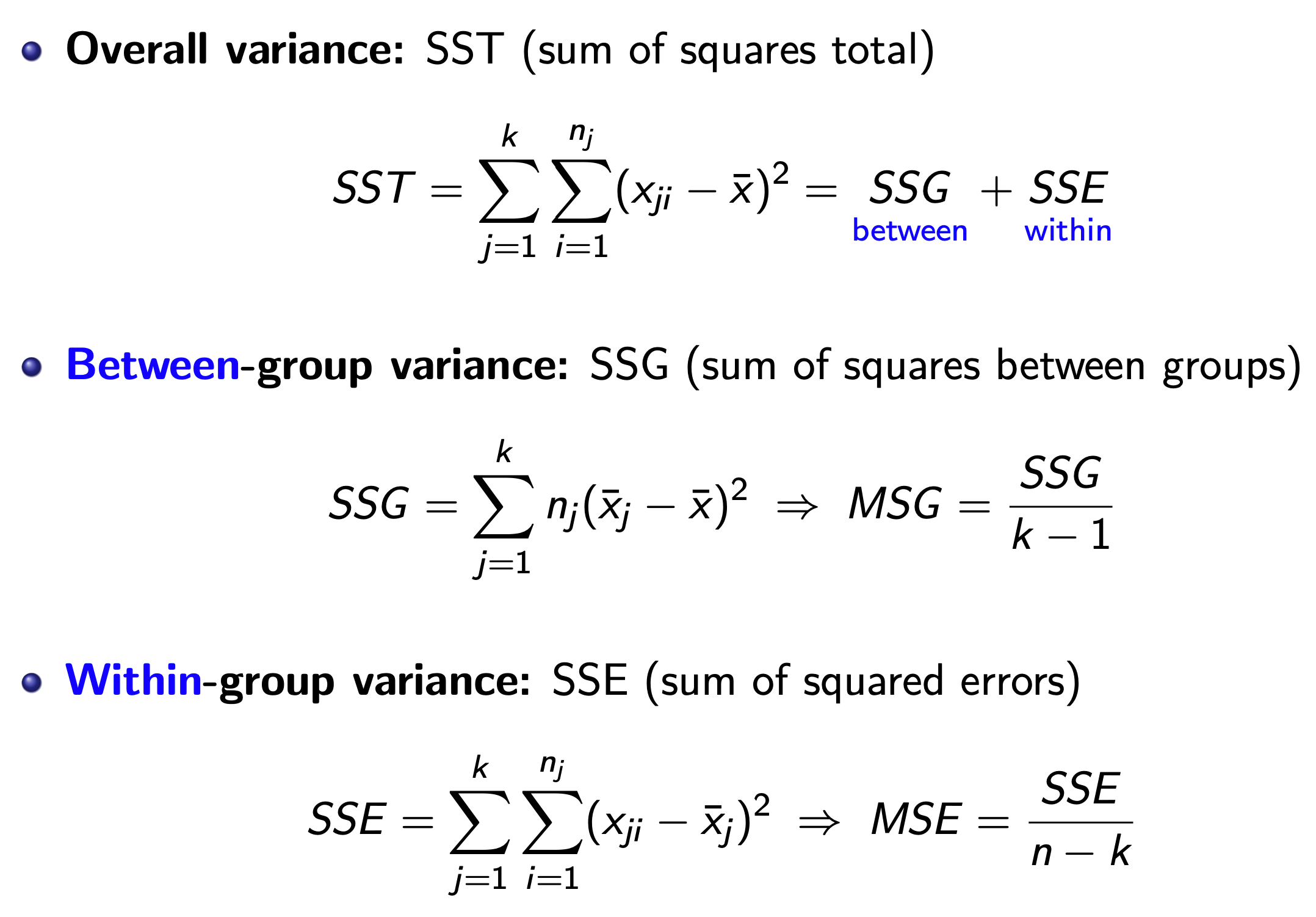
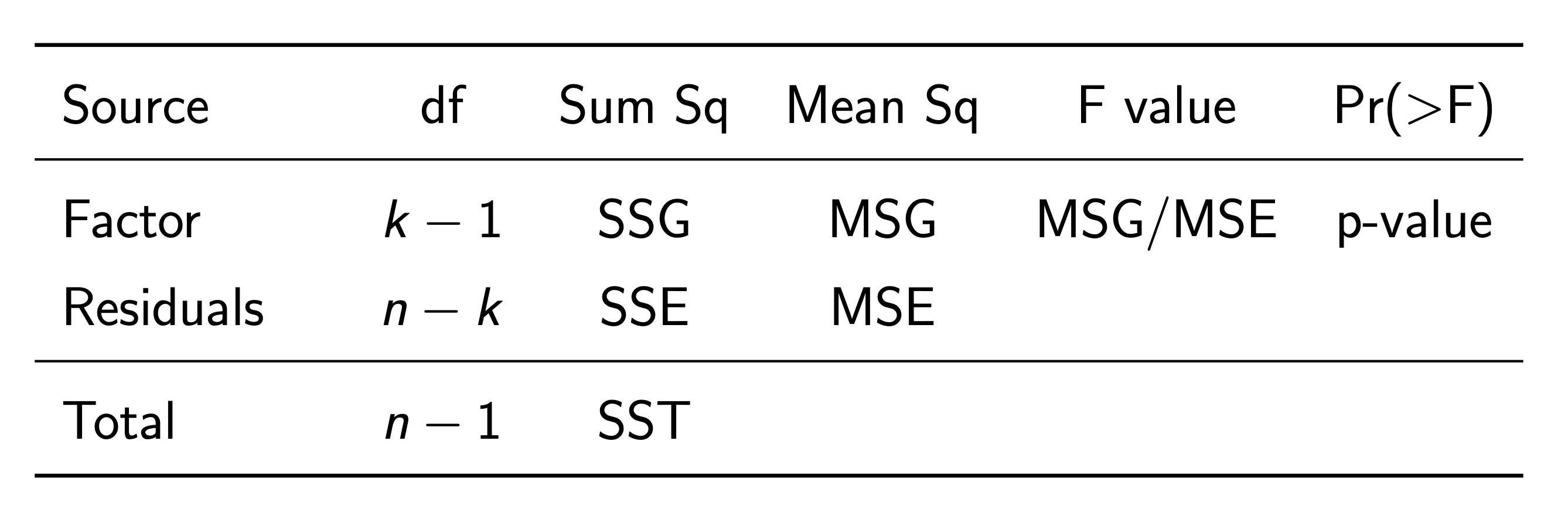
