Industrial Organization¶
Price Elasticity¶
- \(\Delta R = (p+\Delta p)(q+\Delta q)-pq\)
- \(MR=\dfrac{\Delta R}{\Delta q}=p(1-\dfrac{1}{|e|})\)
- e = elasticity
- MR = MC
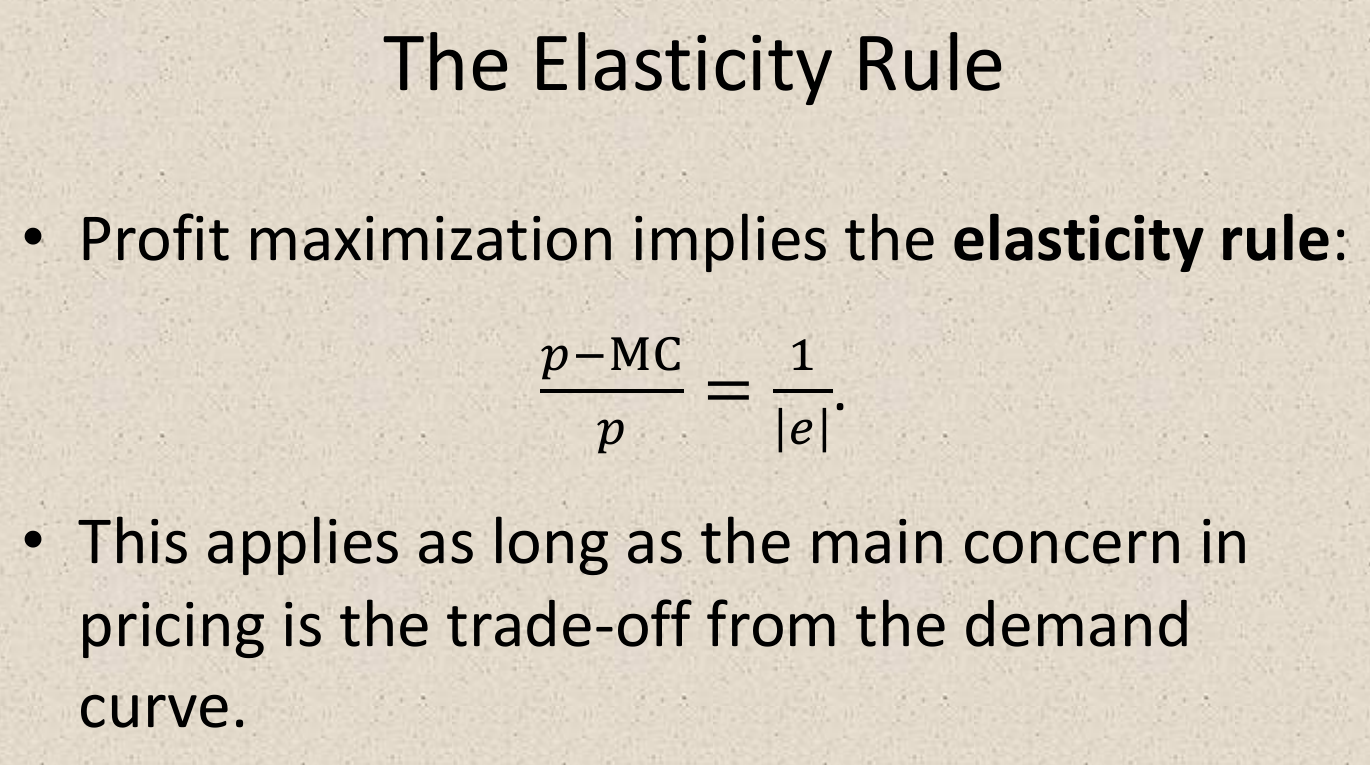
- \(\dfrac{p-MC}{p}=\dfrac{1}{|e|}\)
- elasticity of demand
- Products with close substitutes have elastic demand.
- Demand for an individual brand is more elastic than industry aggregate demand.
- Products with less complements have more elastic demand.
- Demand becomes more elastic in the long run.