ANOVA & F Test¶

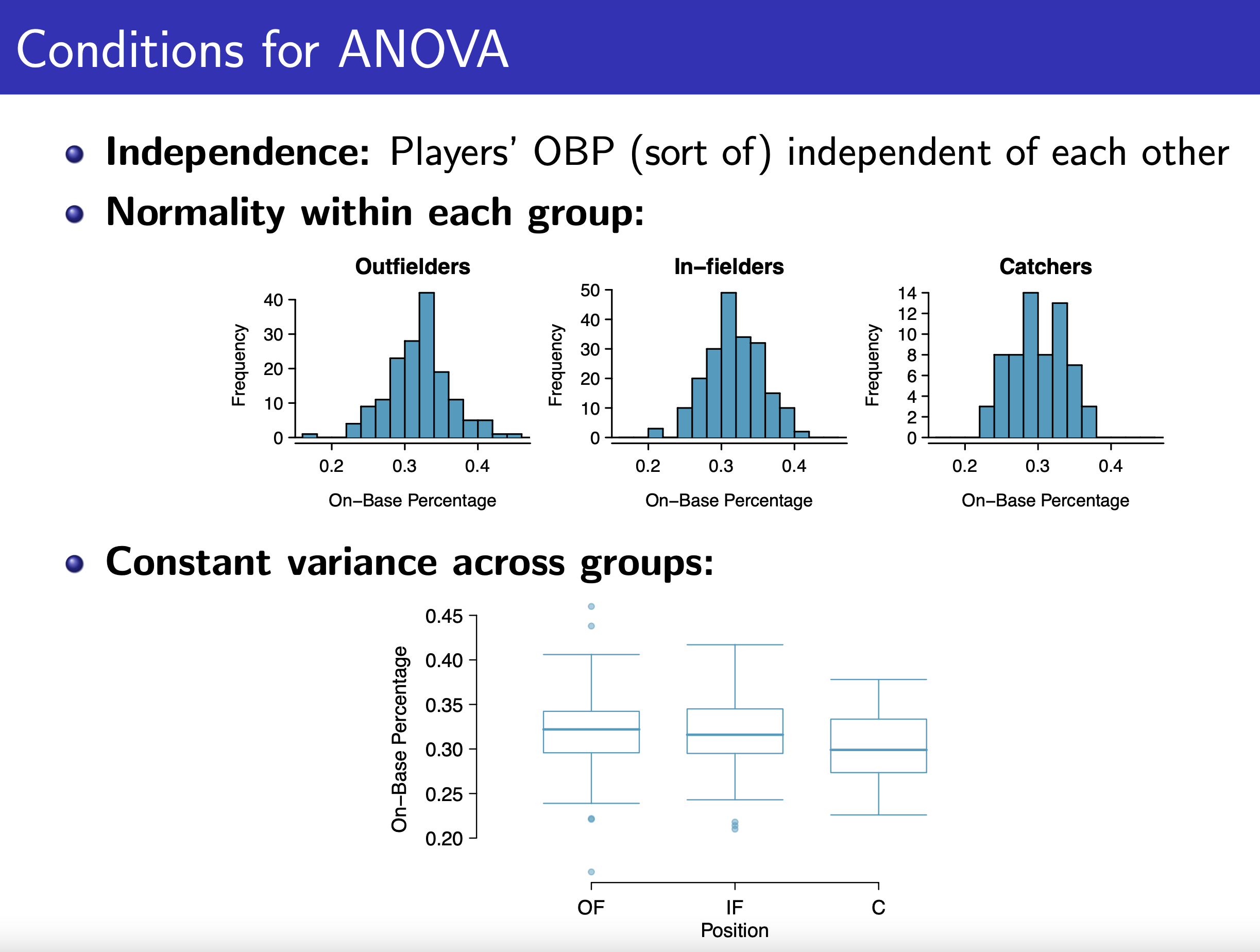

ANOVA Table