- As price increases, demand curves become more price elastic.
- markup = \(\dfrac{P-C}{P}\)
- market segmentation limit
- cost of getting everyone's preference profile
- hard to stop resale
Oligopoly¶
see Oligopoly
Bertrand Model¶
- Bertrand Model
- firms set price simultaneosly
- Nash equilibrium of duopoly is both setting competition price -> Bertrand paradox
Cournot Model¶
- Cournot Model
- firms set output simultaneosly
- Nash equilibrium of duopoly
- given \(MC=c, P(Q)=a-bQ, a>c\)
- \(q_1=q_2=\dfrac{a-c}{3b}, P=\dfrac{a+2c}{3}\)
- P & Q between monopoly & competition
- Nash equilibrium of n firms
- given \(MC=c, P(Q)=a-bQ, a>c\)
- \(q_1=q_2=\dfrac{a-c}{(n+1)b}, P=\dfrac{a+nc}{n+1}\)
- \(n \rightarrow \infty\) -> competition
example: linear city with differentiation¶
- a 1-unit long linear street with evenly distributed customers, and 2 firms at each end
- transportation cost per unit distance = t
- equilibrium price = MC+t
- transportation cost can be translated to product differentiation
- with product differentiation, products can sell above competition price even in Bertran model
collusion¶
- market power = \(\dfrac{p-MC}{p}\)
- how much is the firm able to sell above MC
- system profit in Bertrand competition < system profit of monopoly
- repeated game
- infinite period
- discount factor \(\delta\)
- 1 in this period -> \(\delta\) in next period
Grim Trigger Strategy¶
- algo
- initially both firms set p = monopoly price
- if history price was always the monopoly price, set p = monopoly price
- else set p = MC
- analysis
- don't deviate -> share monopoly profit
- deviate -> get all the profit this period
- to deviate
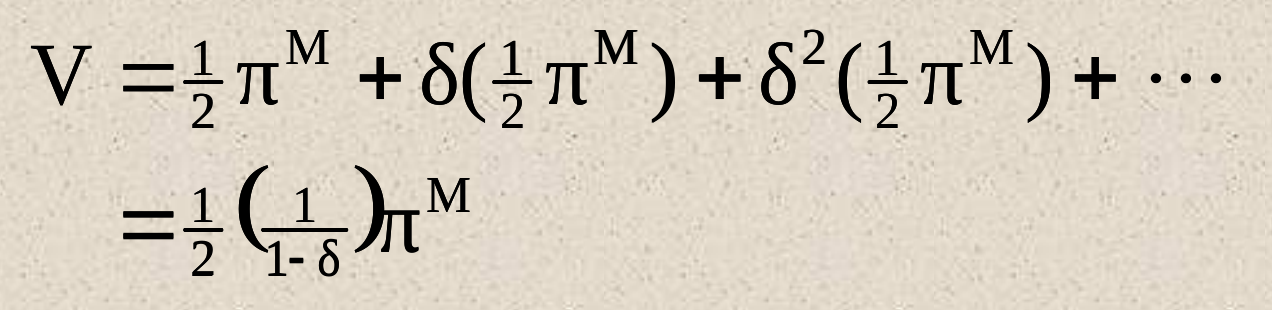
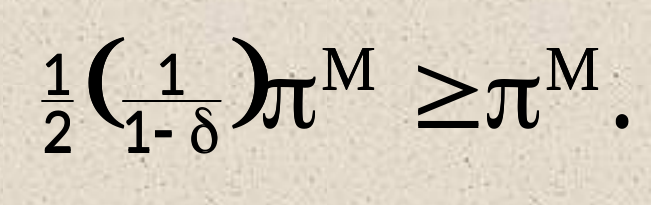
- \(\delta \geq \dfrac{1}{2}\)
final¶
https://hackmd.io/lgE6h18aSzyV4I7PrE0zzg
miscellaneous¶
- gross profit margin vs. operating profit margin
- gross profit = revenue - direct cost of the products sold
- operating profit = revenue - all cost
- https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/010815/what-difference-between-gross-profit-margin-and-operating-profit-margin.asp