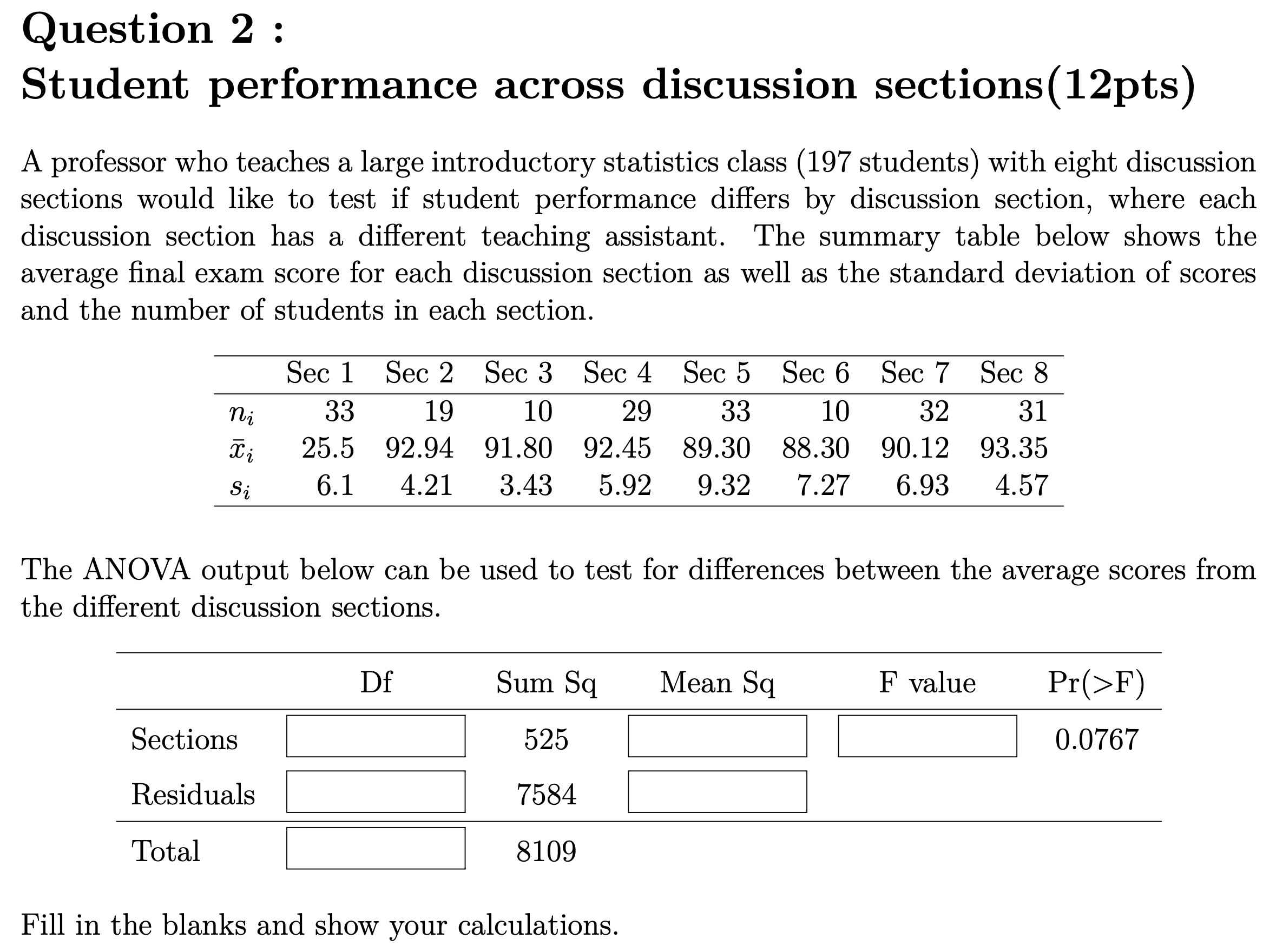
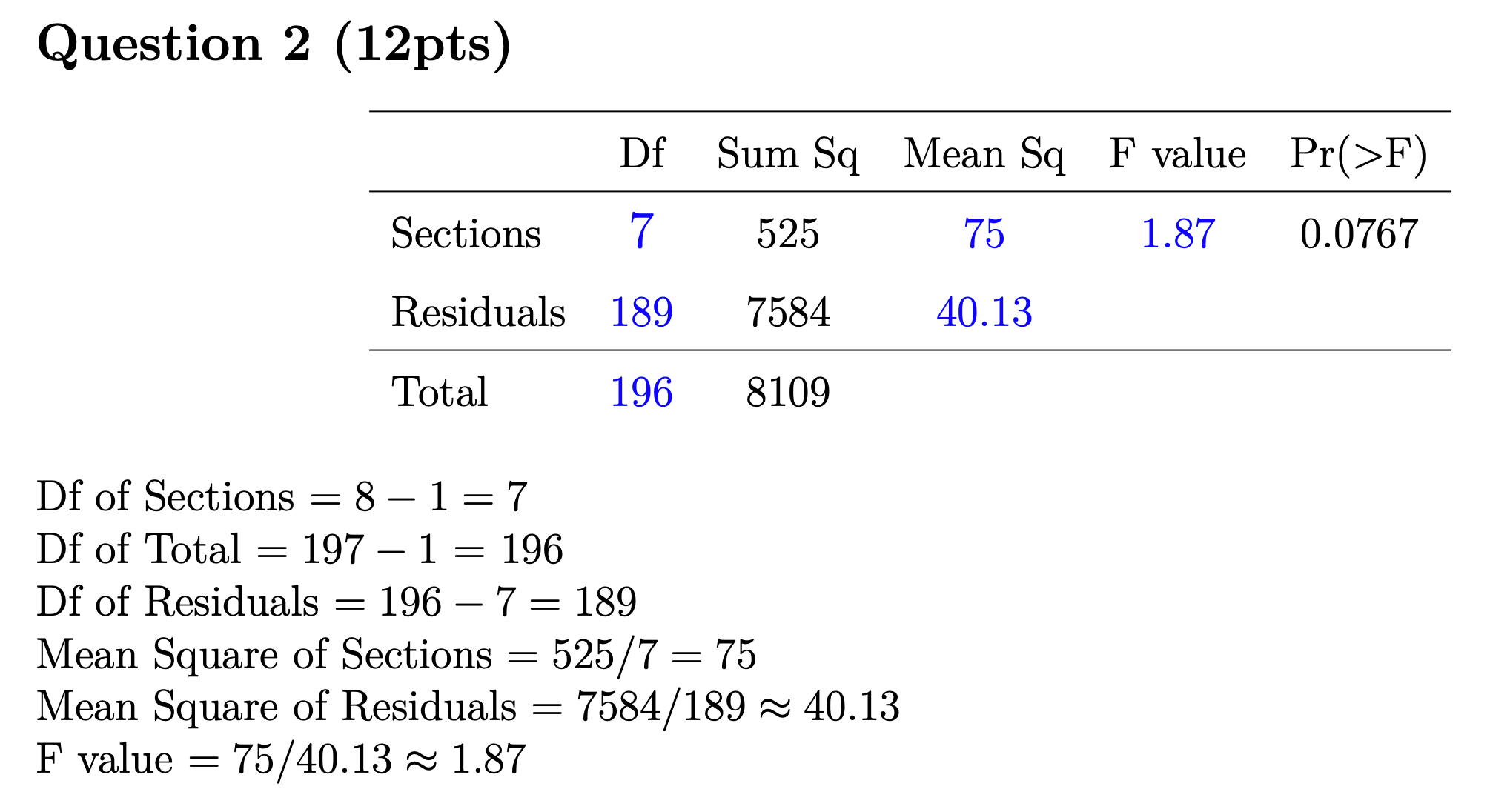
Problem
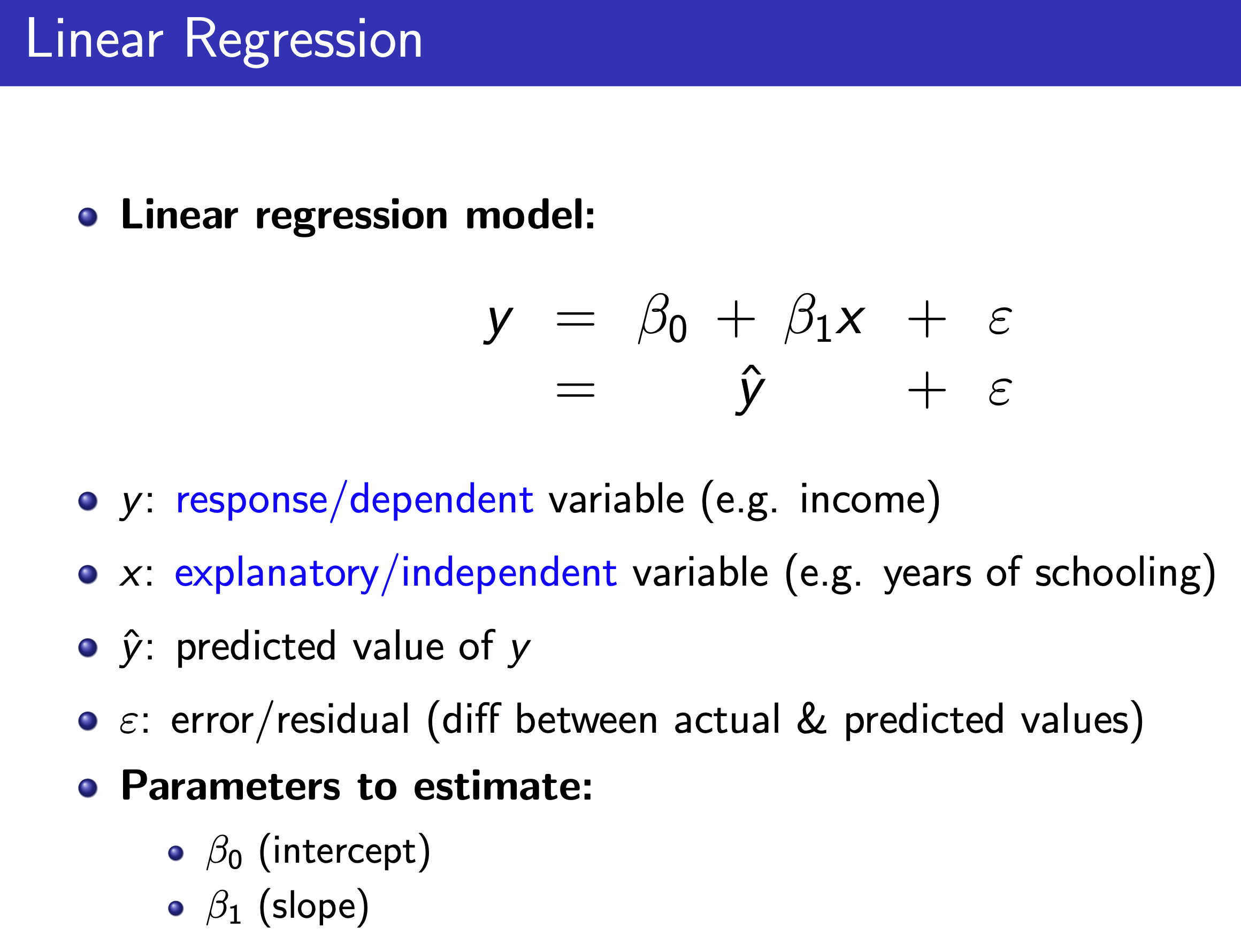
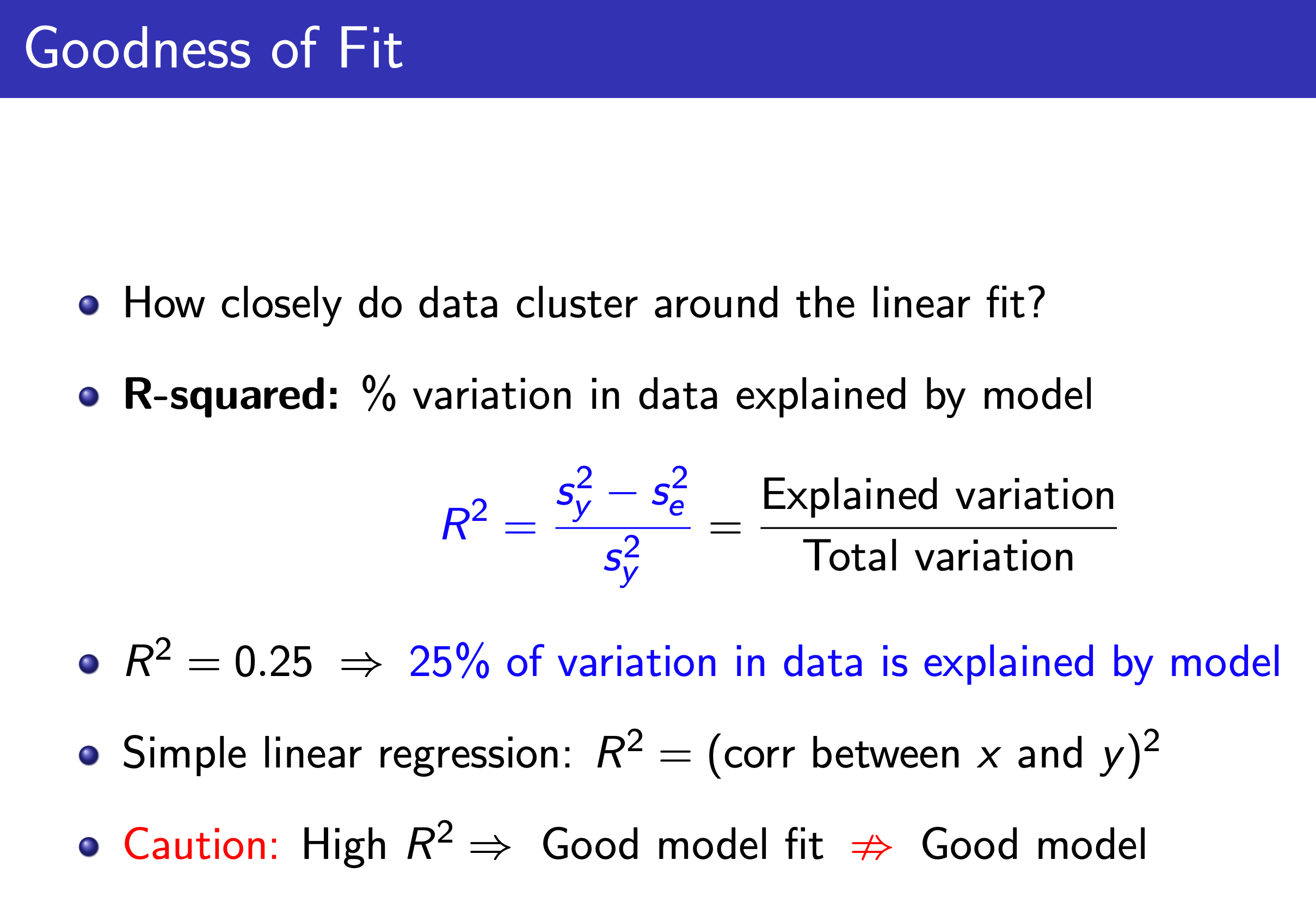
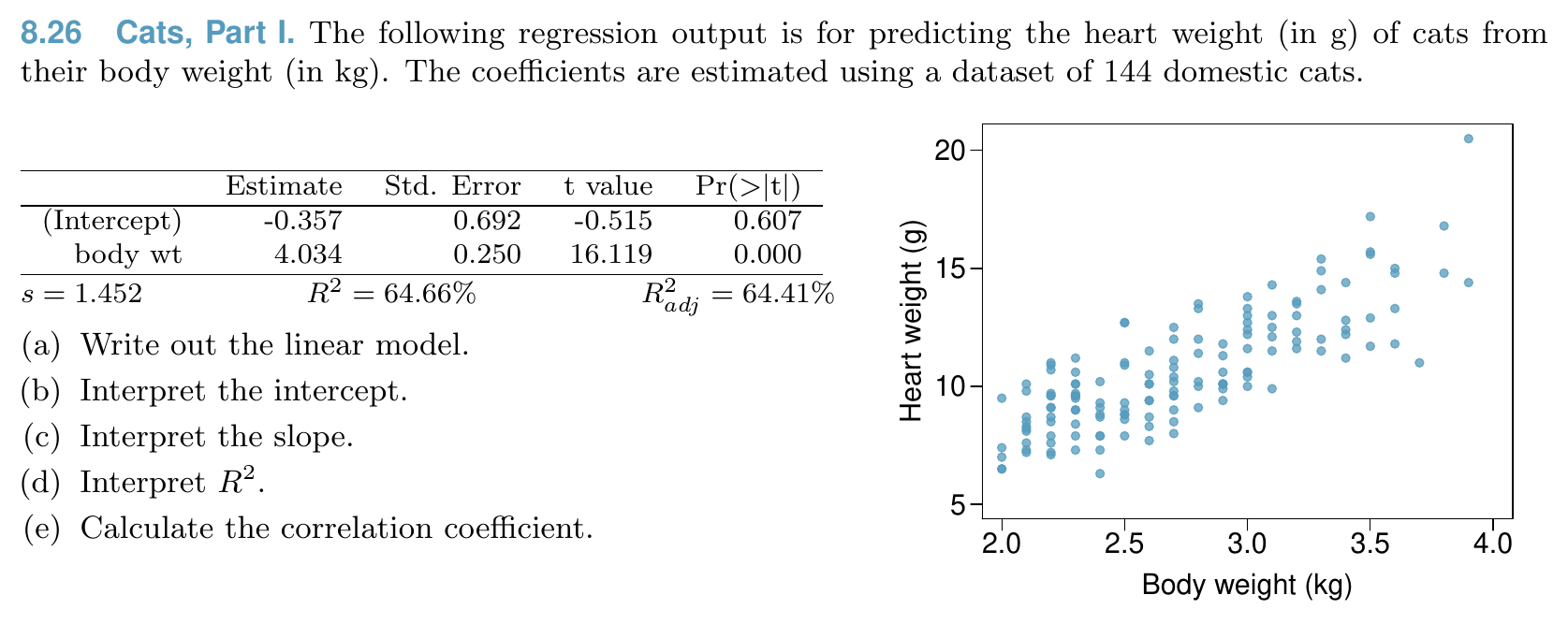
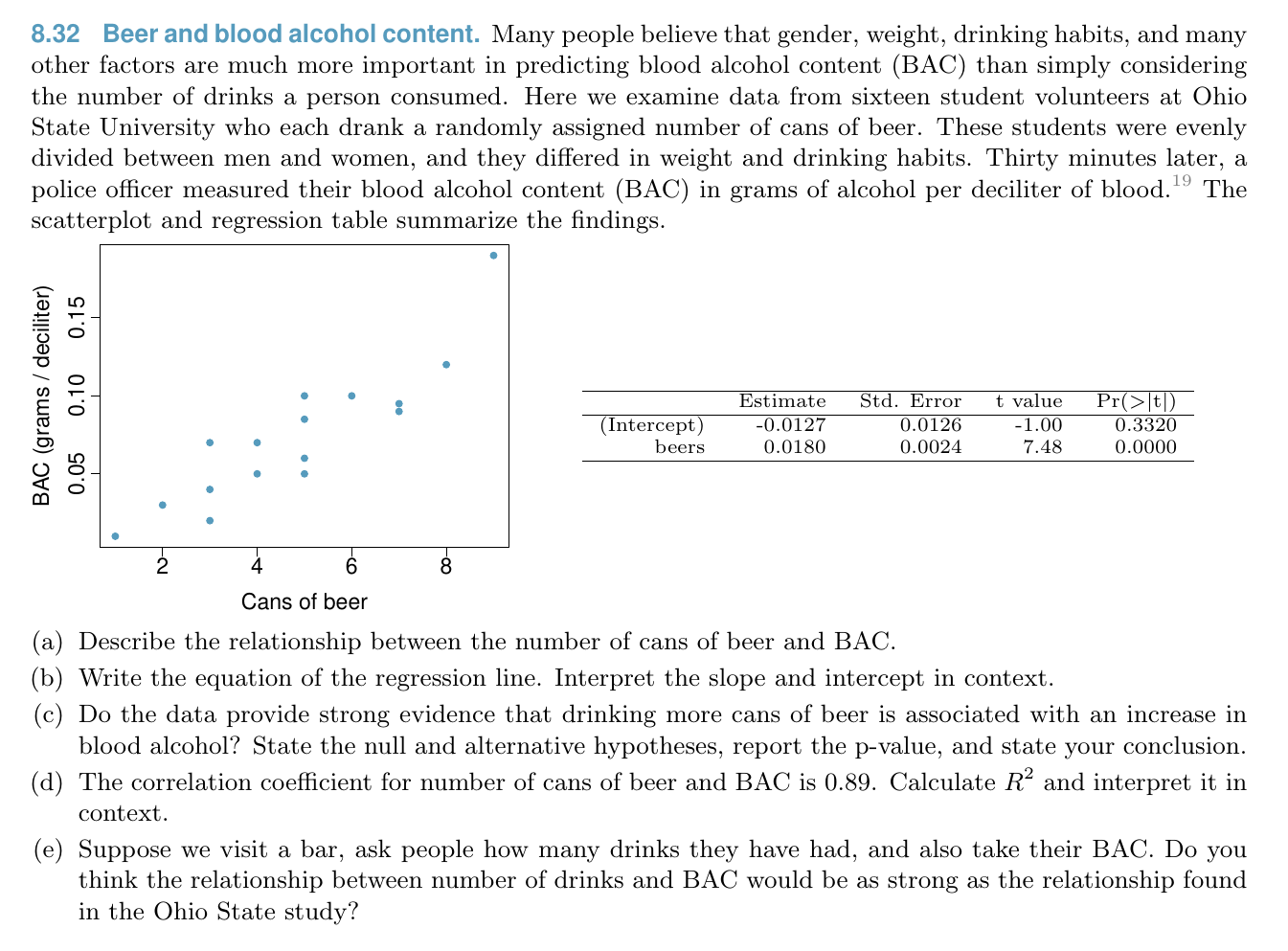
Linear Regression¶
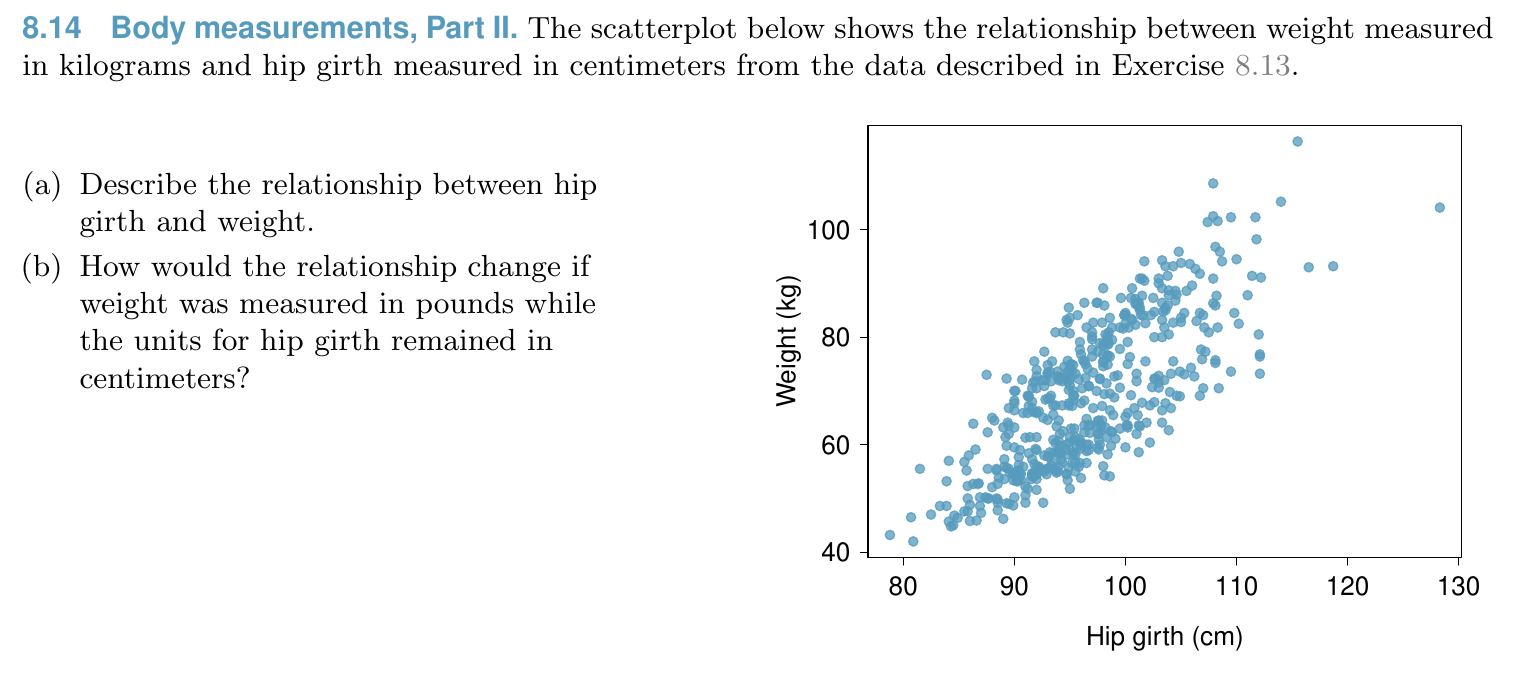
Relationship¶
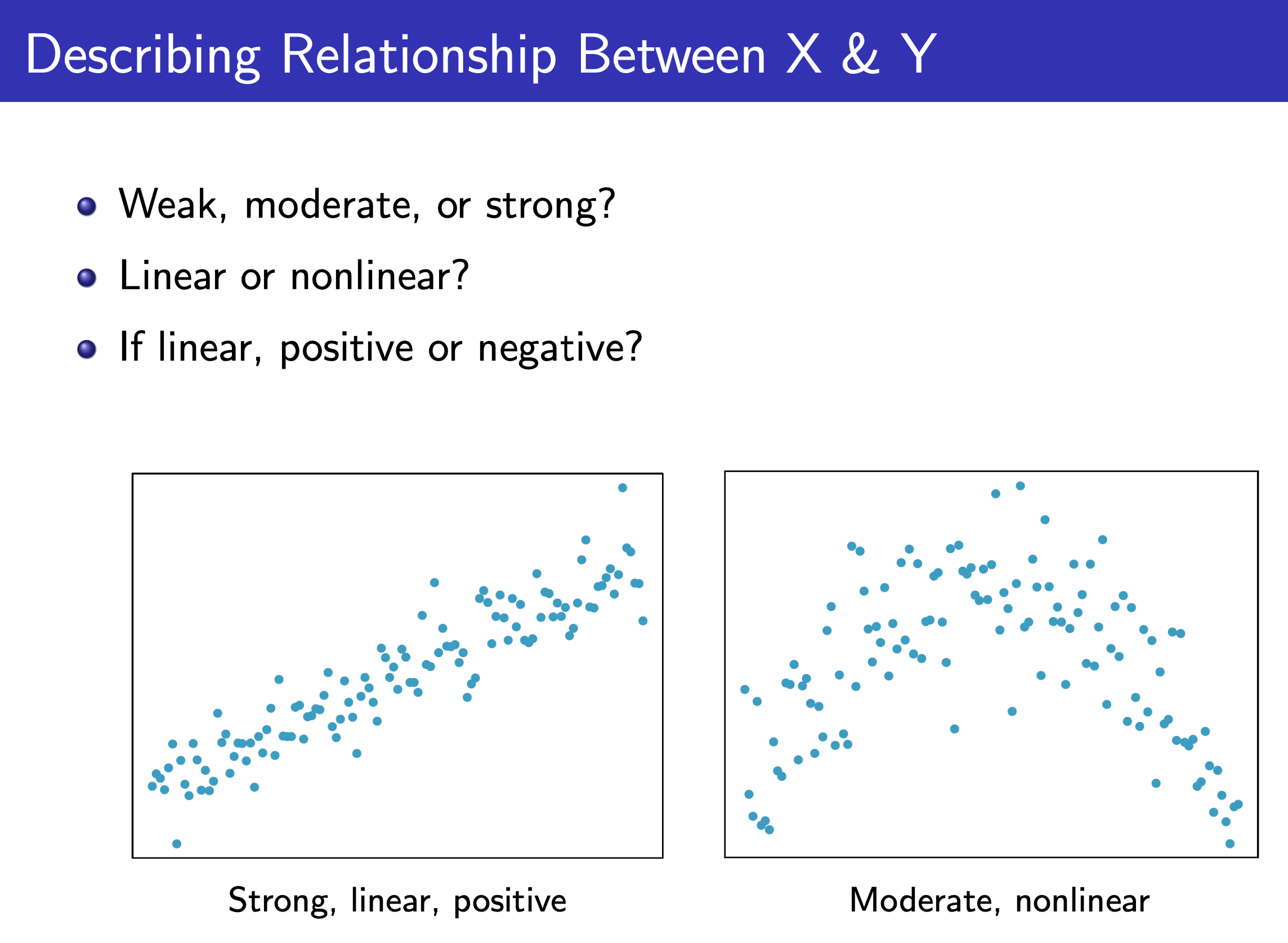



Model¶
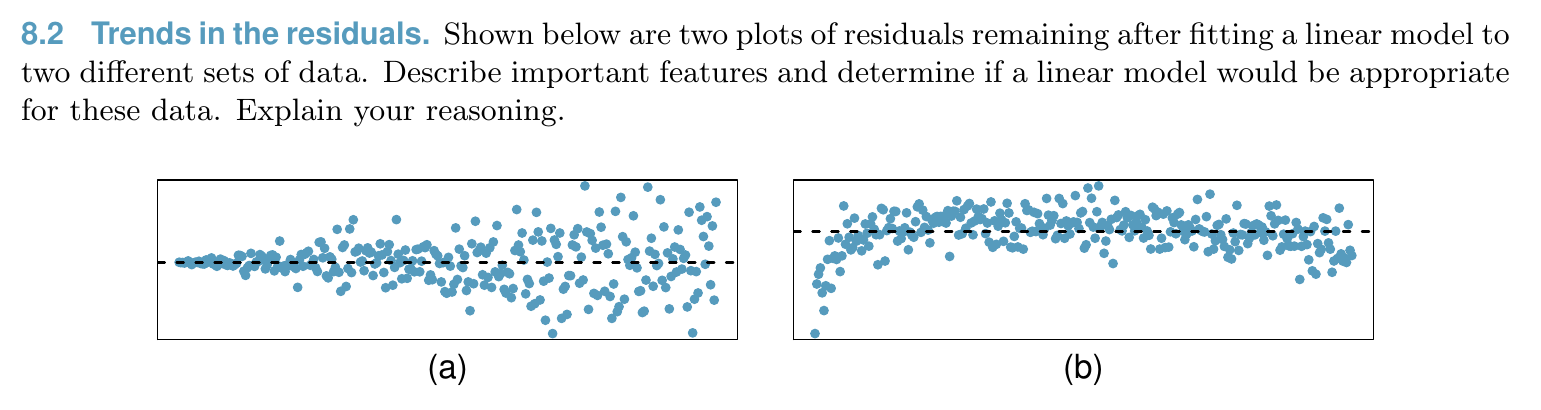
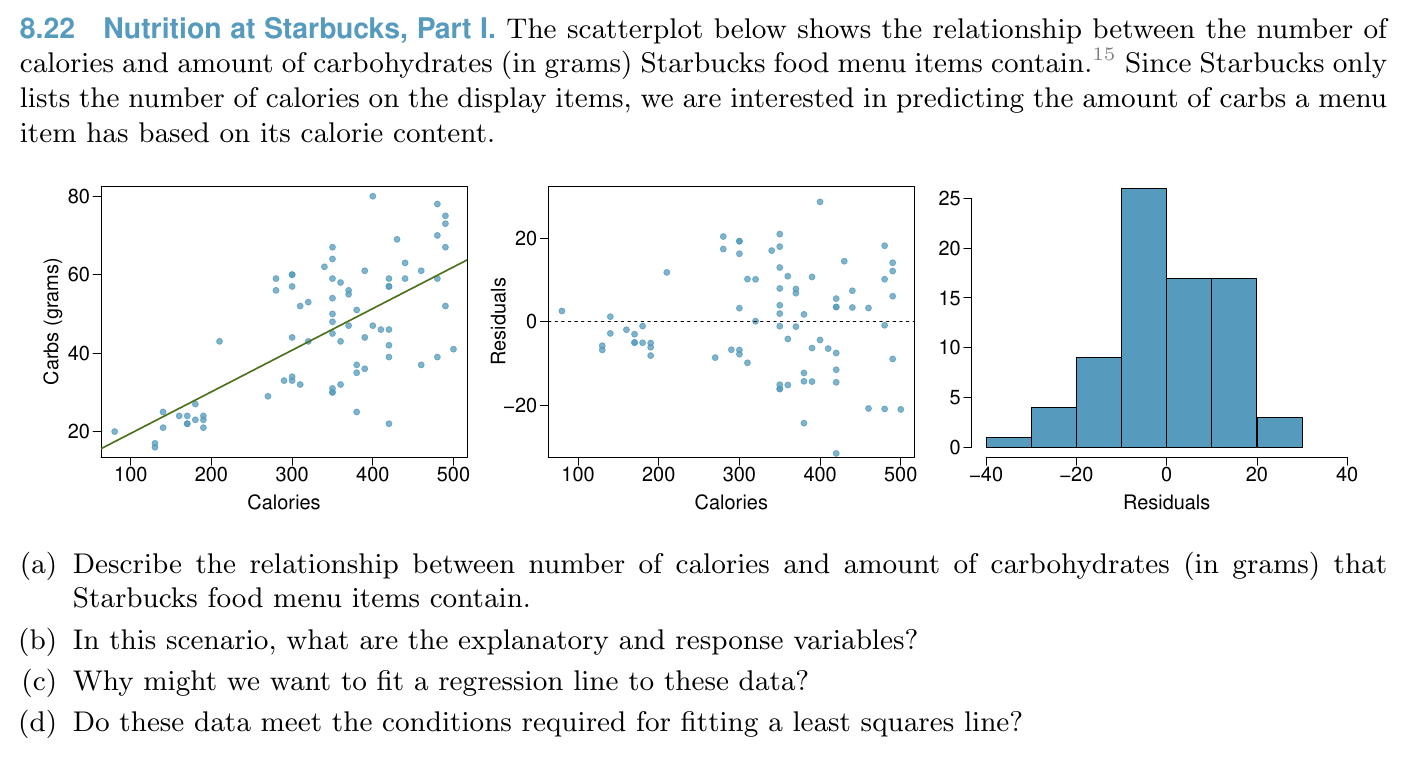
Condition of least square line